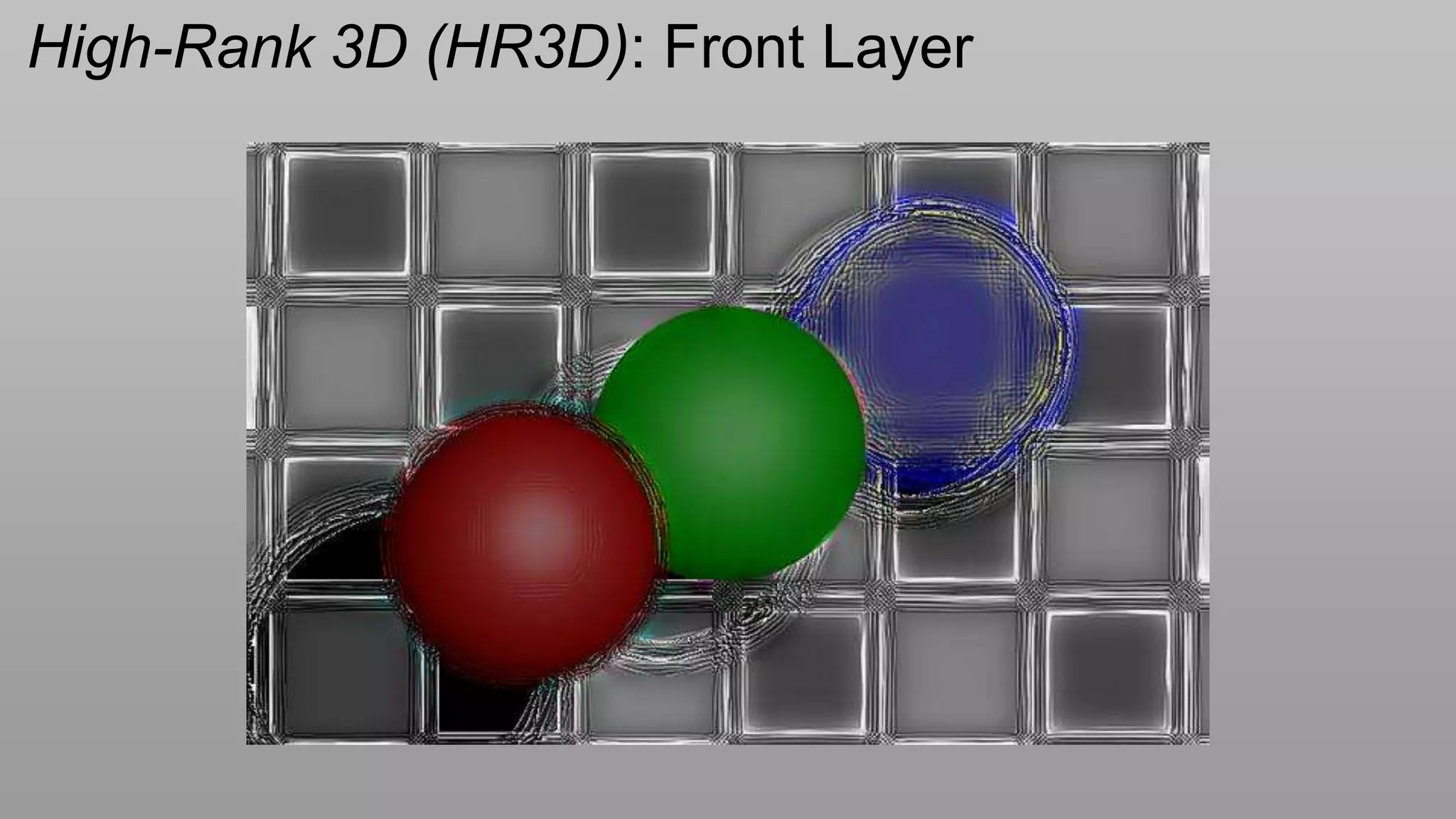
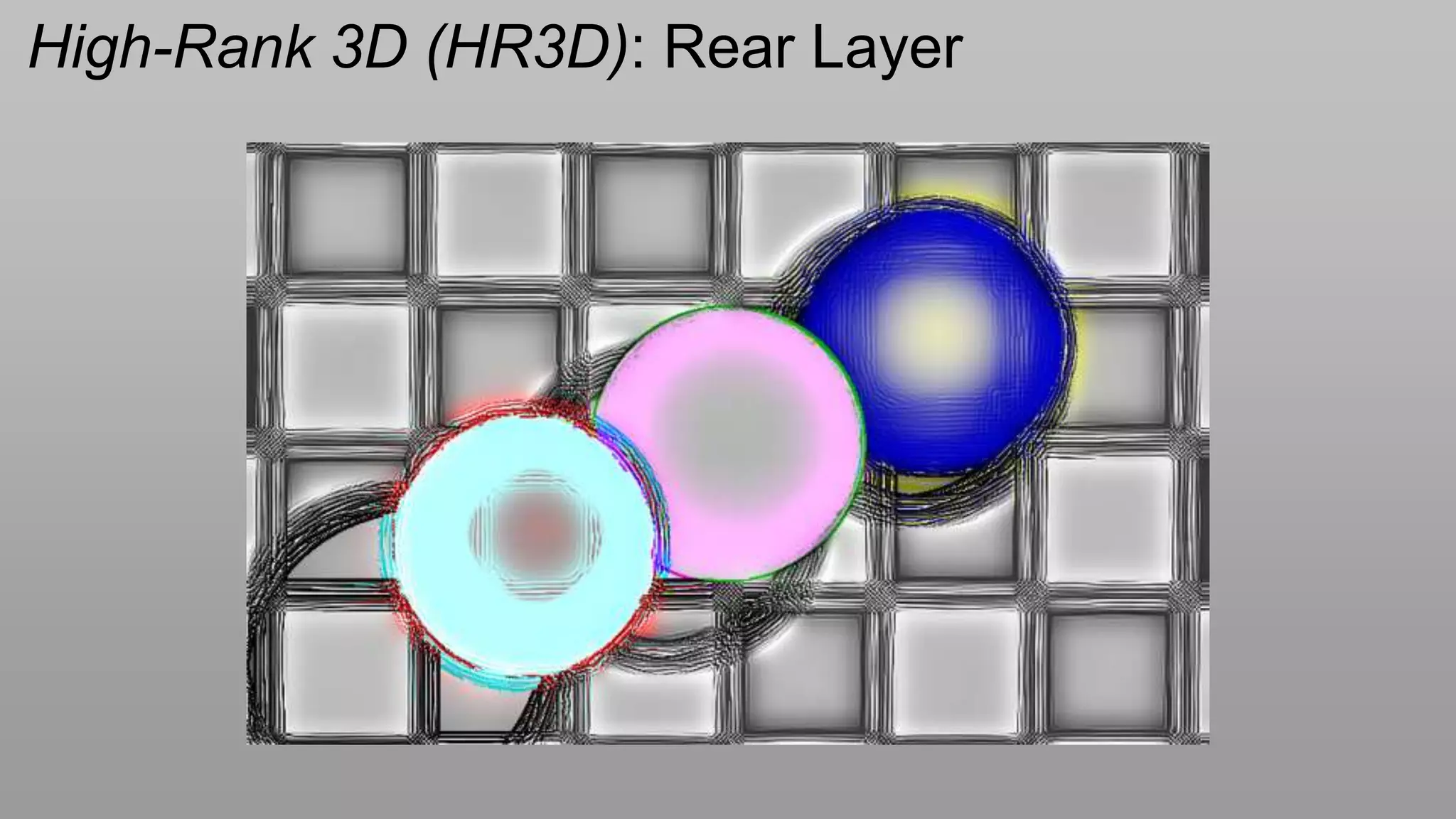
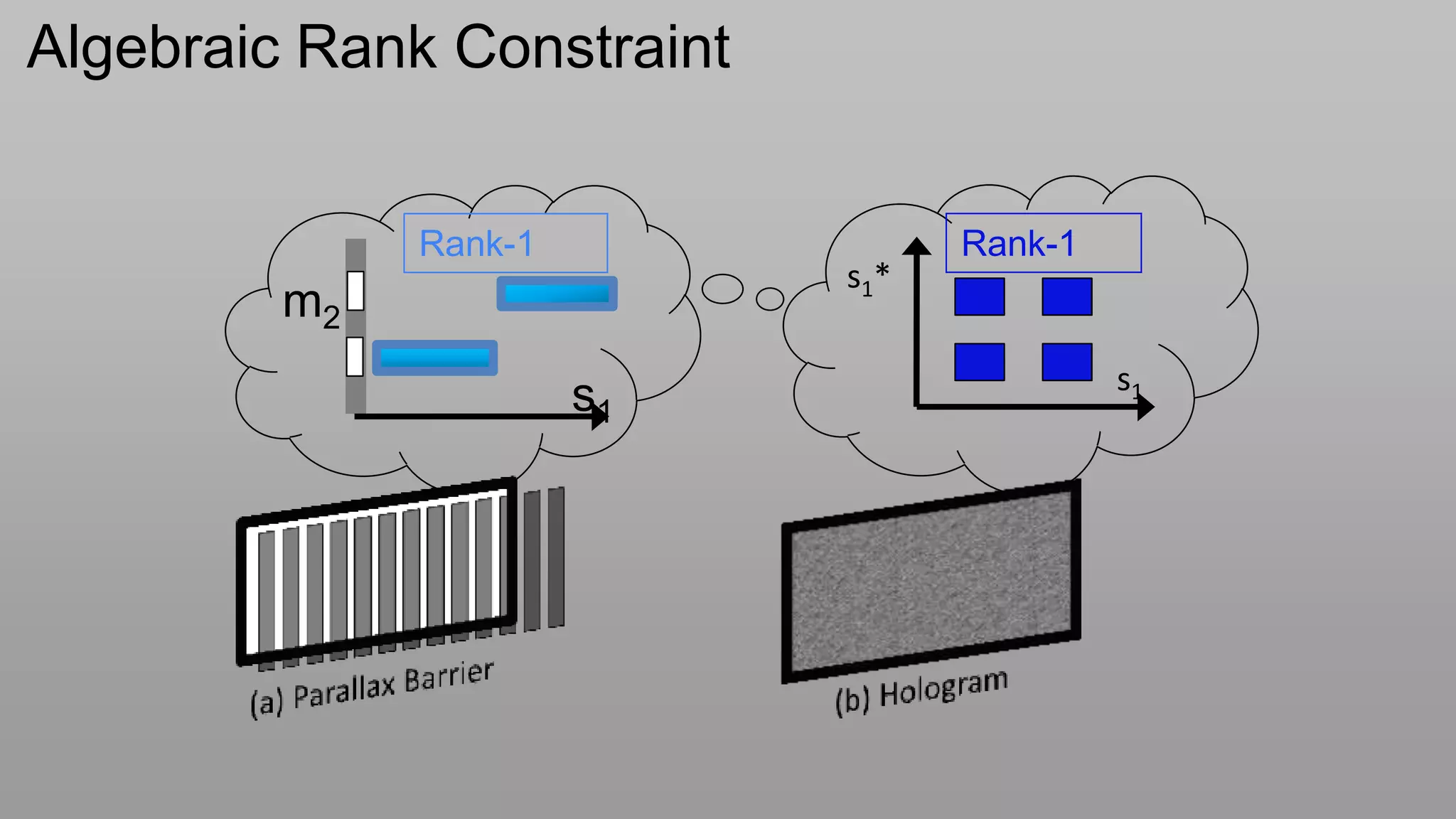
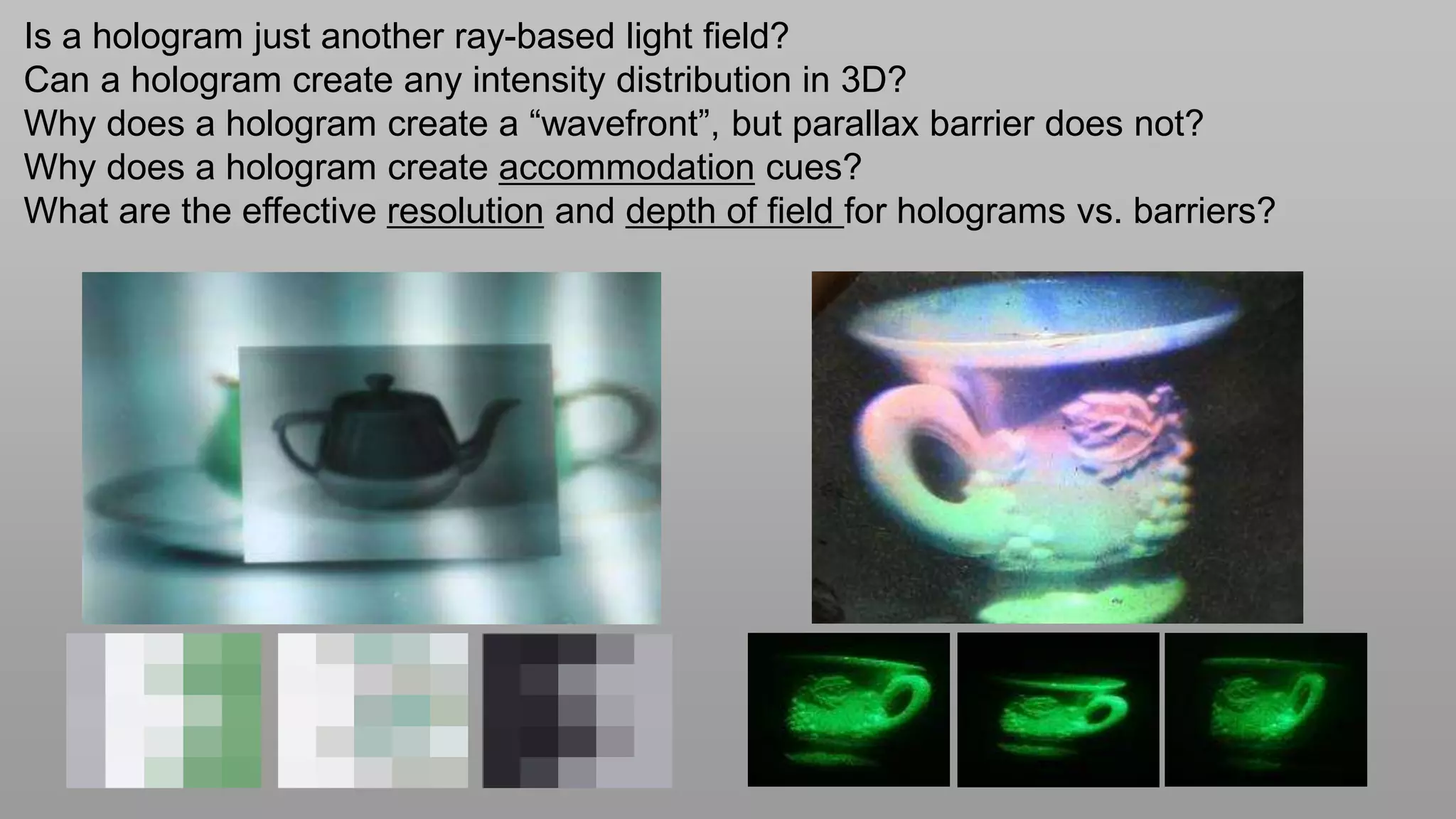
