Embed presentation
Download to read offline



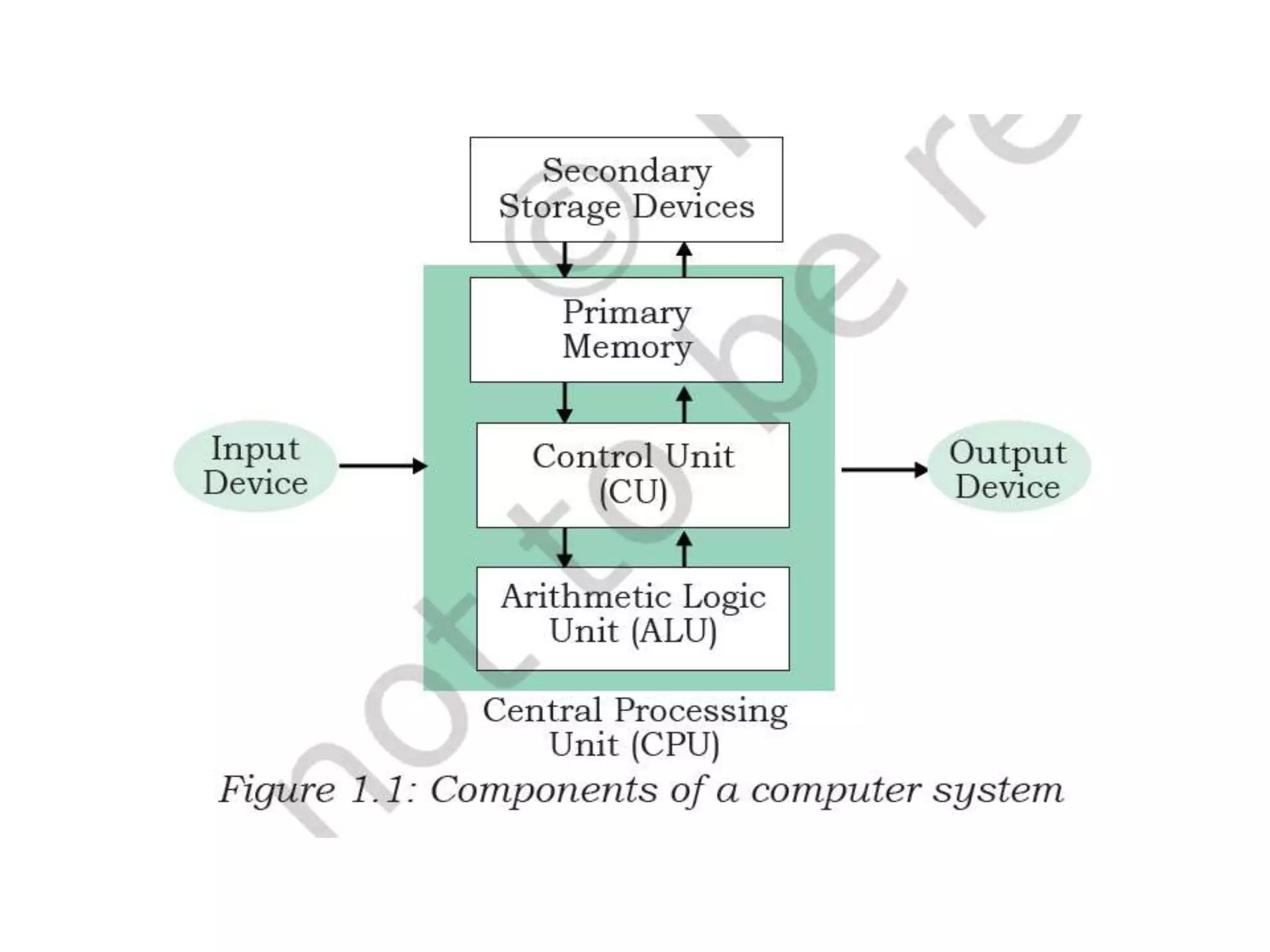


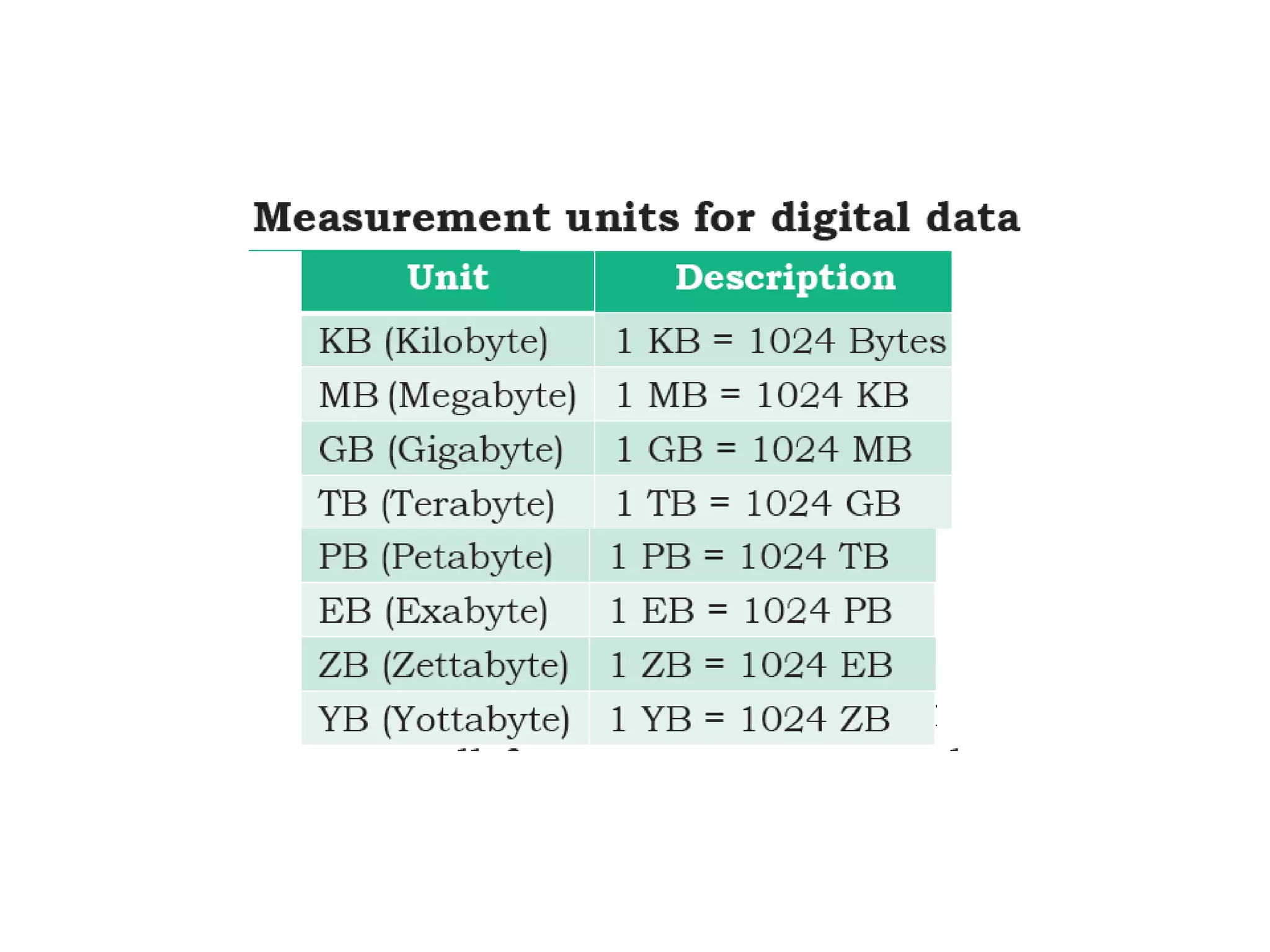
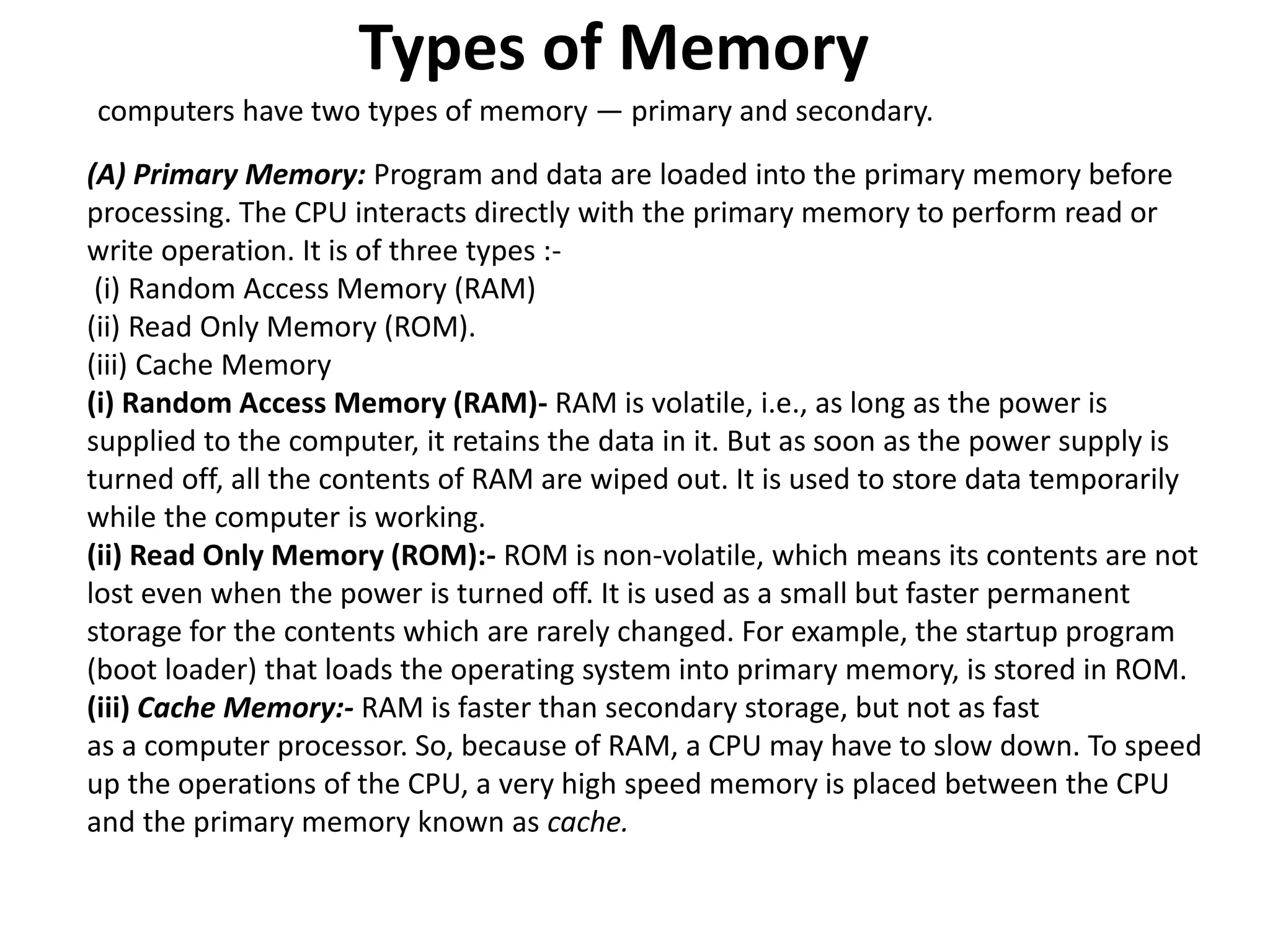


