Embed presentation
Downloaded 195 times
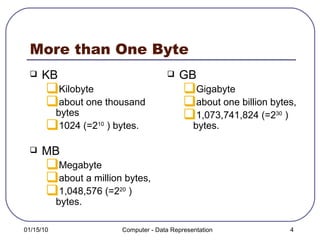


A bit is the smallest unit of digital information used by computers, representing either 1 or 0. Bytes are made up of 8 bits and are used to represent larger units of data storage like kilobytes, megabytes, and gigabytes. Computers use the binary numeral system of 1s and 0s to represent all data and perform calculations.