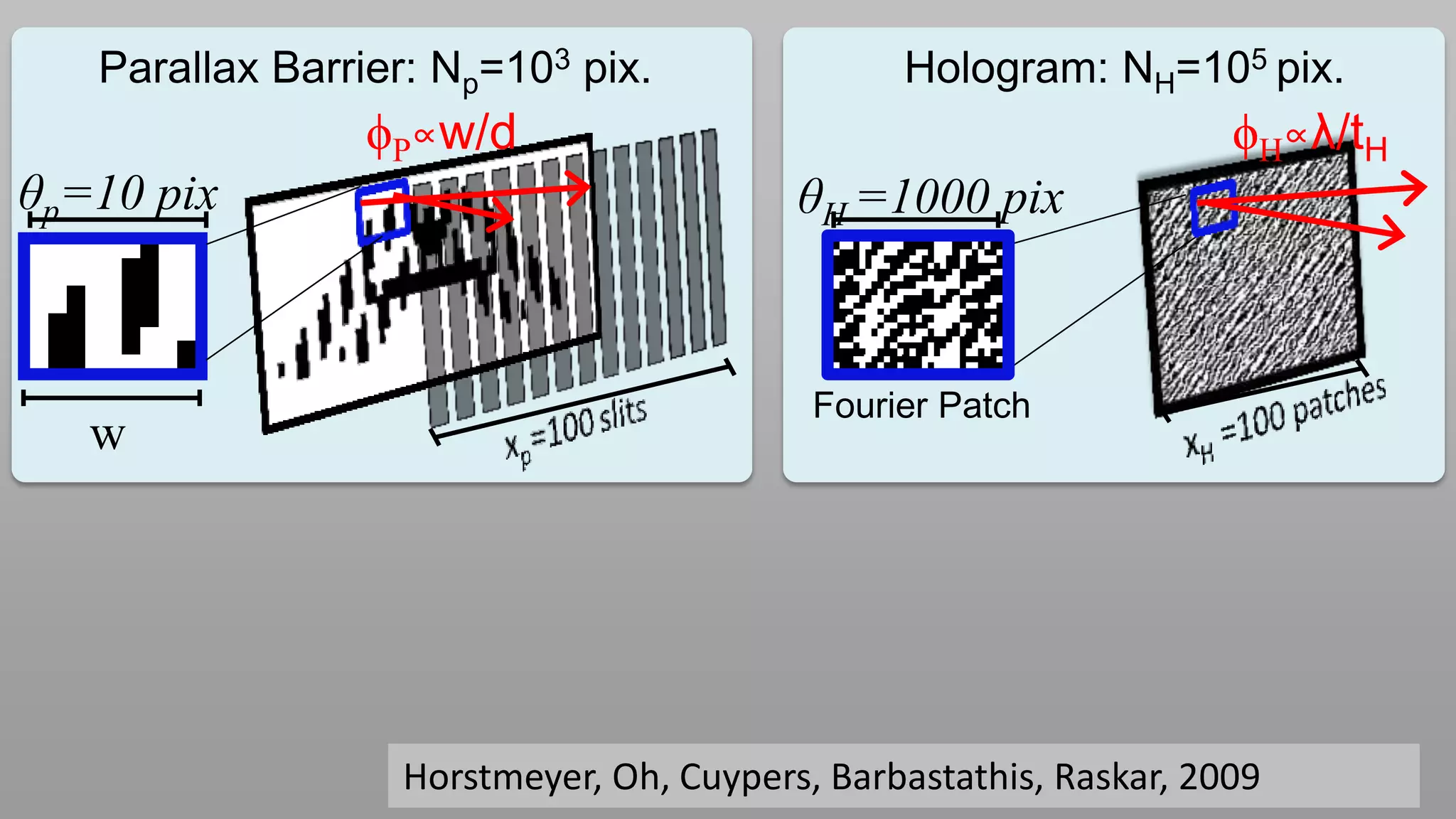
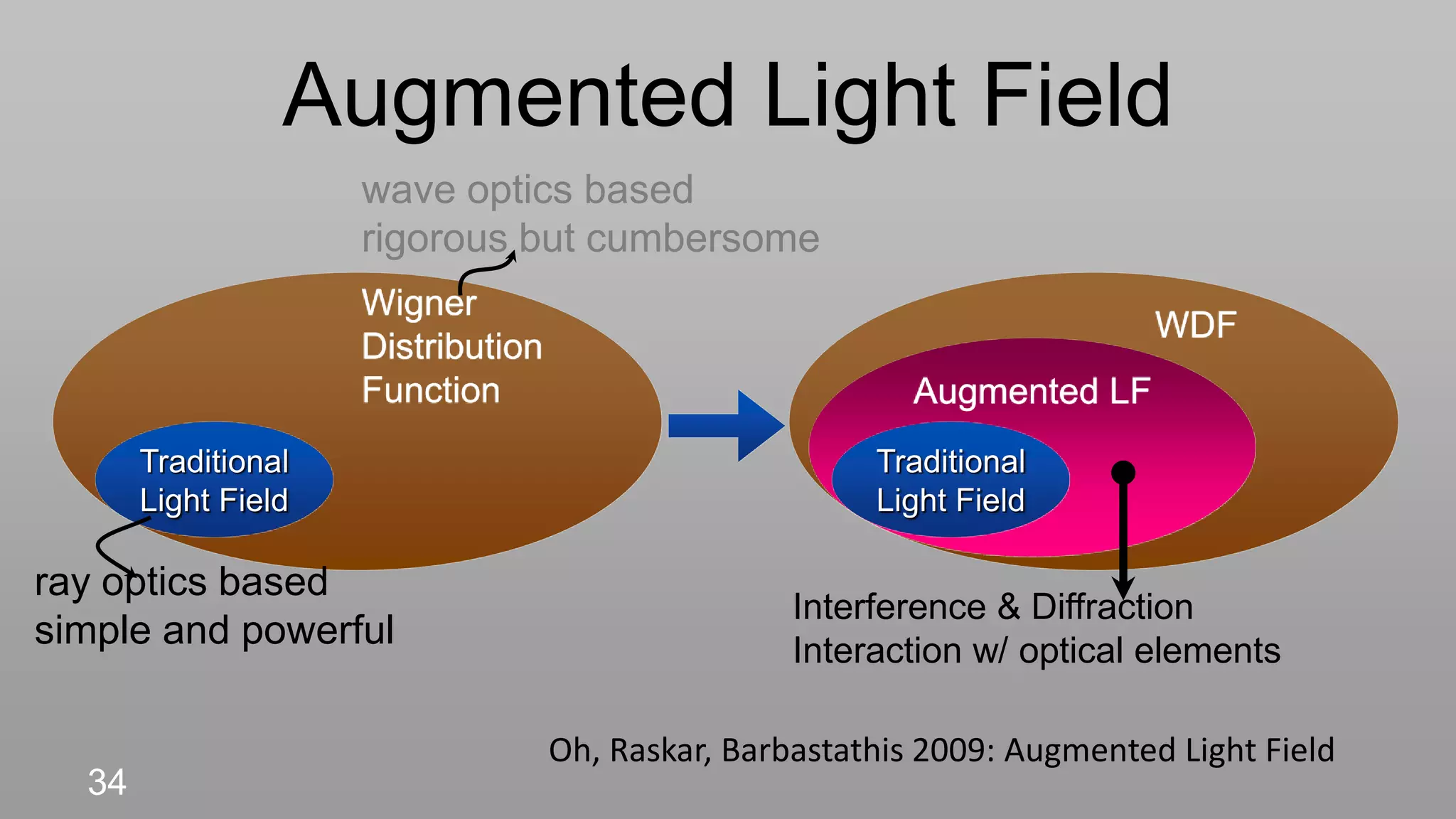
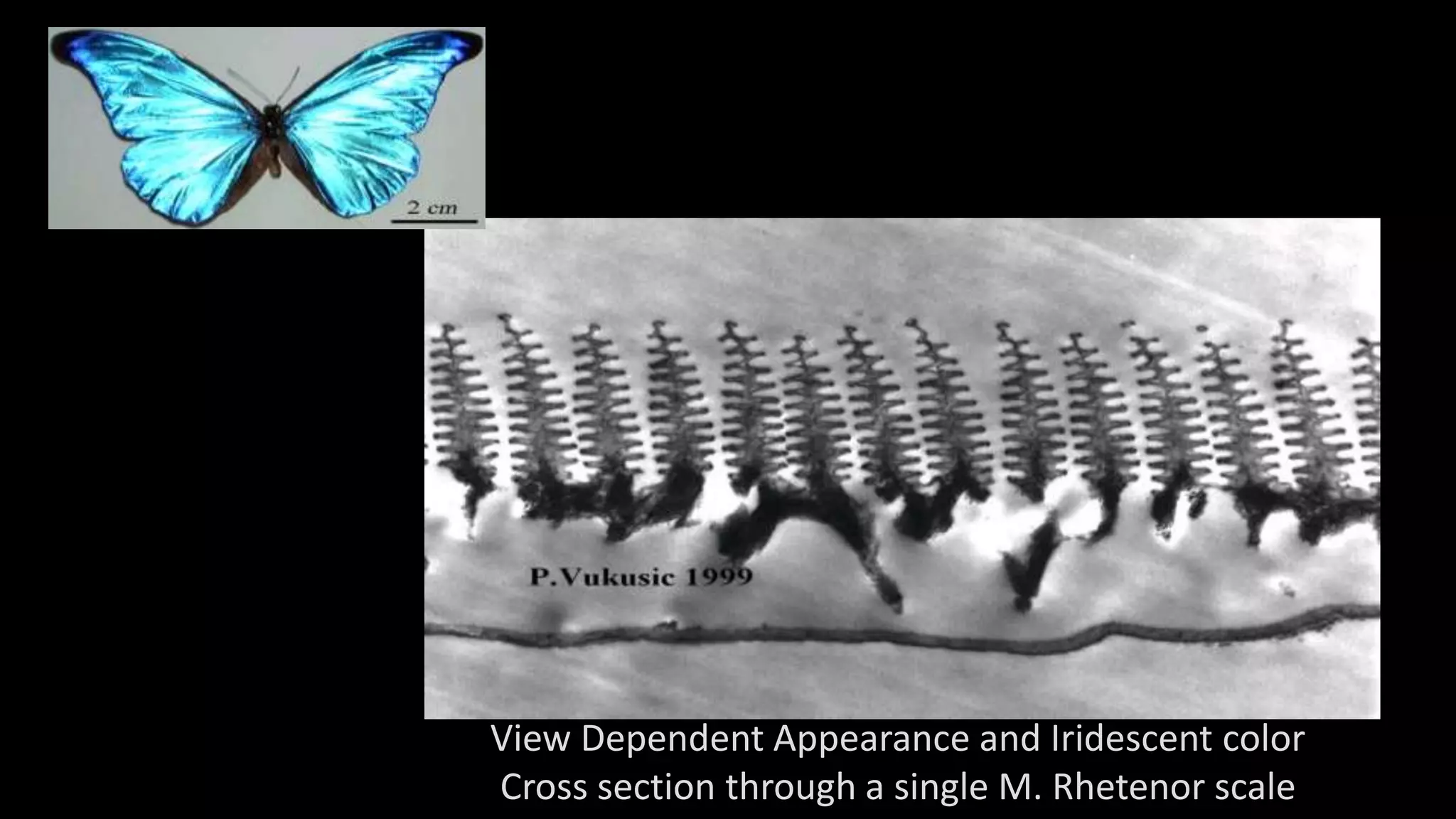
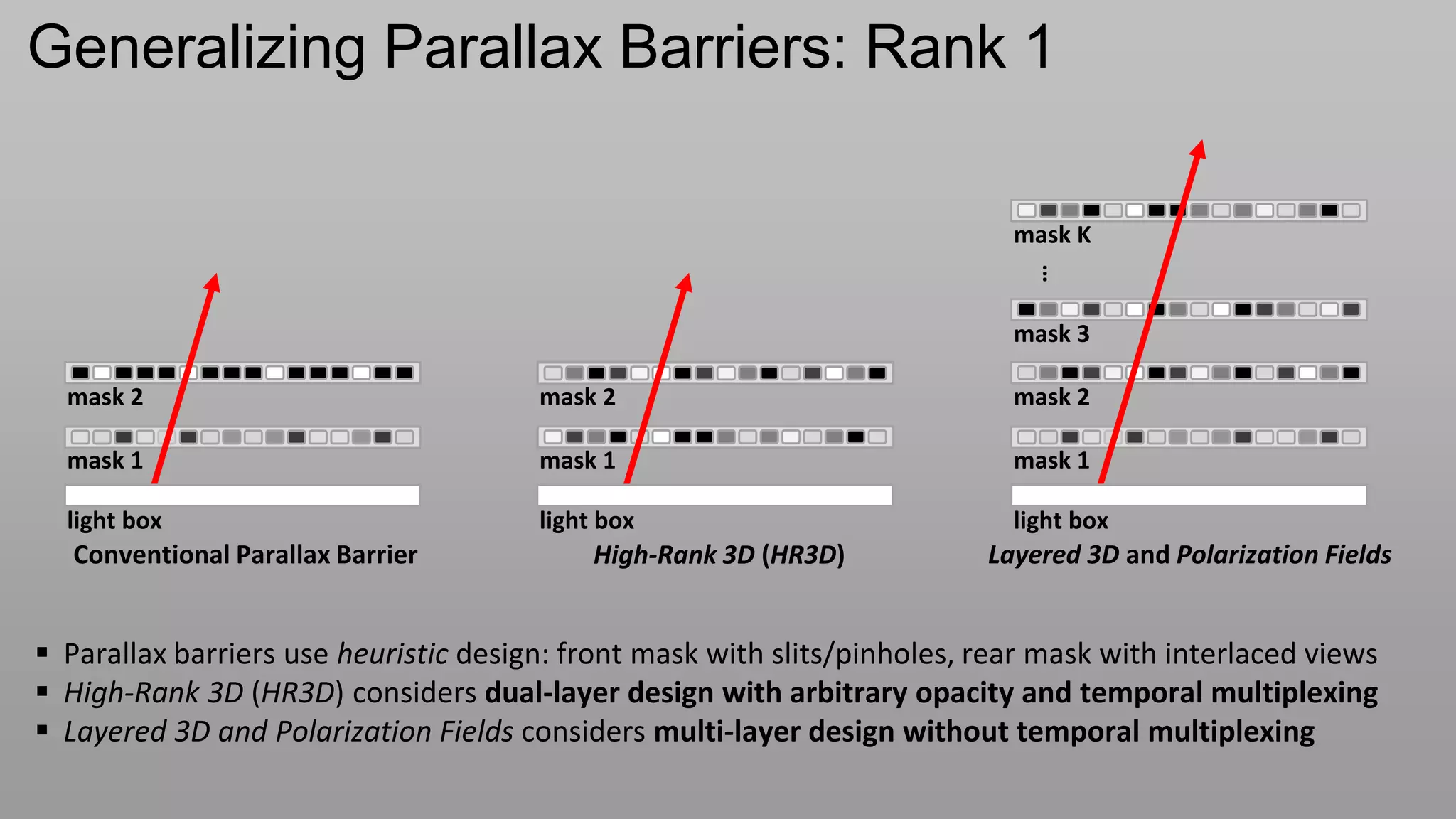
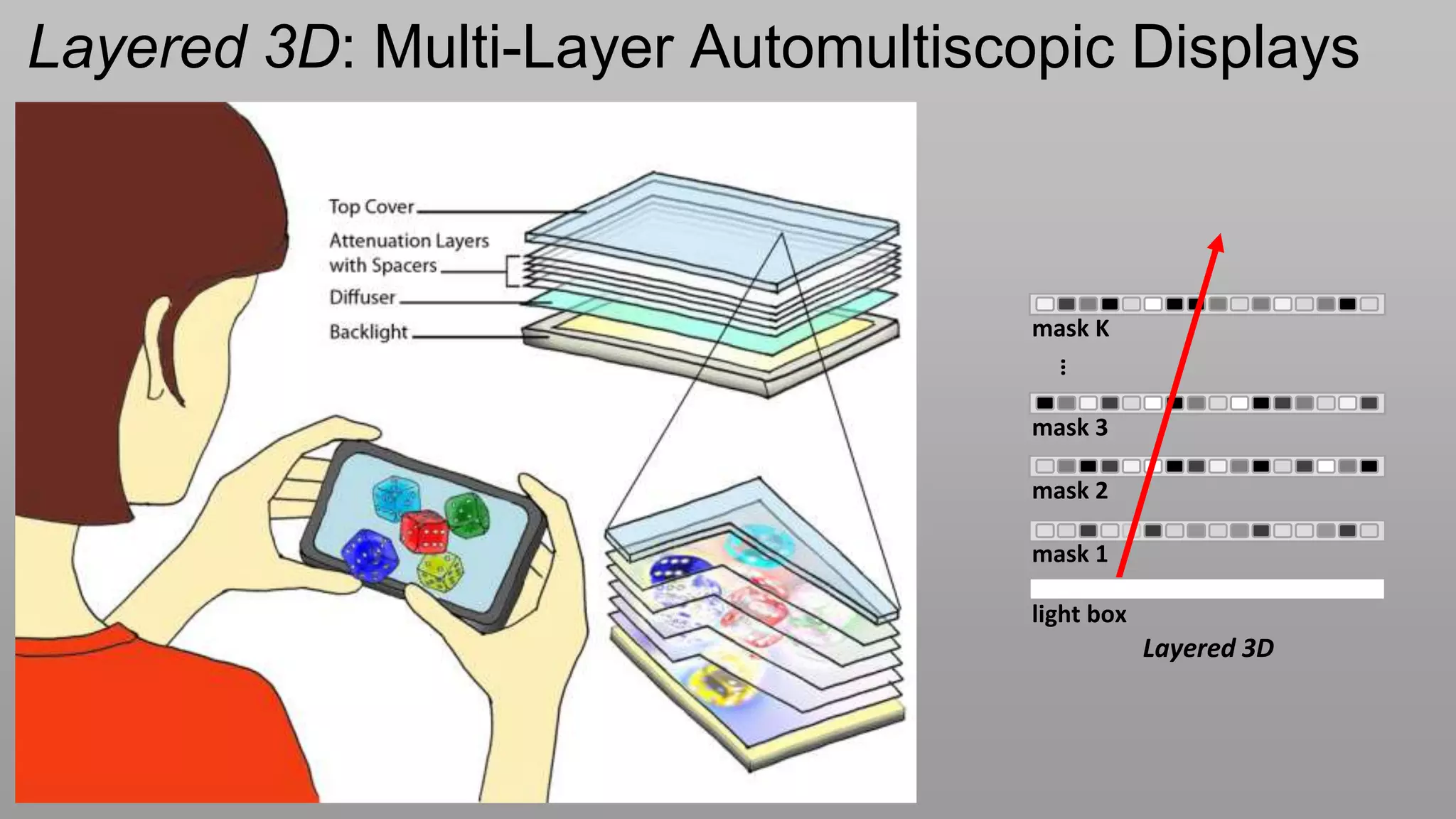