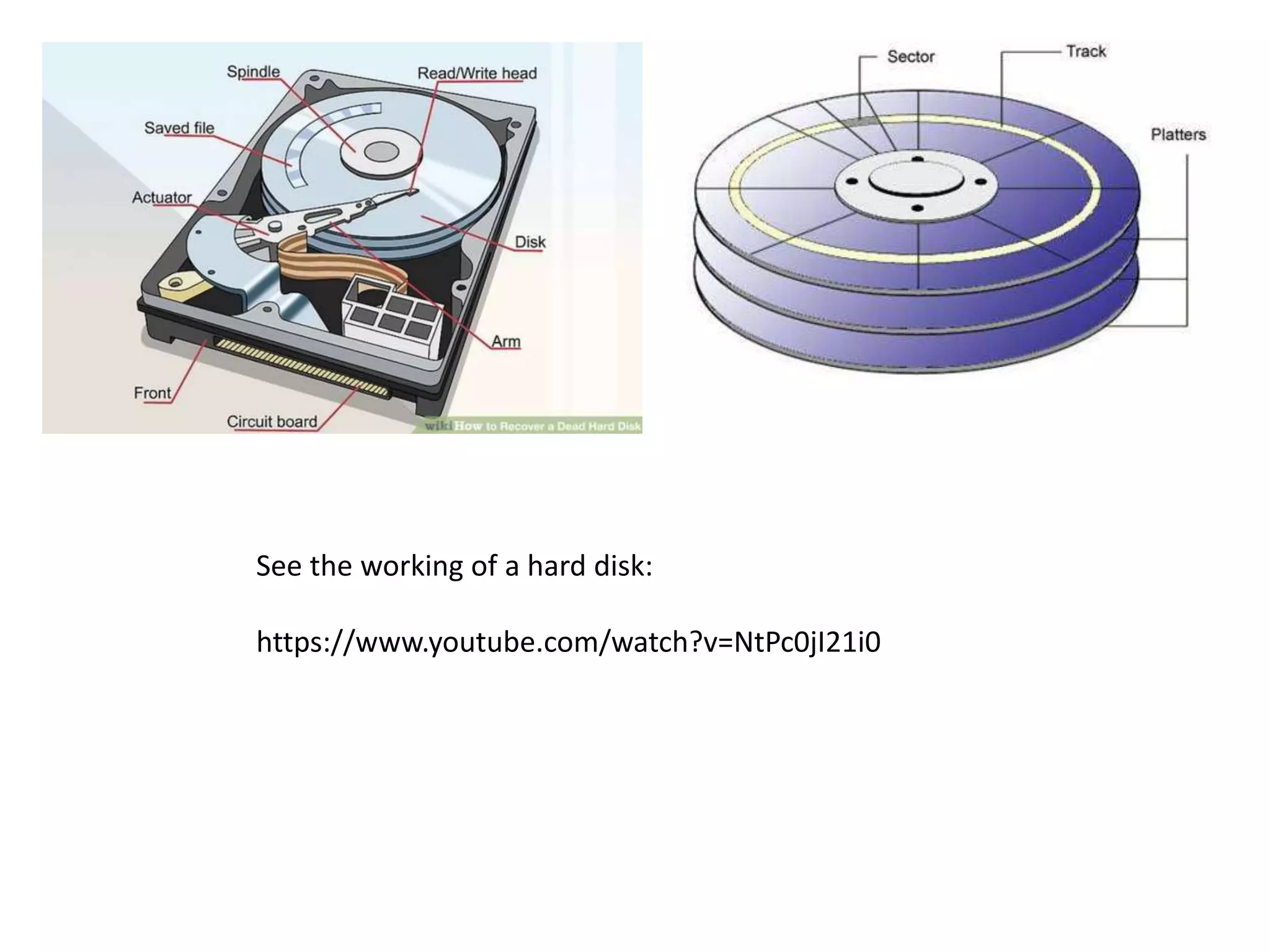



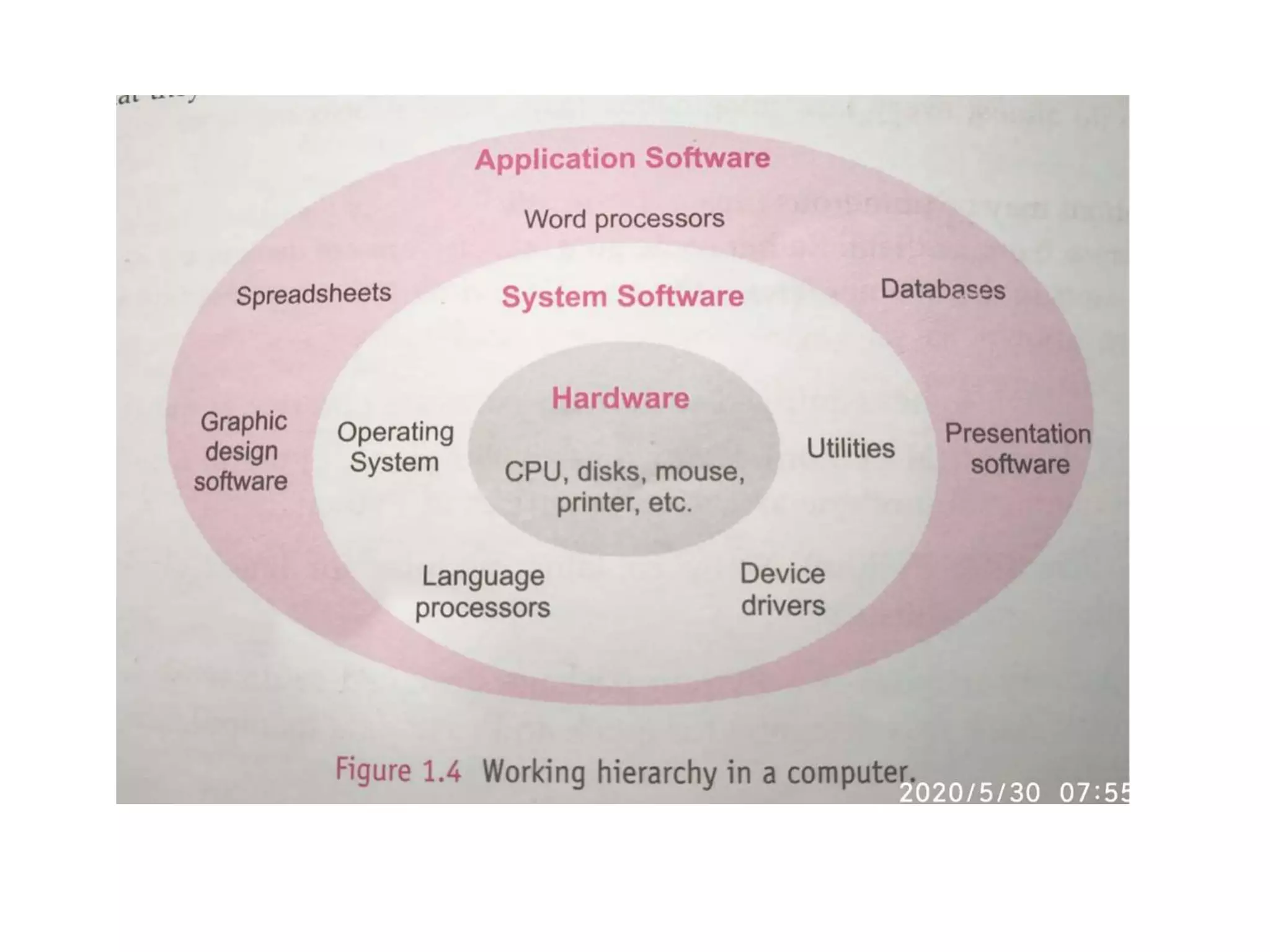




The document discusses the key components of a computer system including the central processing unit (CPU), memory, input/output devices, and storage devices. It describes the different types of computer memory including primary memory like RAM, ROM, and cache and secondary memory like hard disk drives. It also discusses the different types of software including system software like operating systems, language processors, and utilities as well as application software used for specific tasks.


















