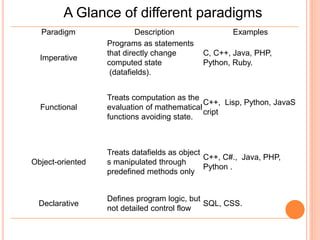
This presentation provides an overview of various programming paradigms including imperative, declarative, functional, object-oriented, and multi-paradigm. It discusses the basic concepts and definitions of each paradigm, provides examples of commonly used languages, and briefly compares the different approaches. The presentation concludes that while no consensus exists on the best paradigm, procedural and object-oriented paradigms using languages like C, C++, and Java tend to be most popular for introductory courses.