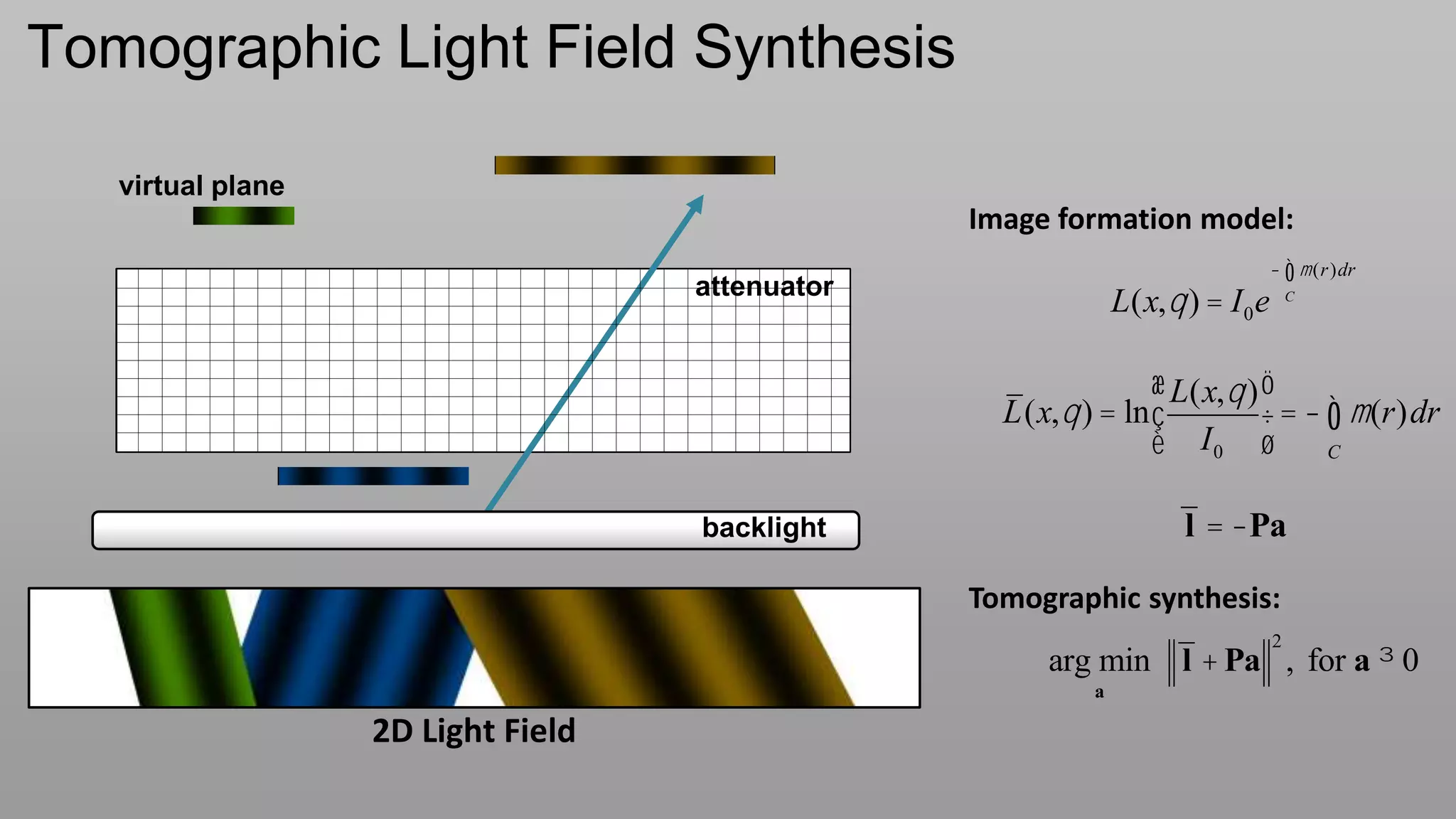
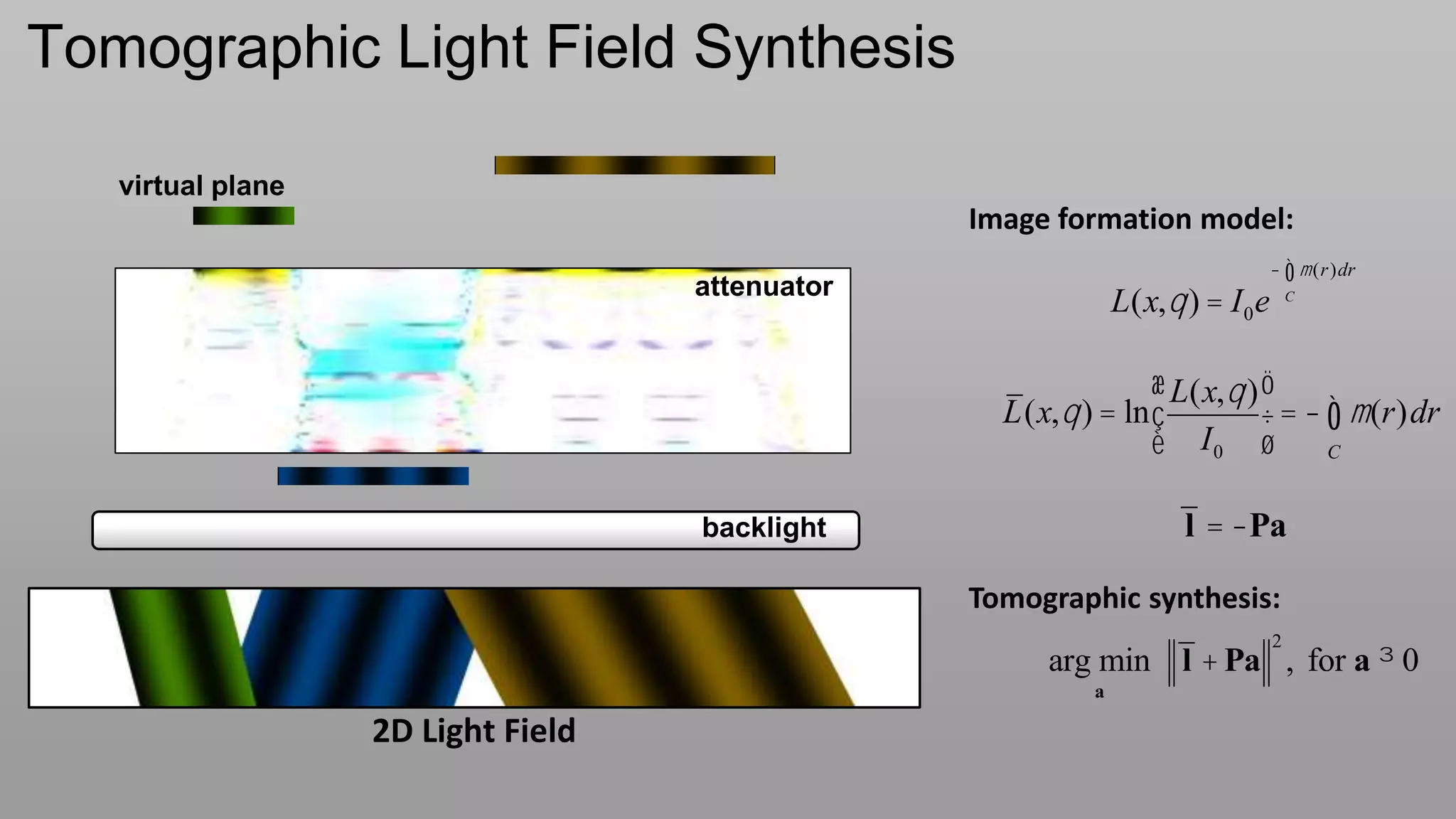
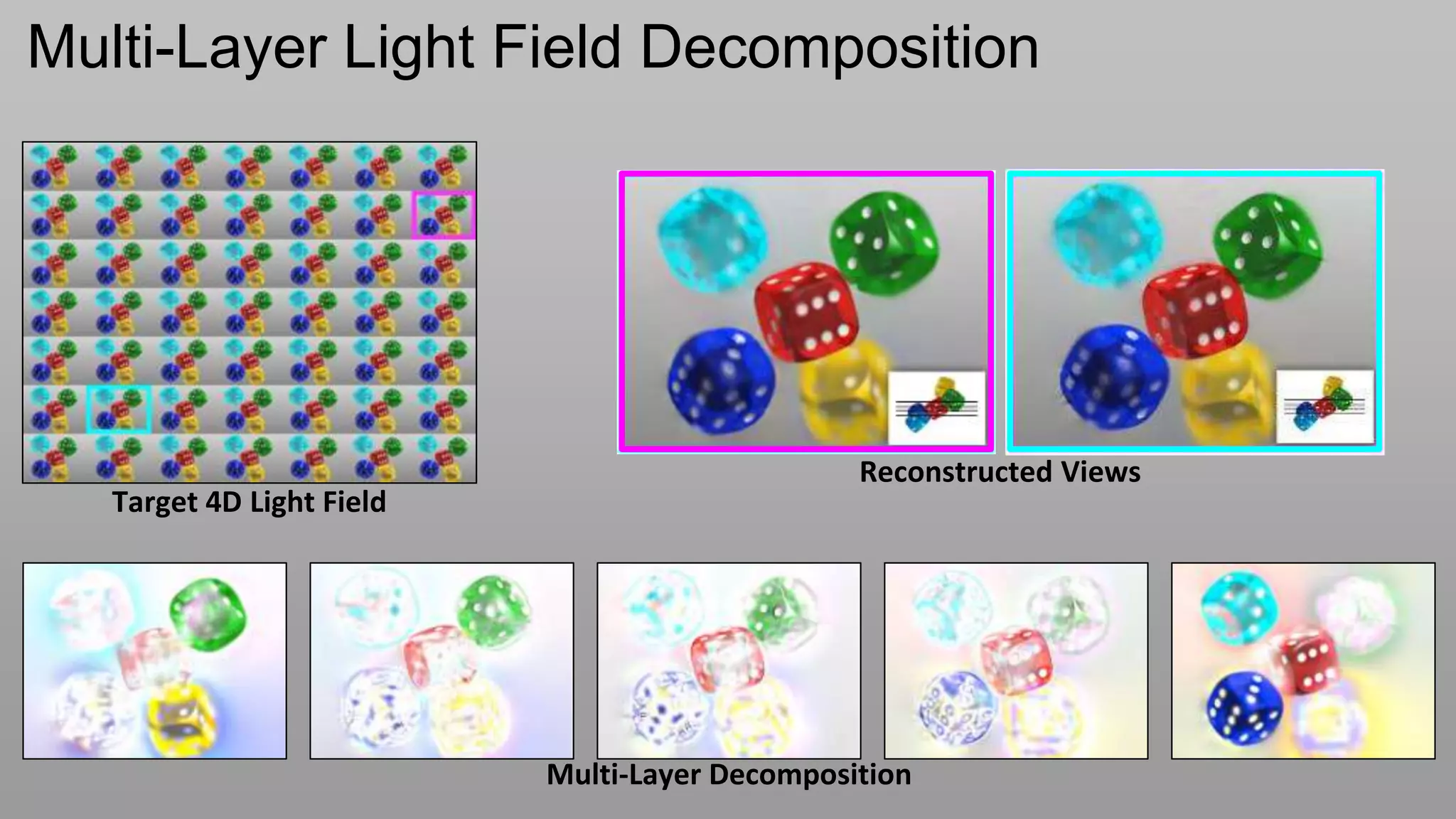
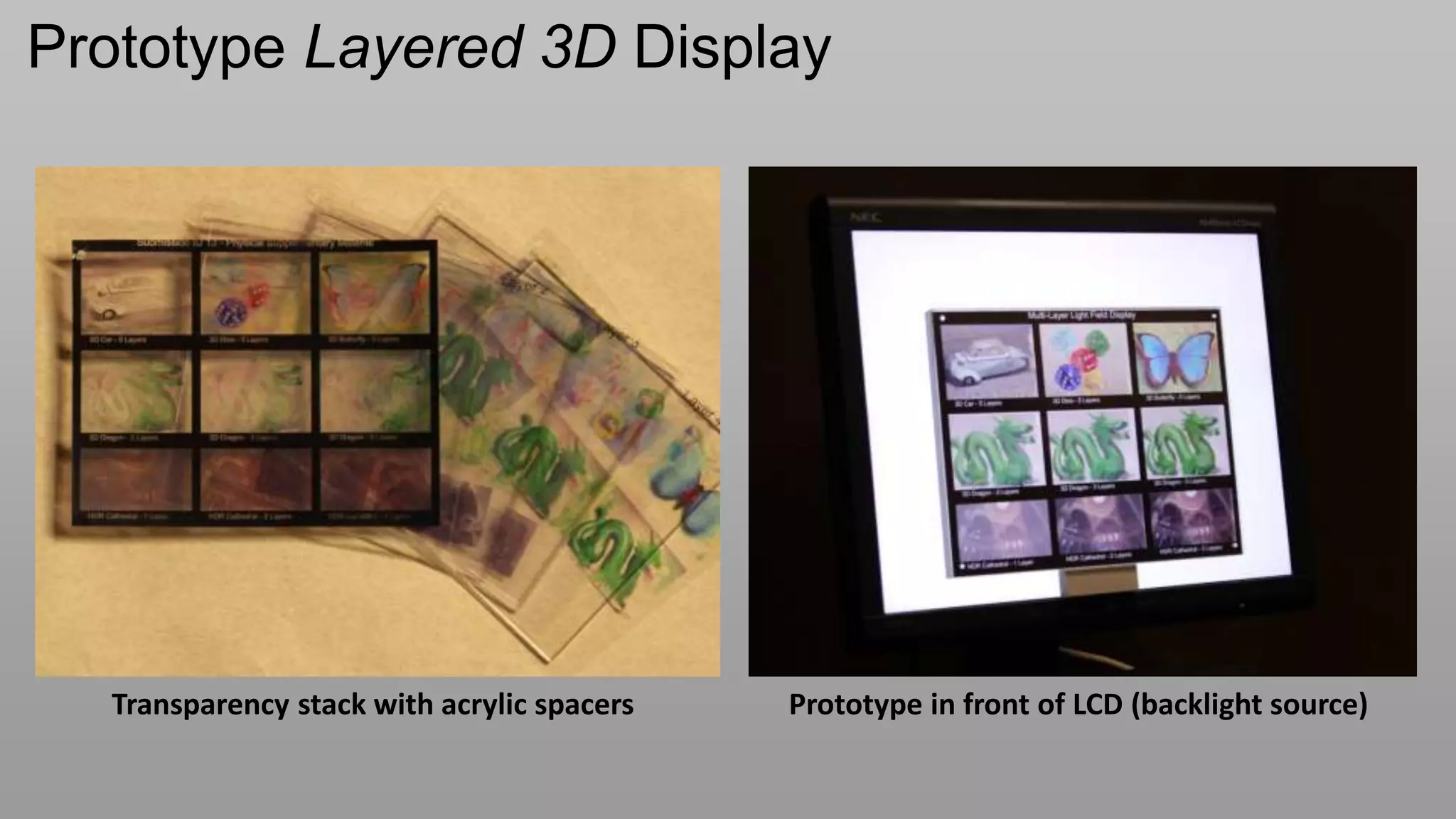
