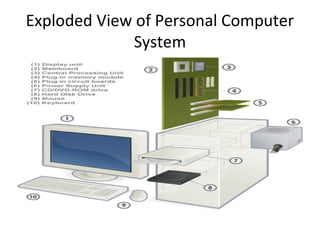
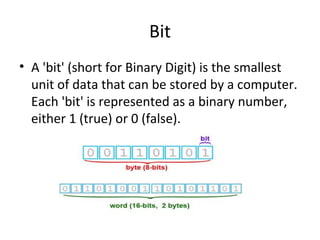
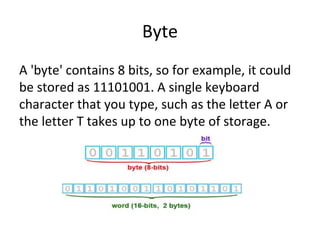
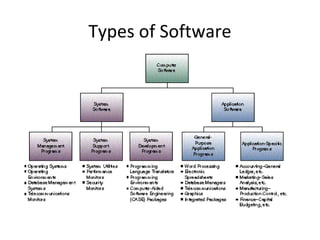
This document discusses the key components of a computer system including hardware and software elements. It describes the main hardware components like the input, processing, output and storage units. It explains the functions of these units and provides examples. It also discusses software types like system software which manages computer resources, and application software which performs specific tasks for users. Examples of operating systems, word processors and other application types are provided.