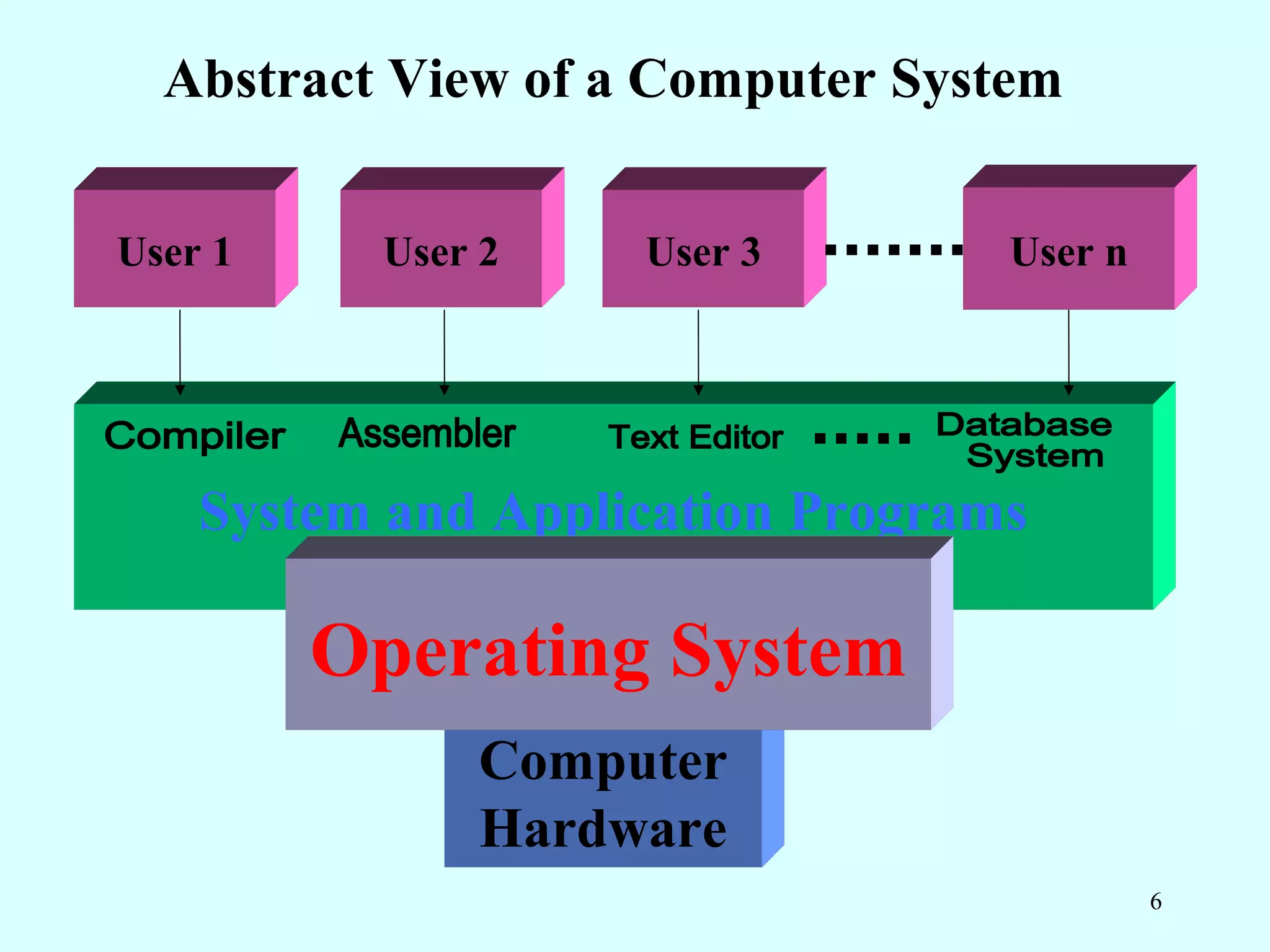
The document defines operating systems and describes their basic components and functions. It discusses how operating systems provide an interface between hardware and software, manage system resources, and allow for the execution of user programs. The goals of an operating system are to provide convenience for users and efficient operation of the computer system. An operating system is a type of system software that coordinates hardware and software and controls and allocates resources.