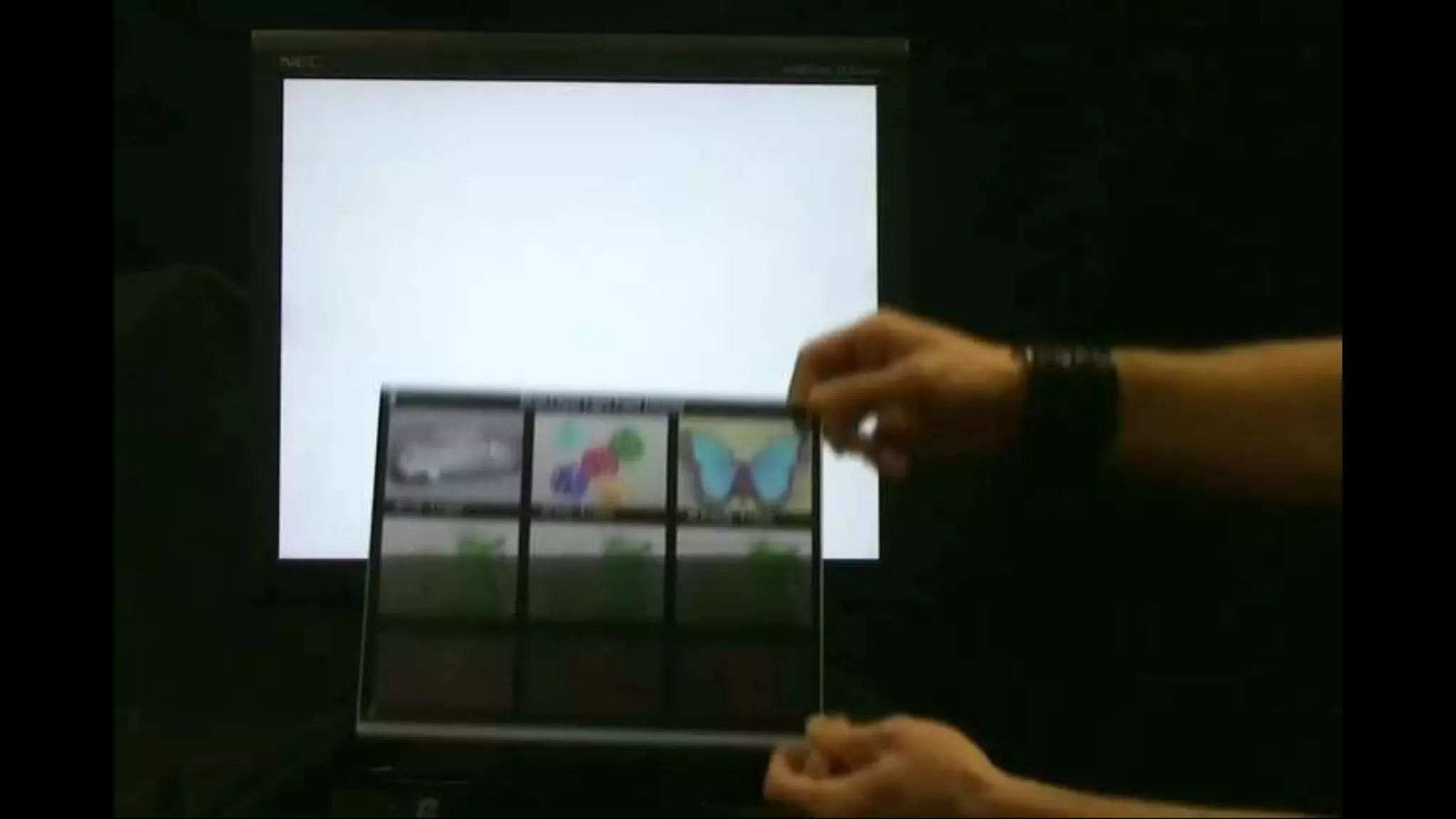
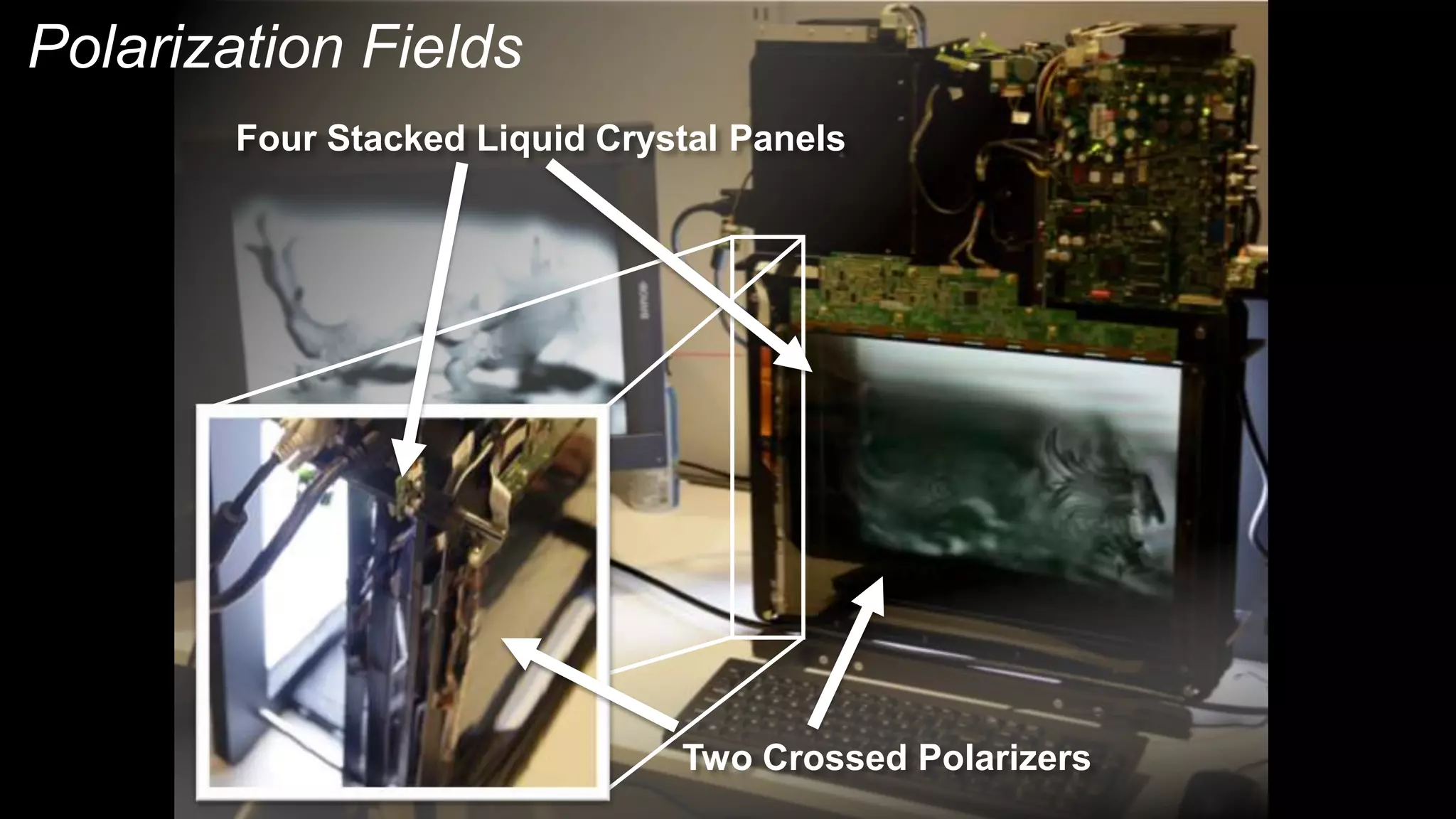
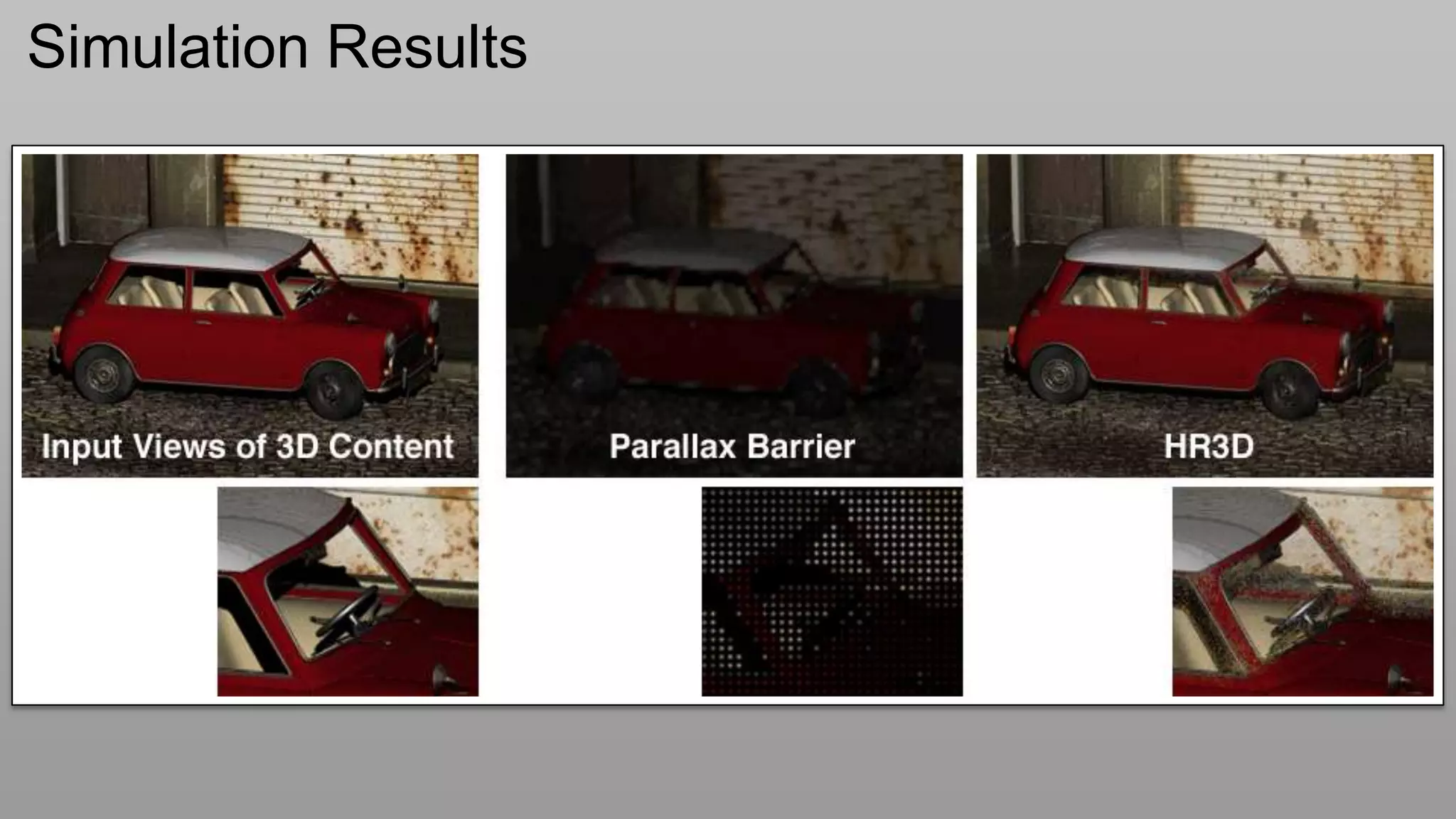
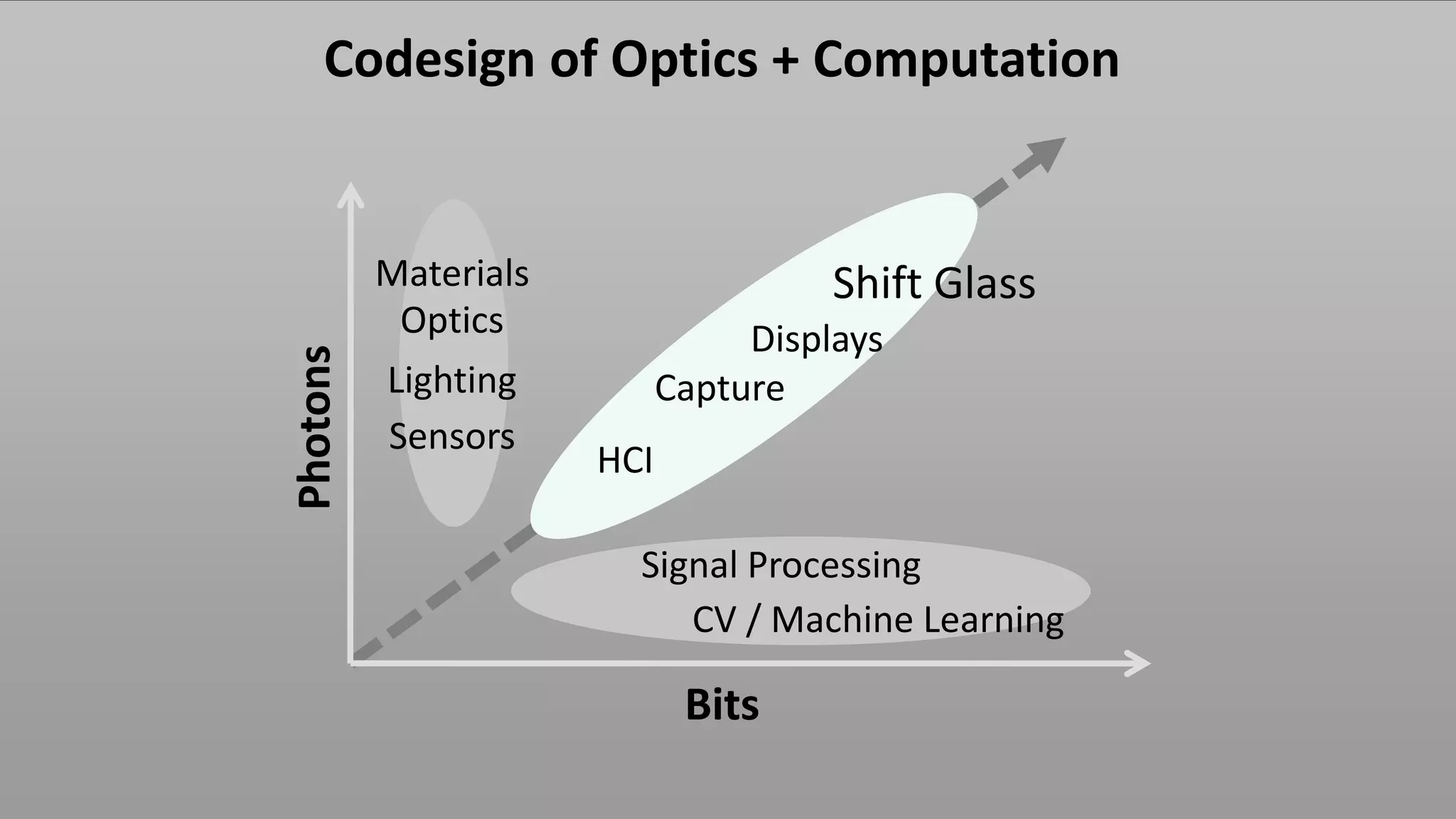
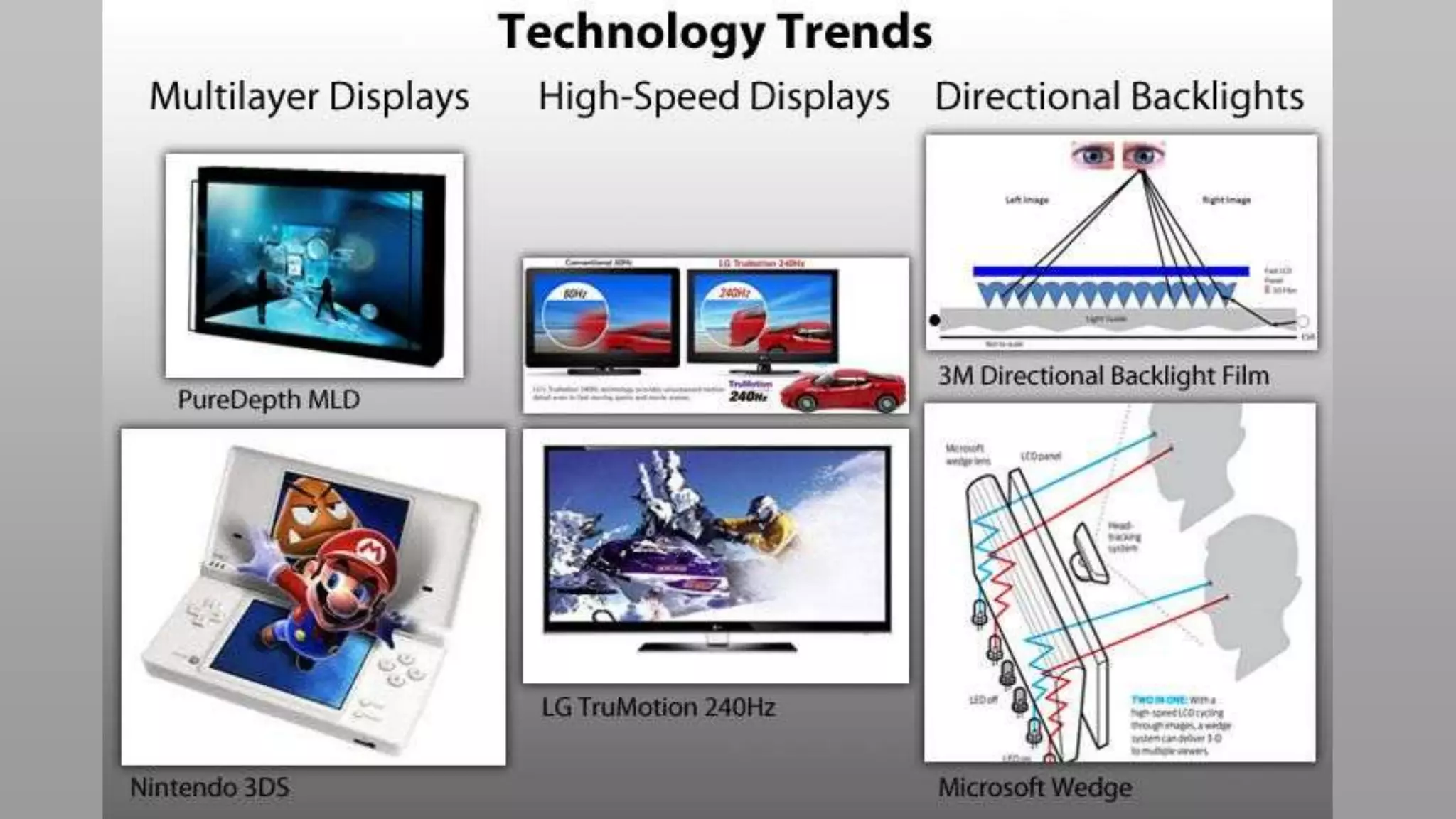
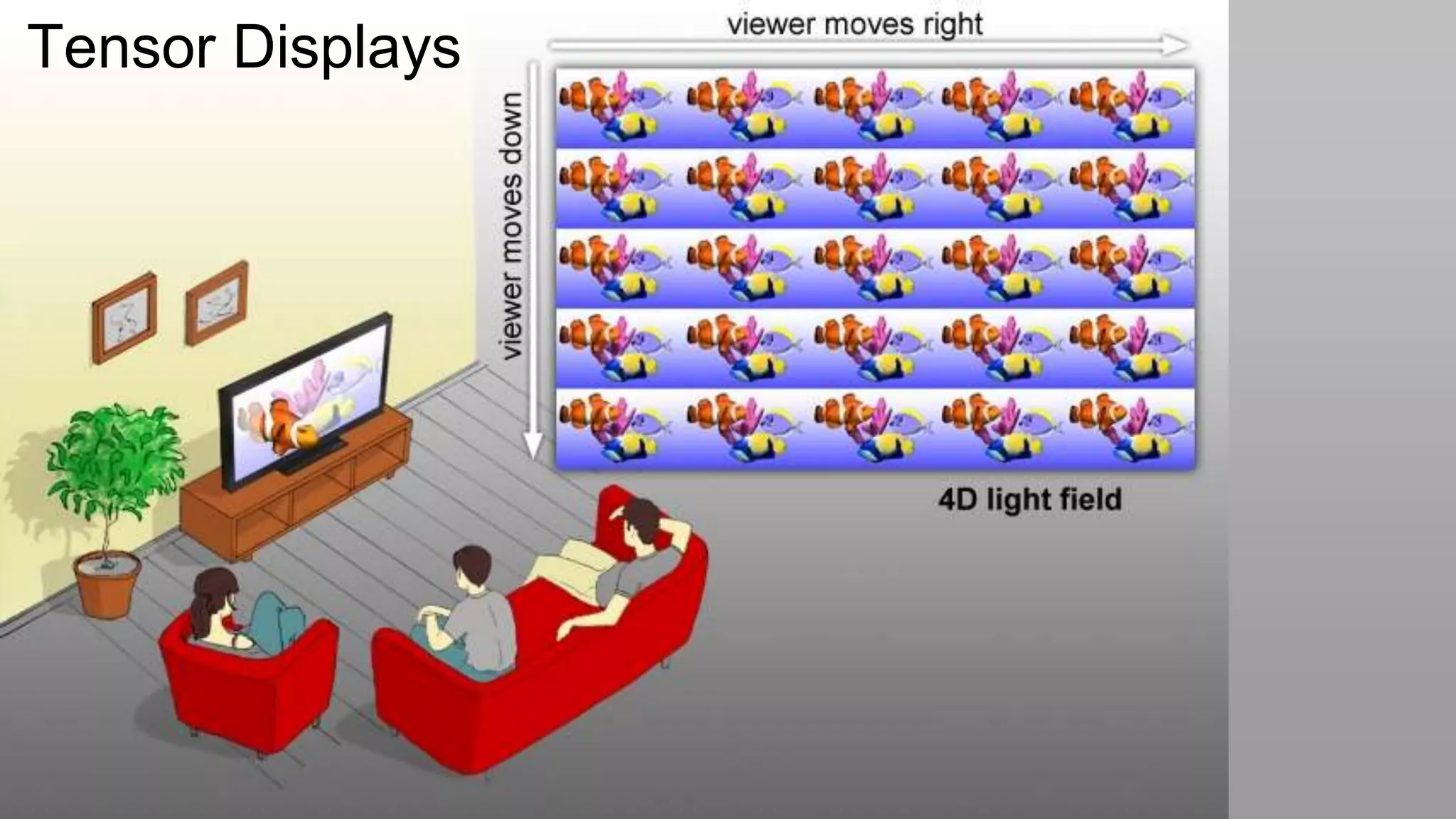
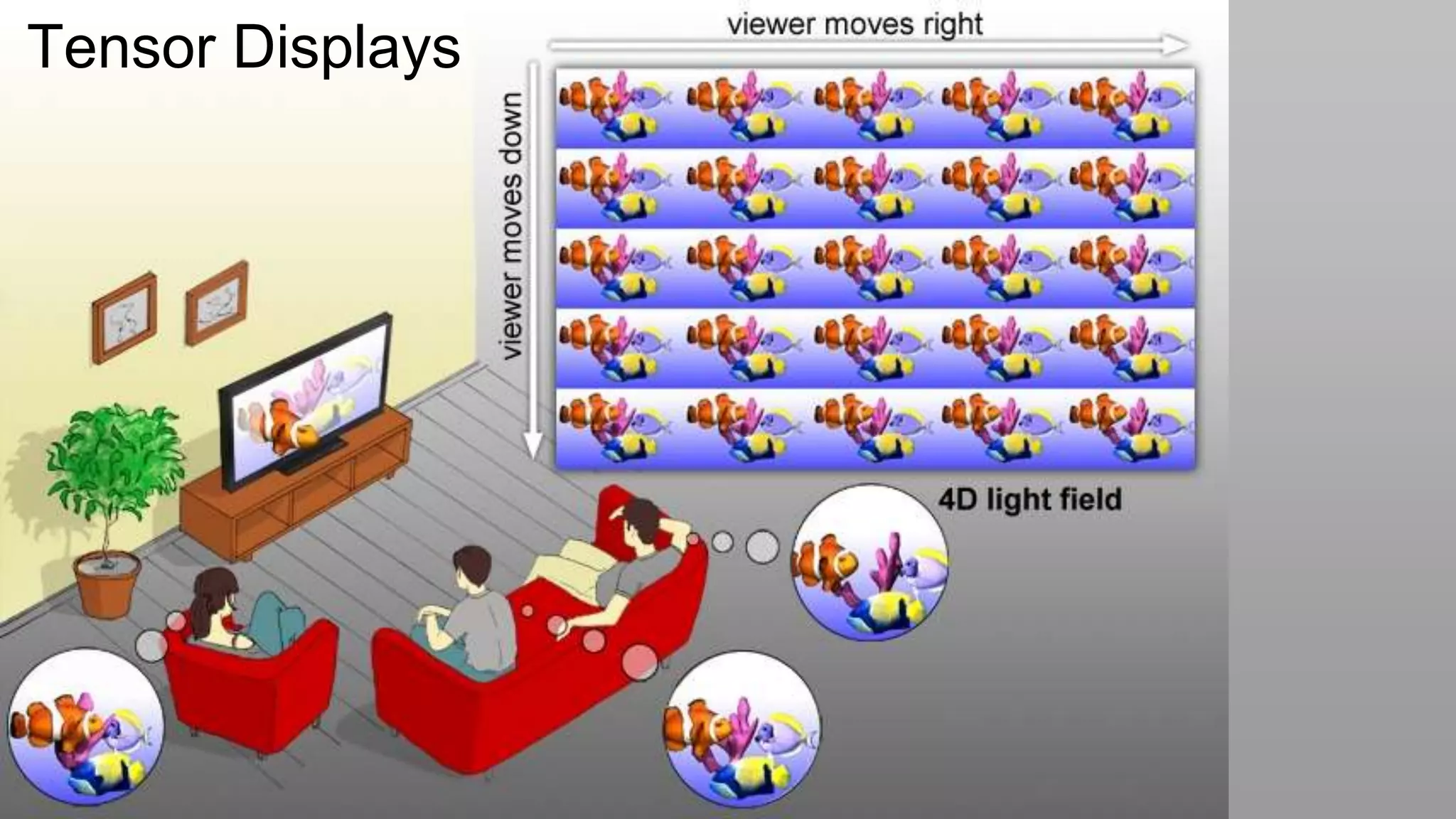
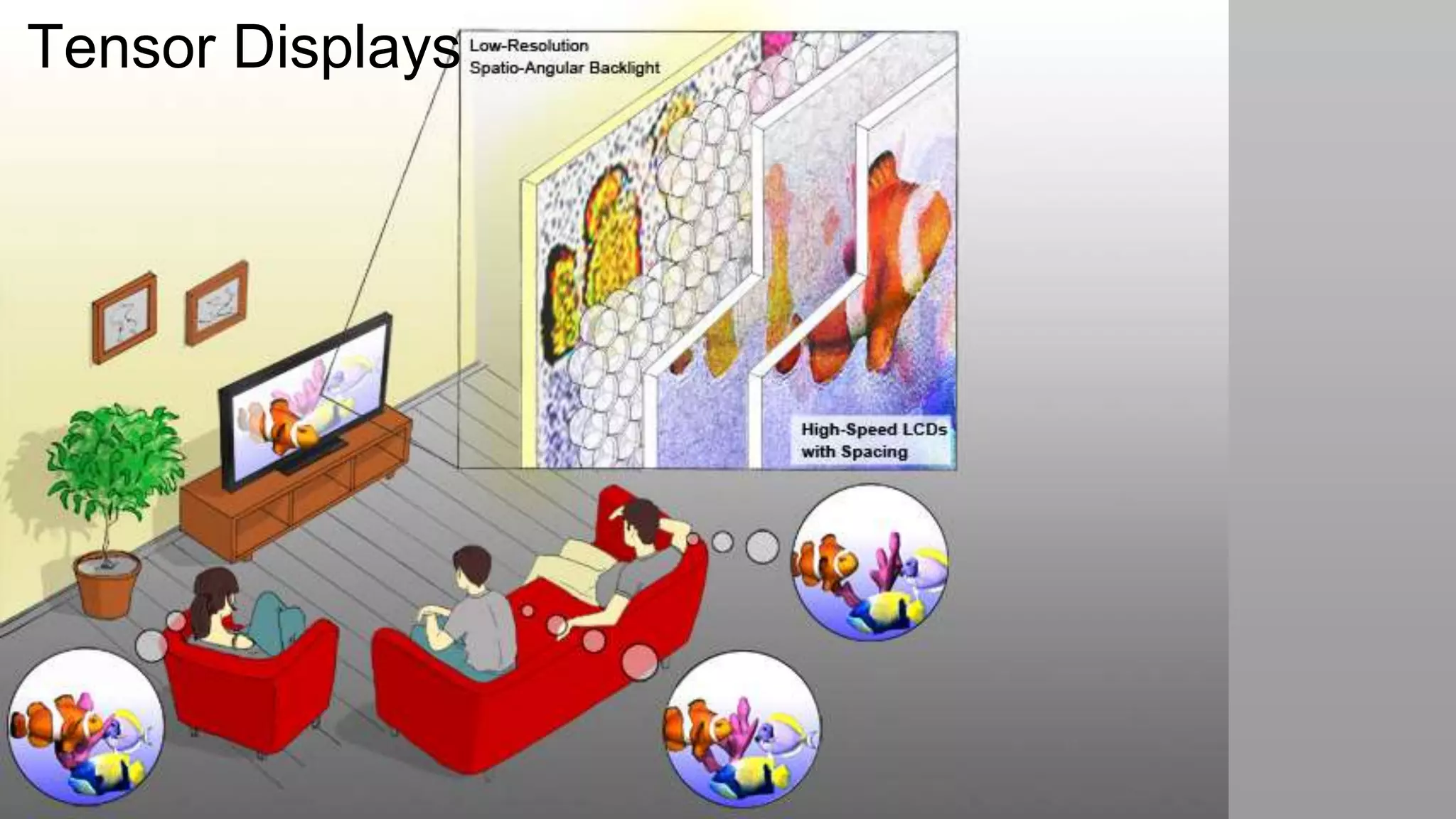
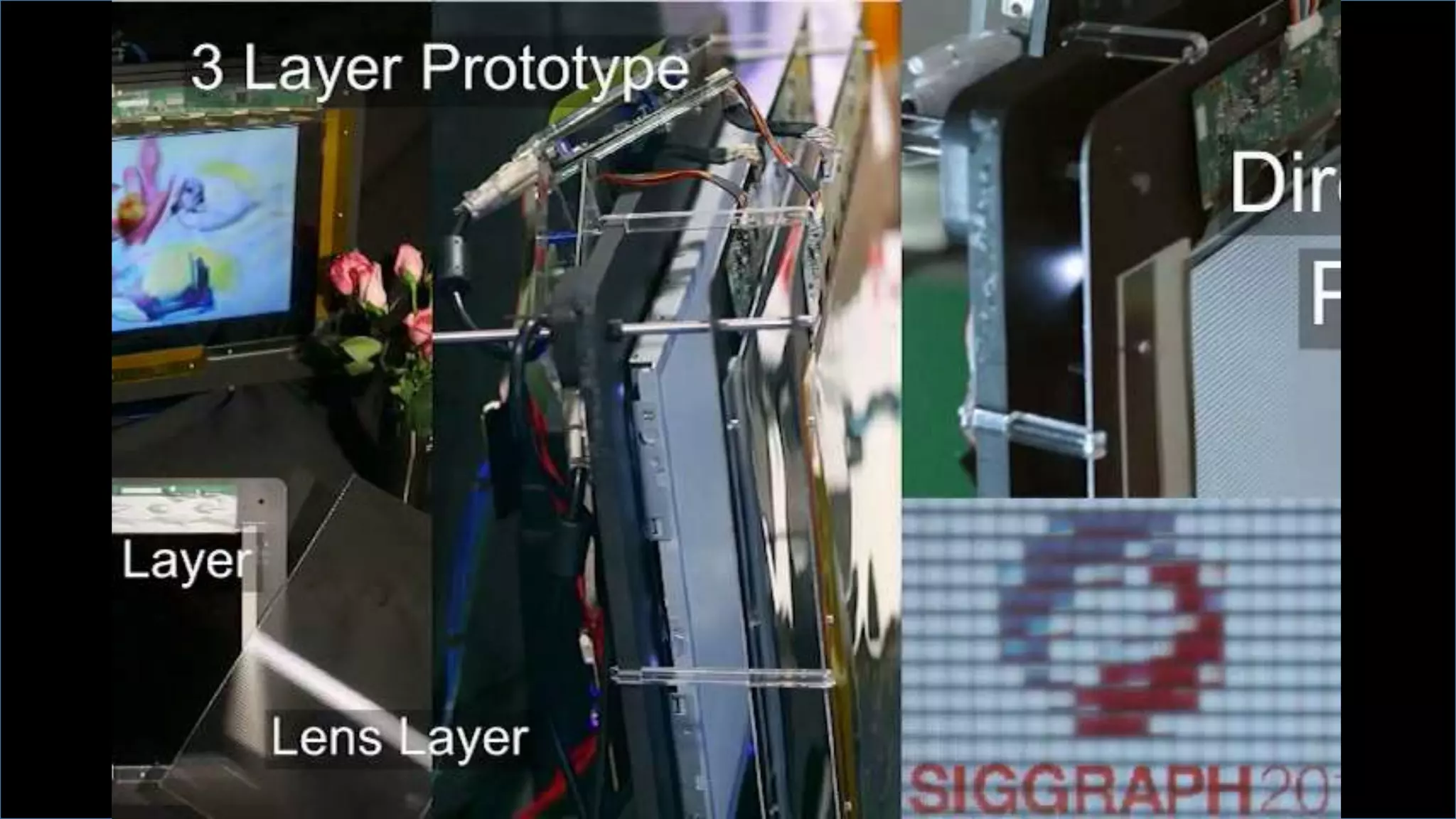
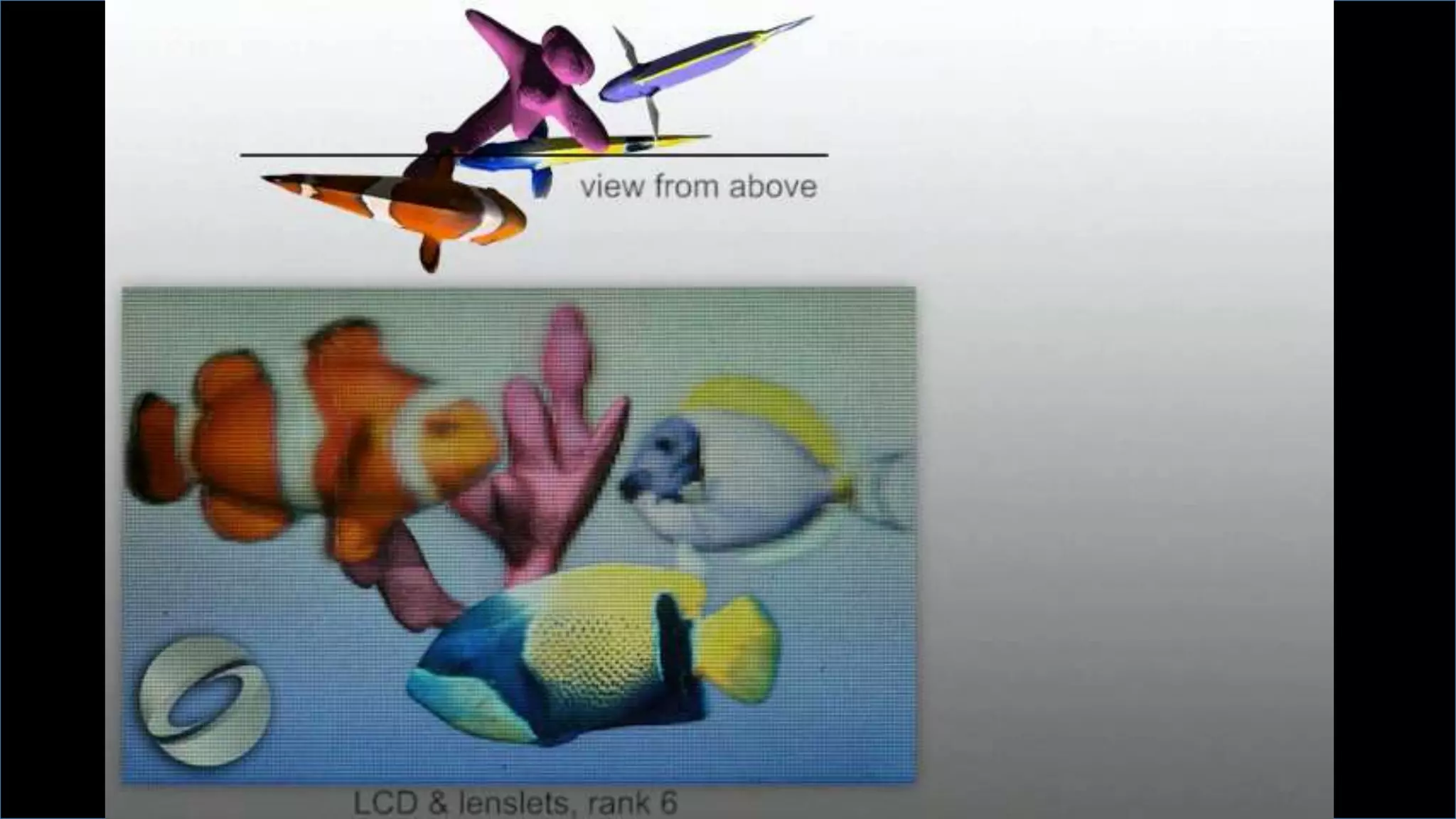
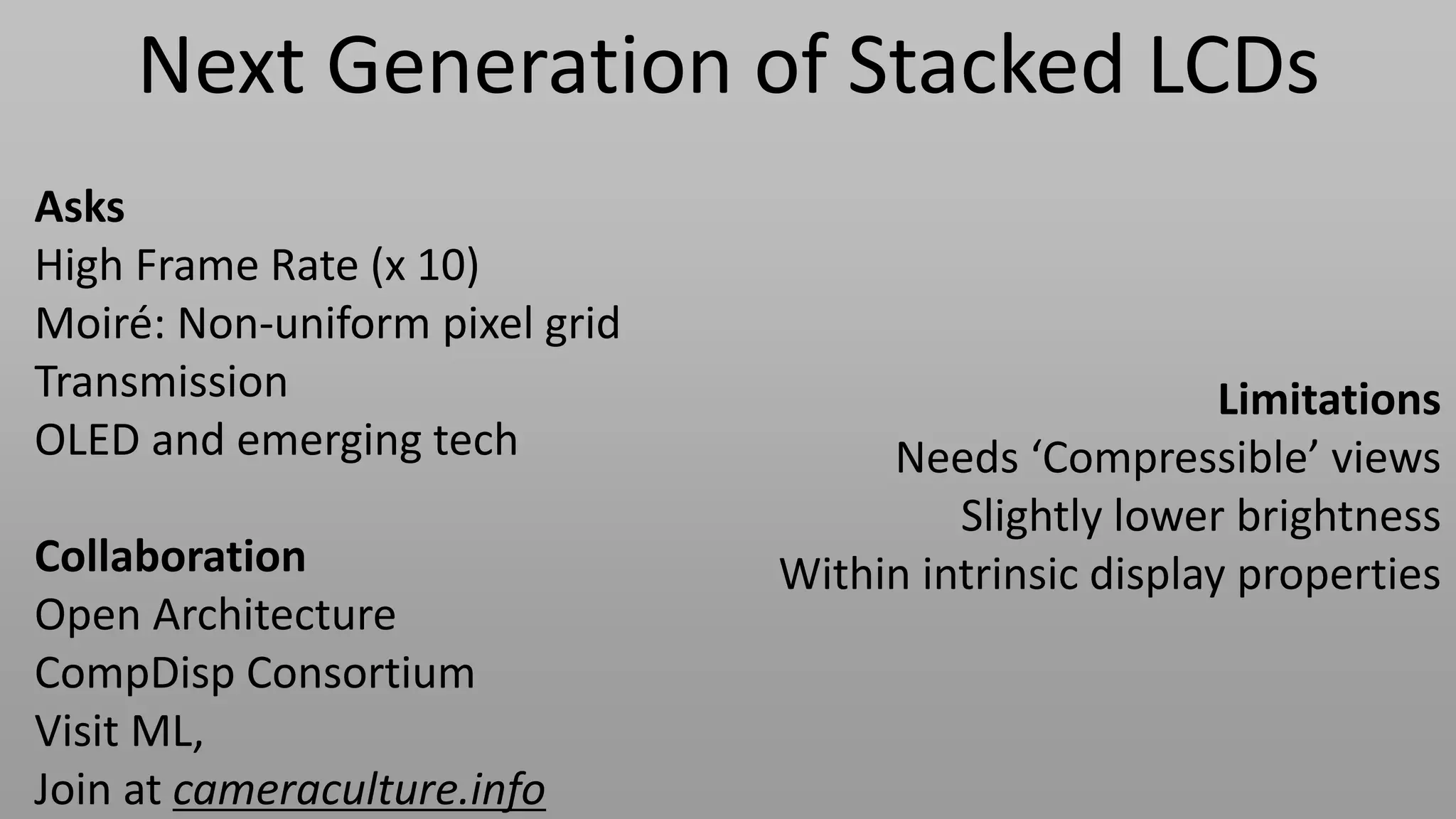
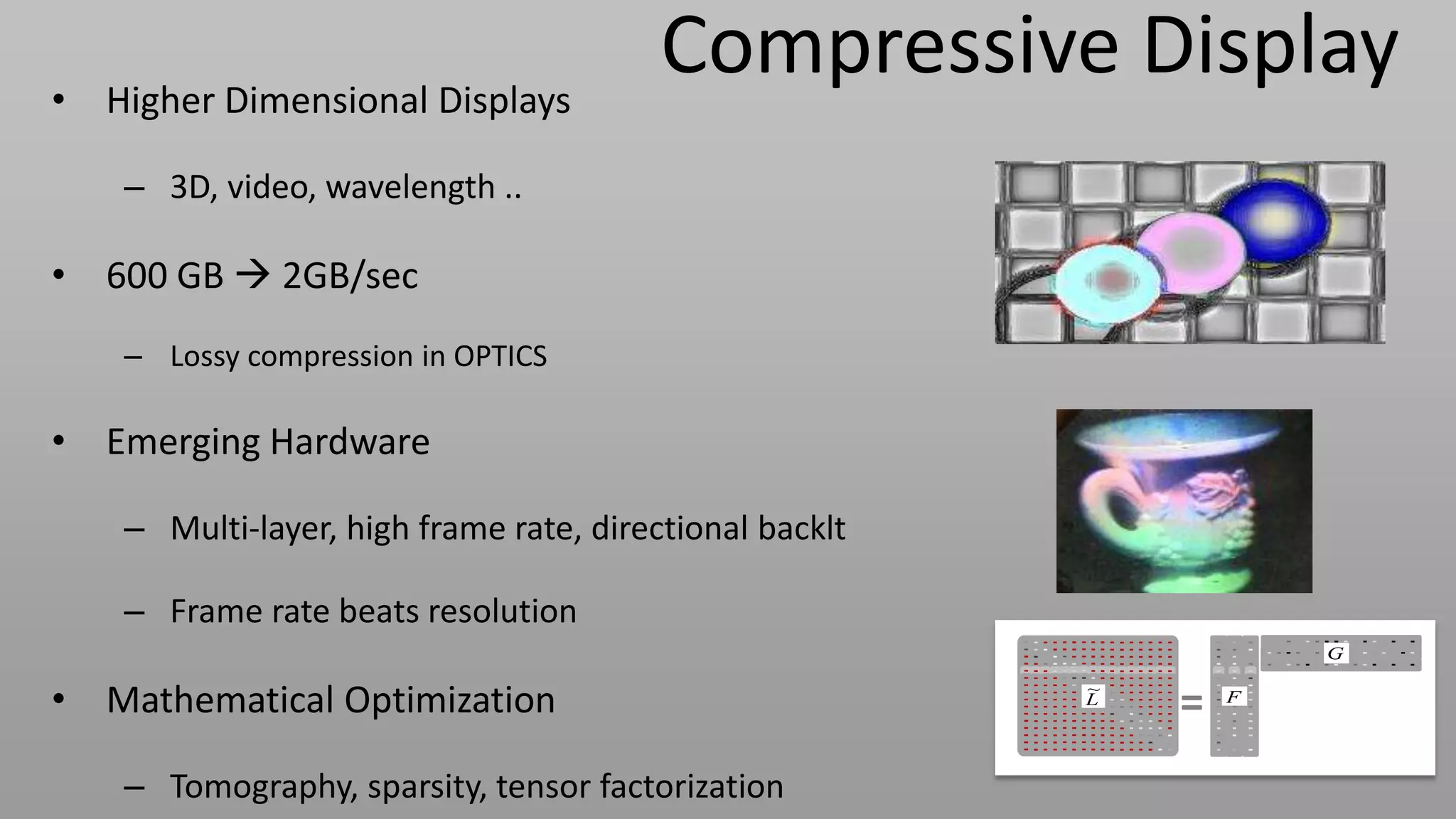
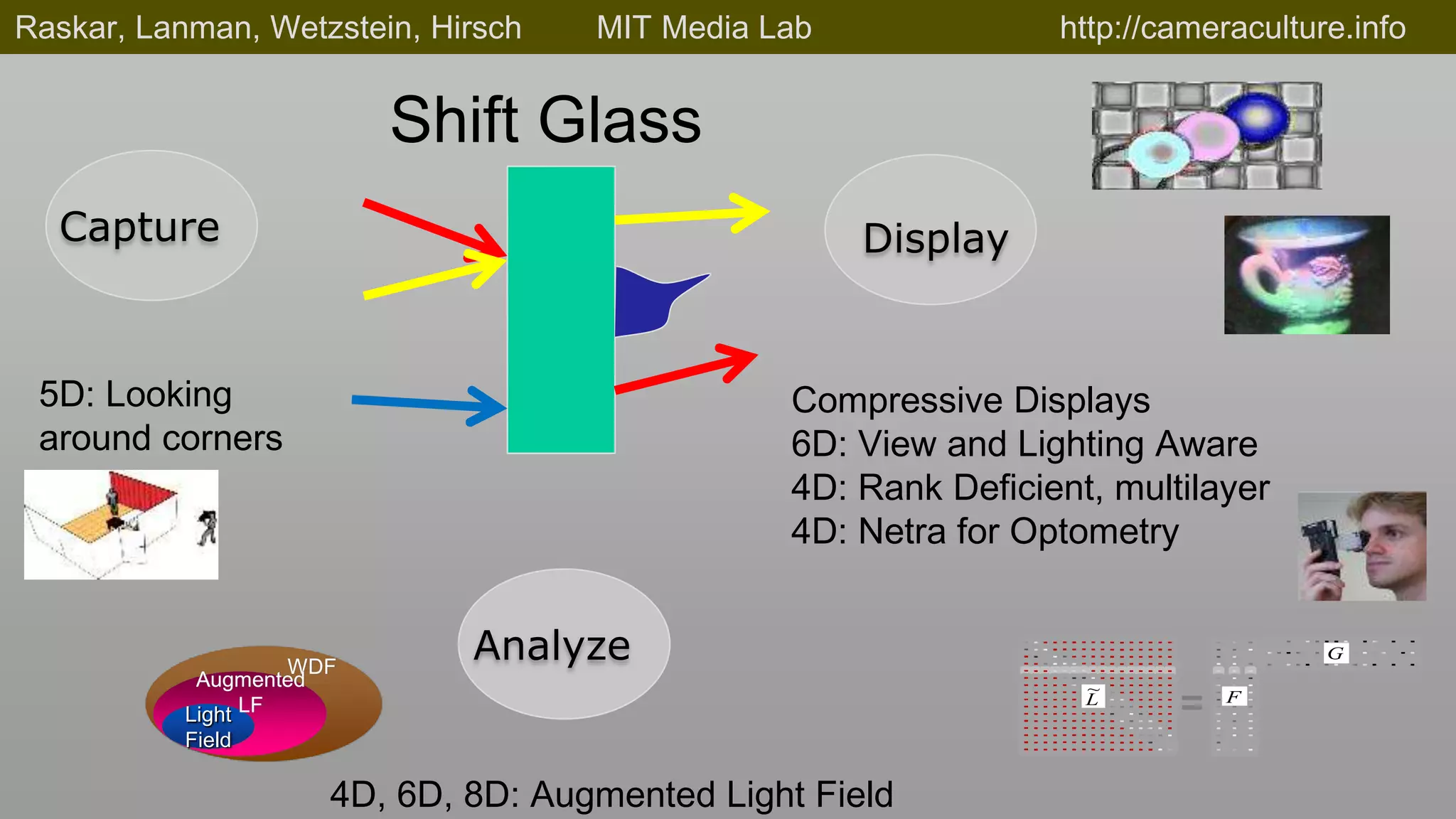
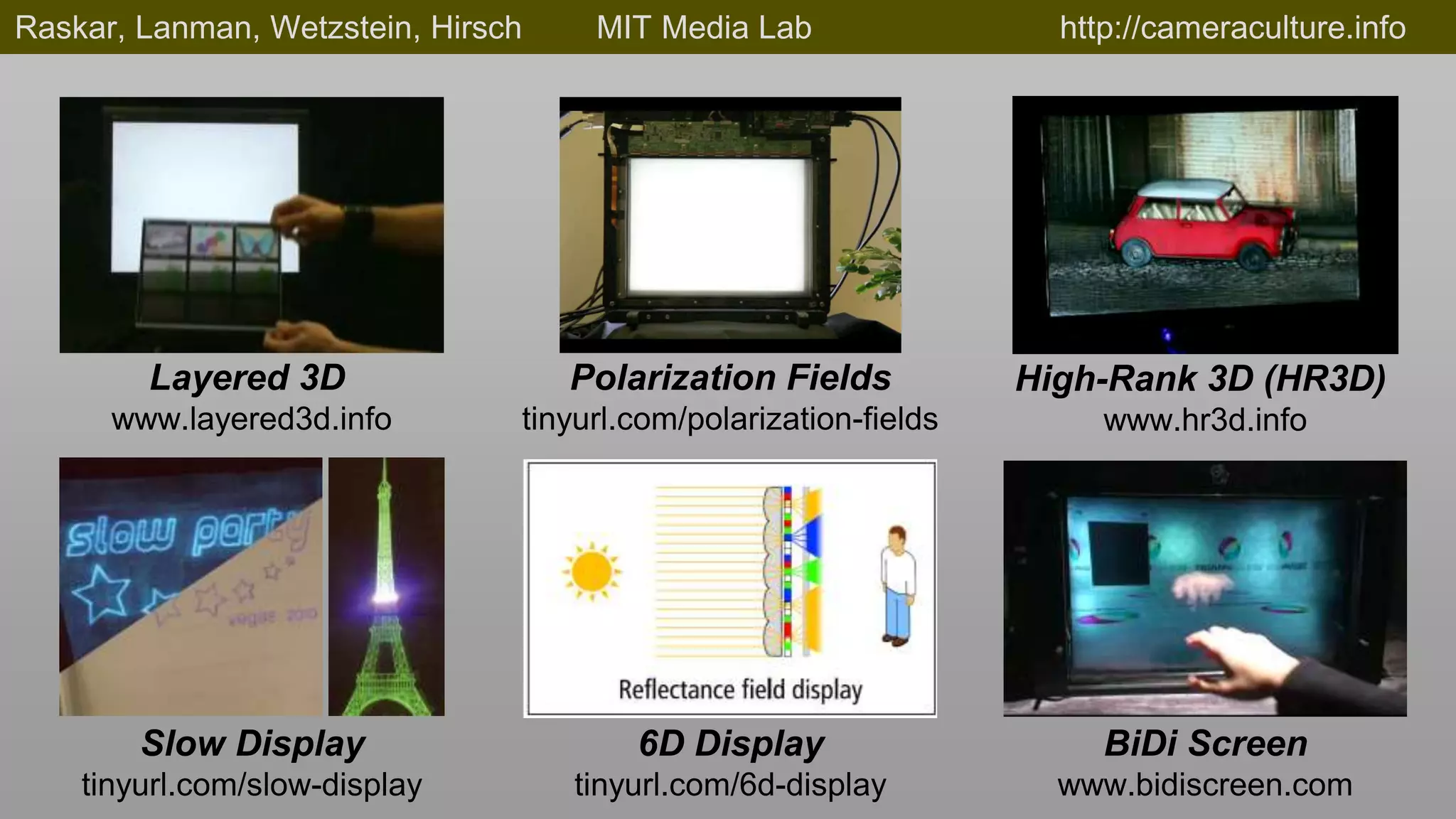
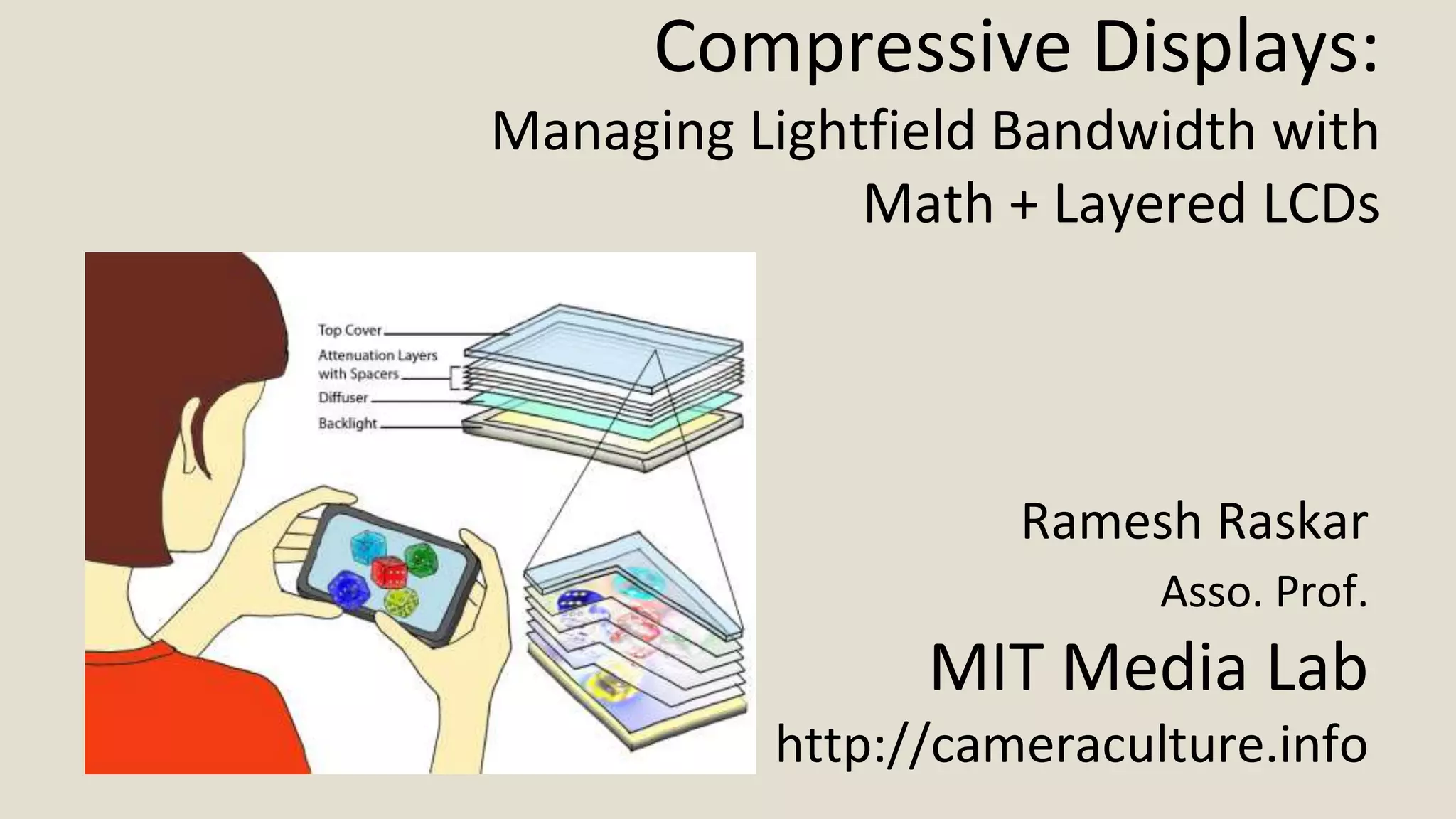
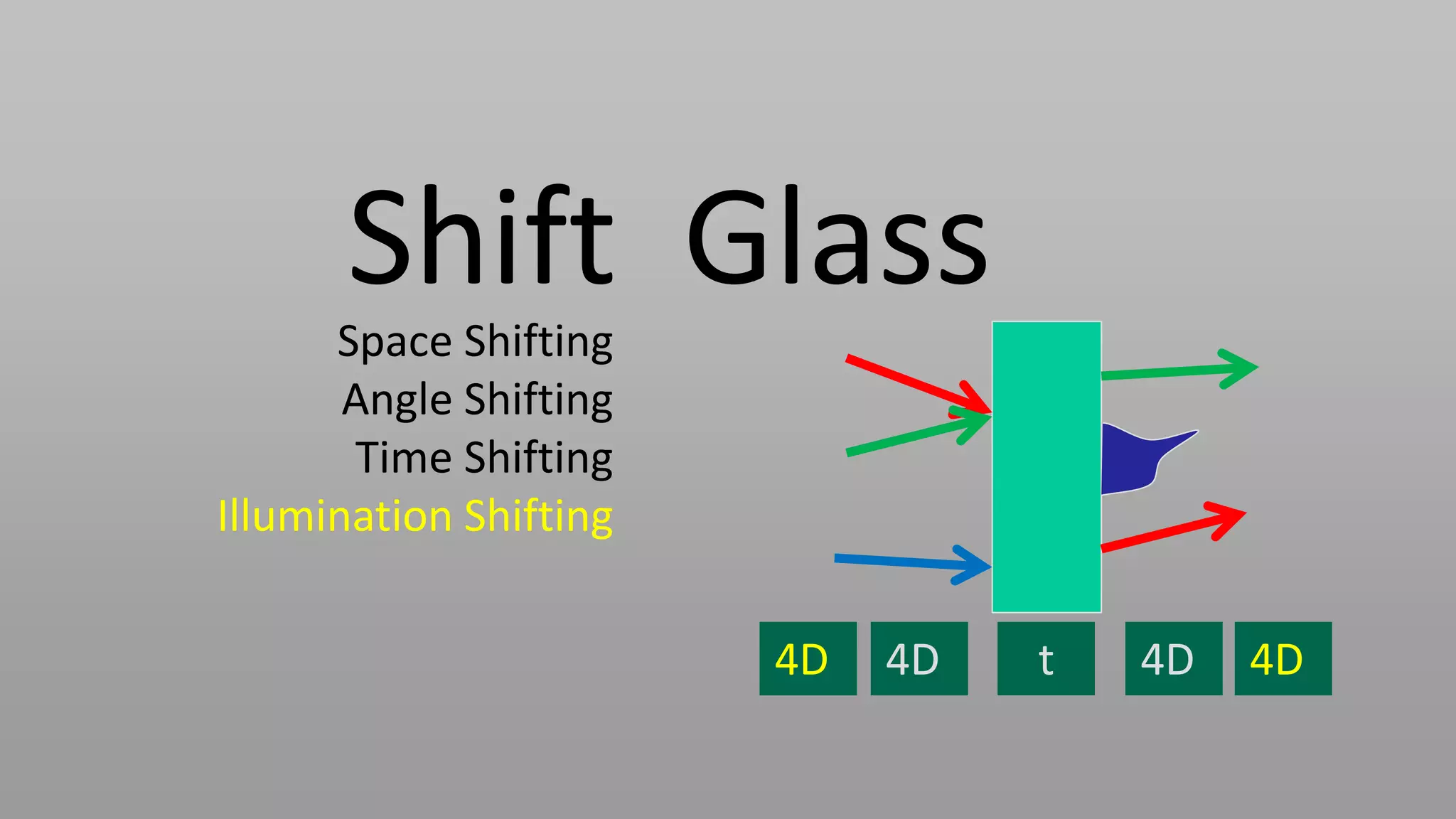
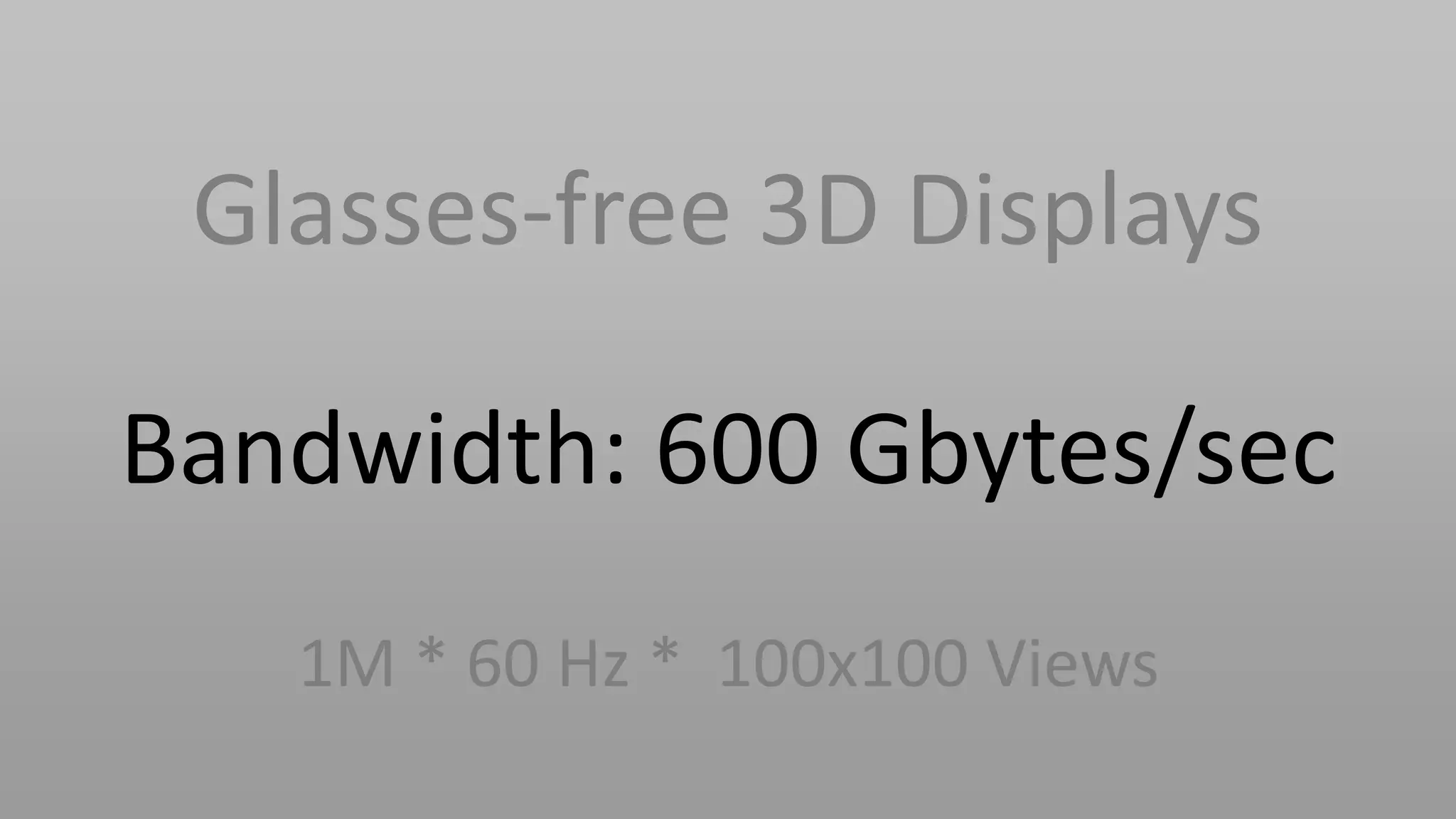
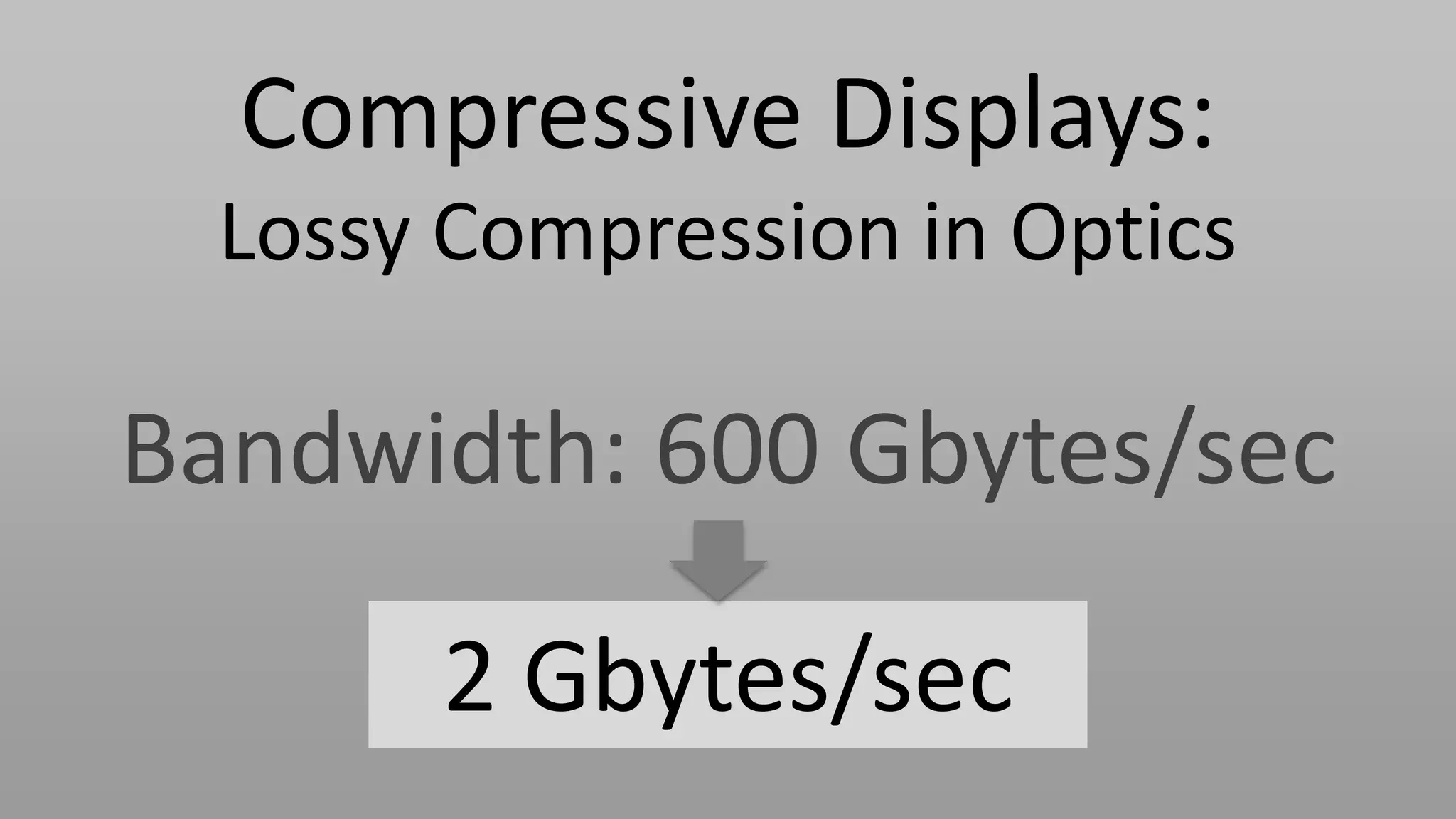
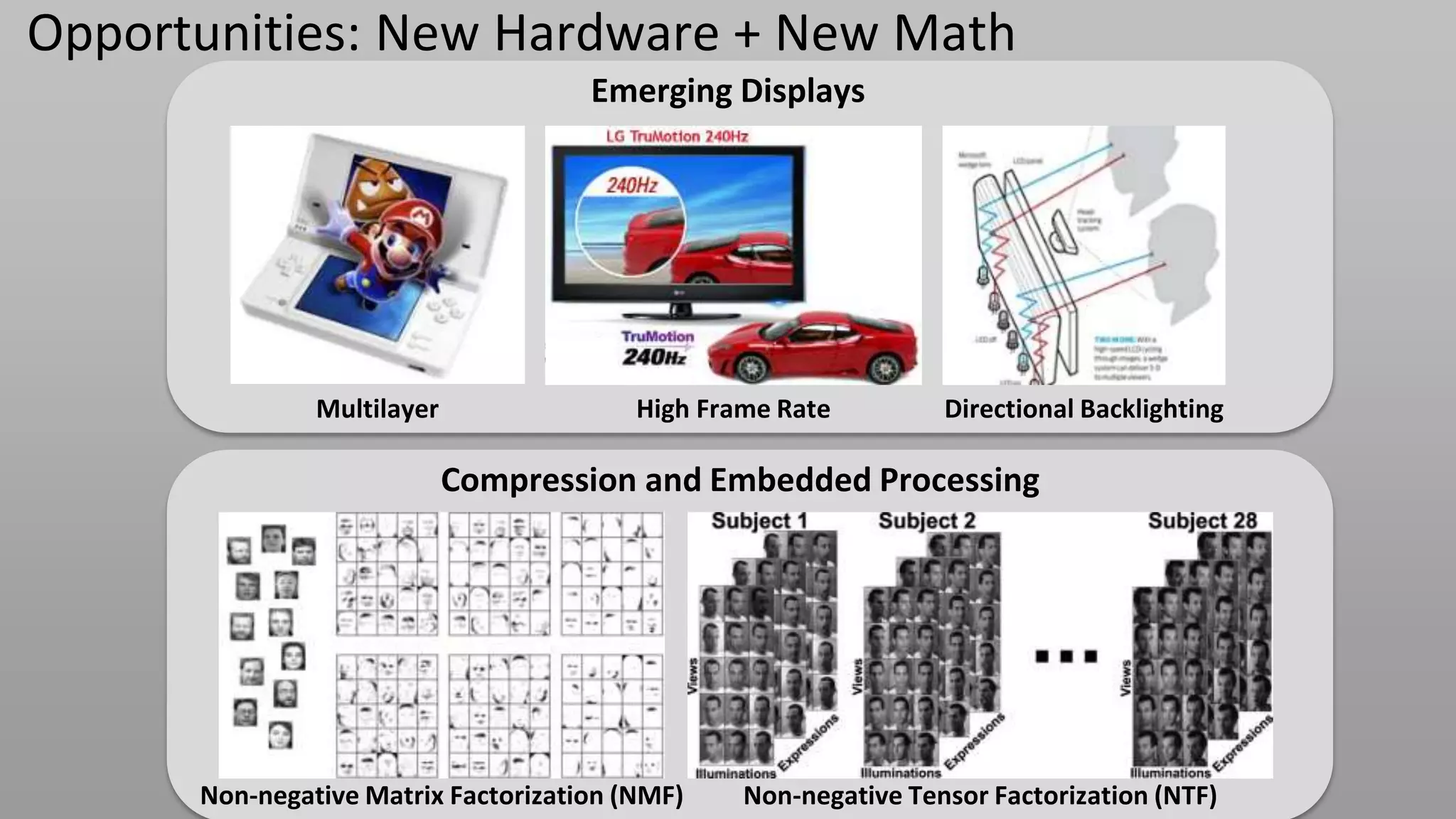
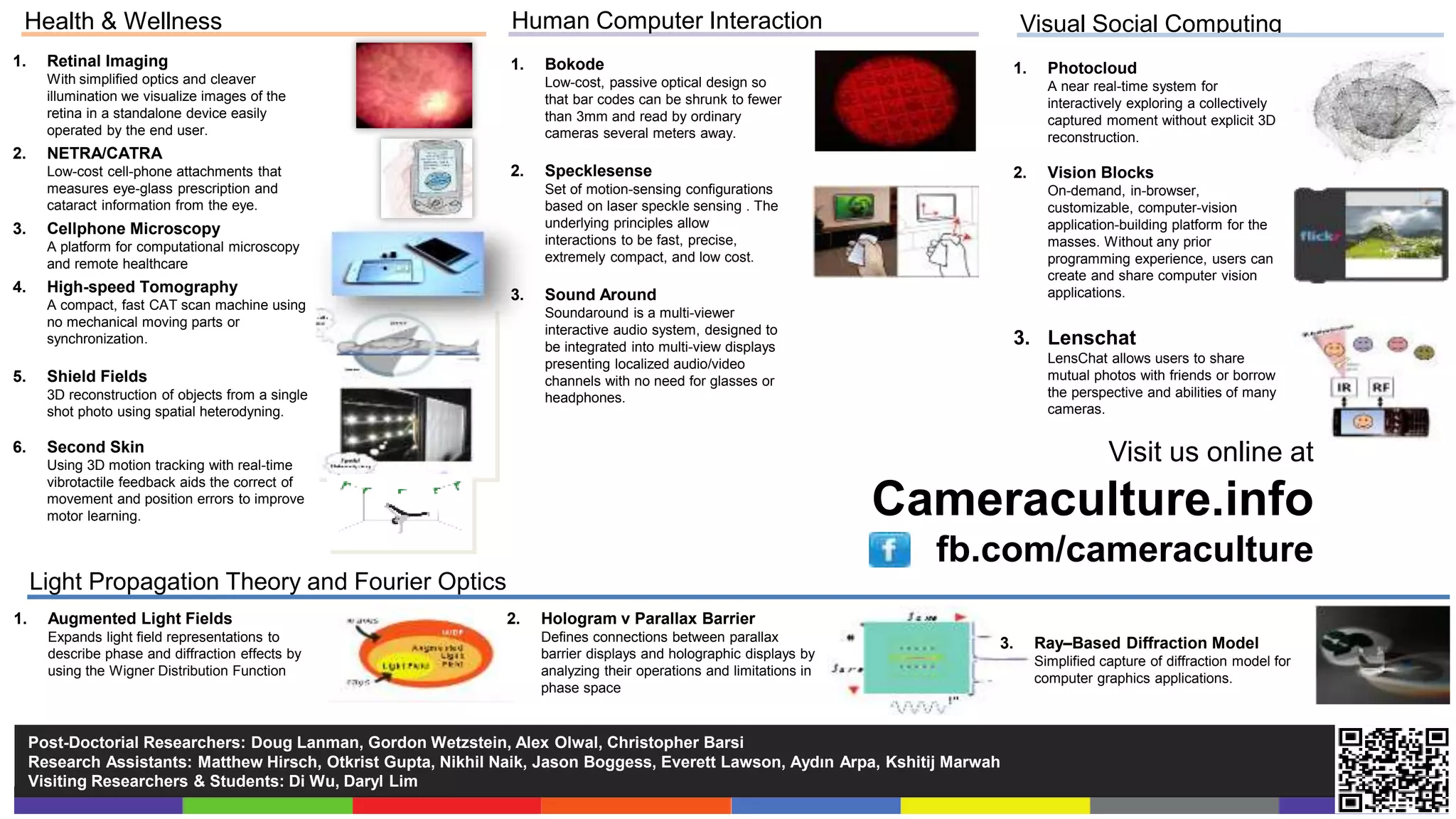
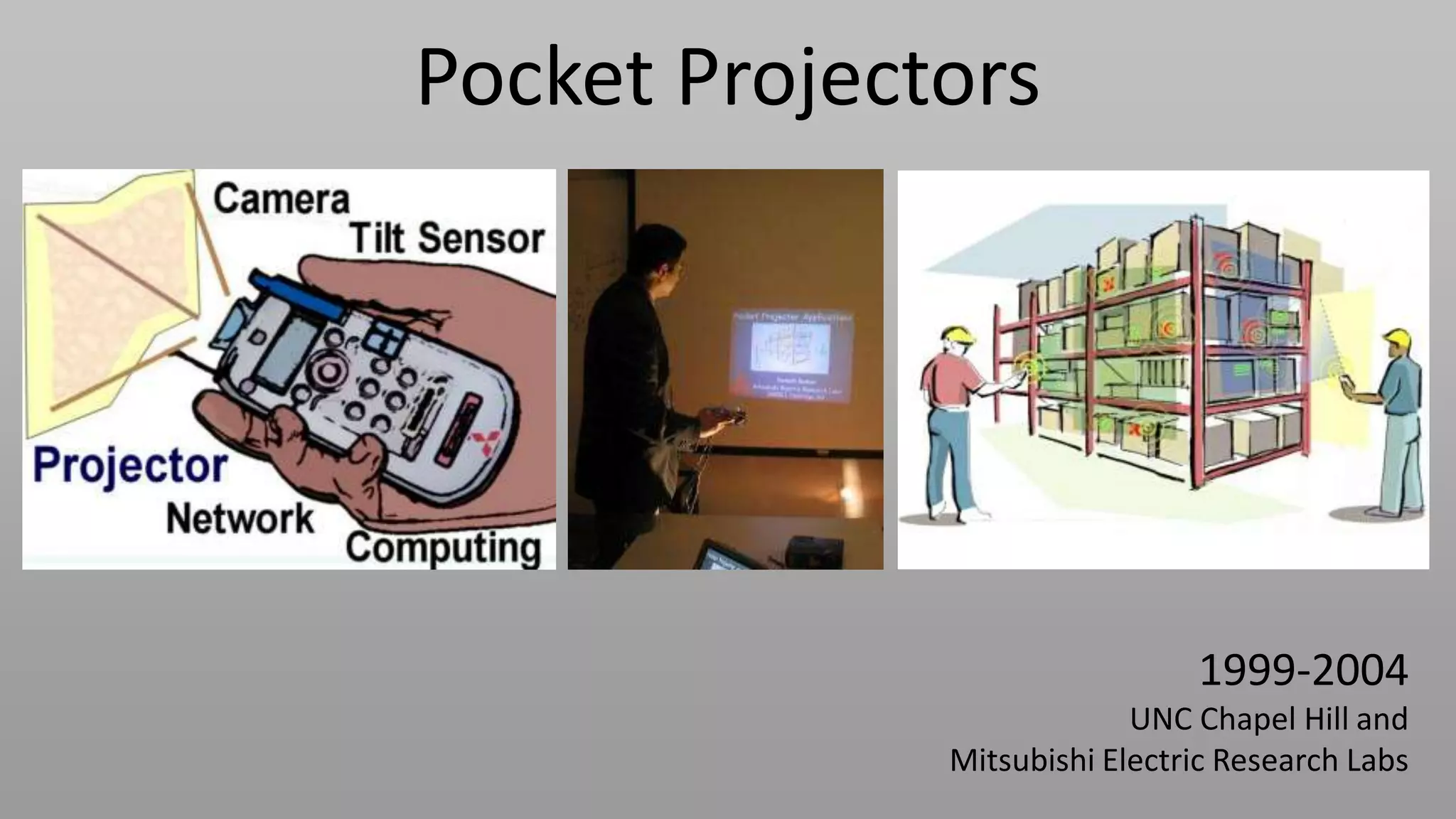
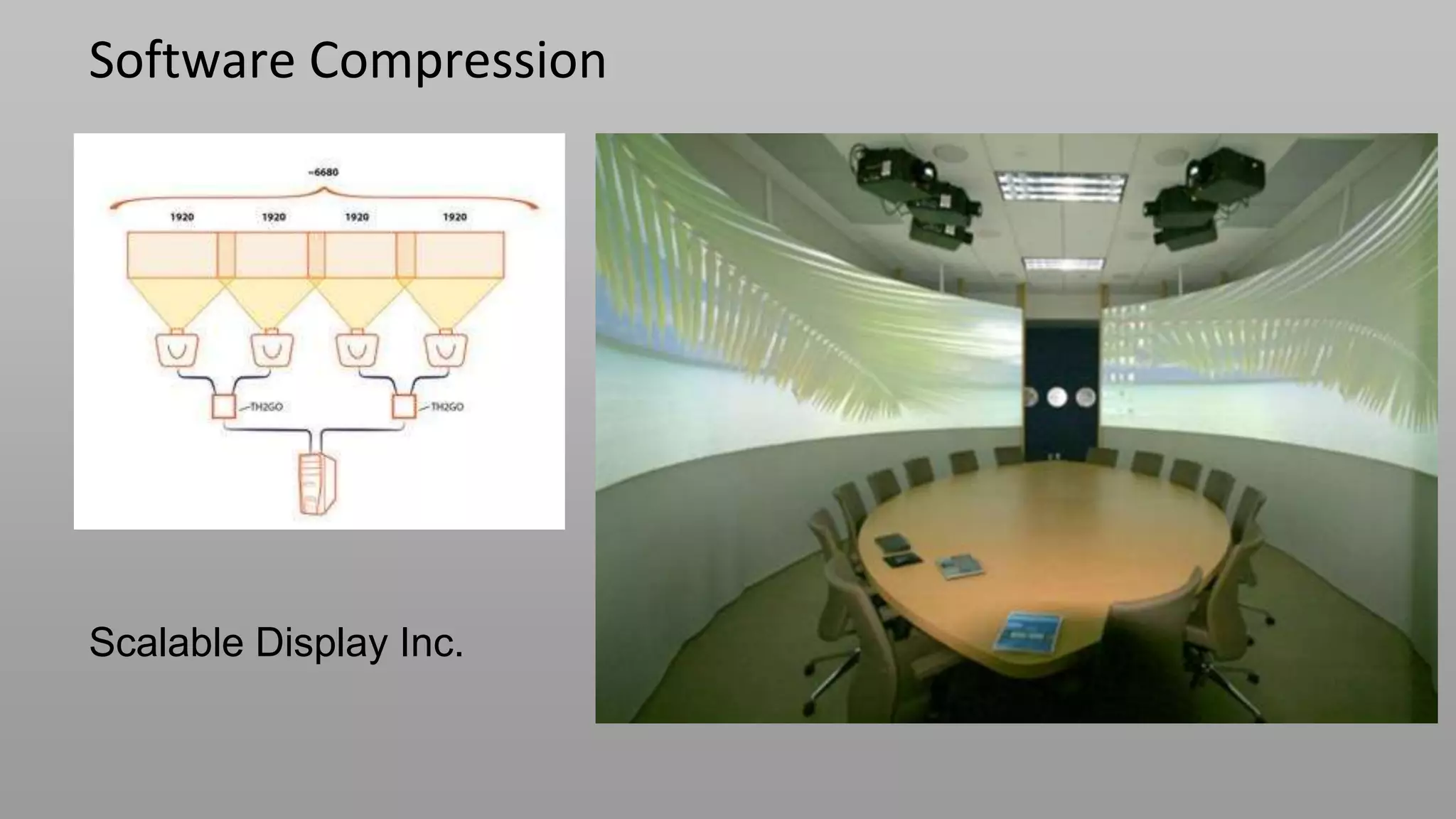
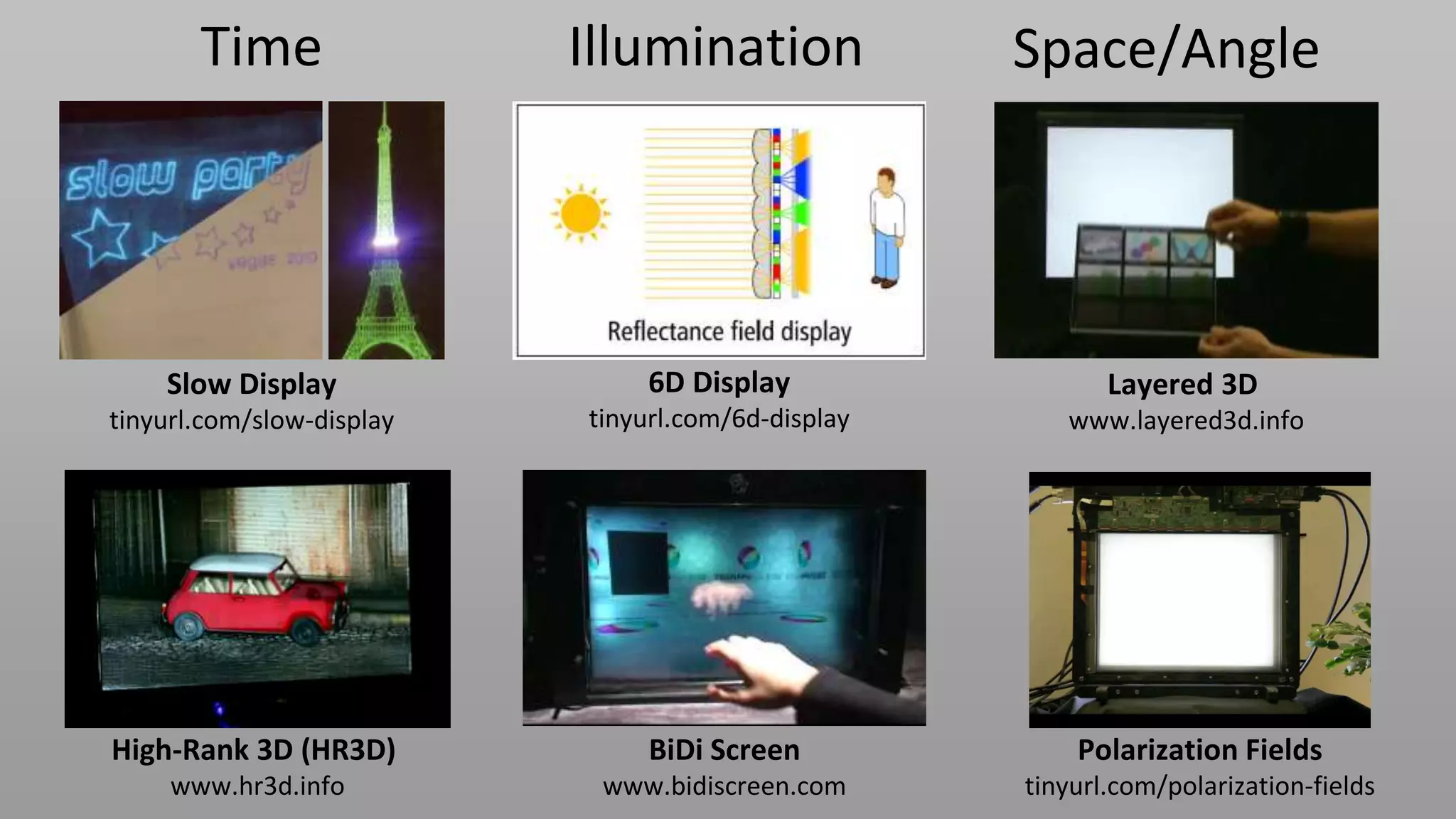
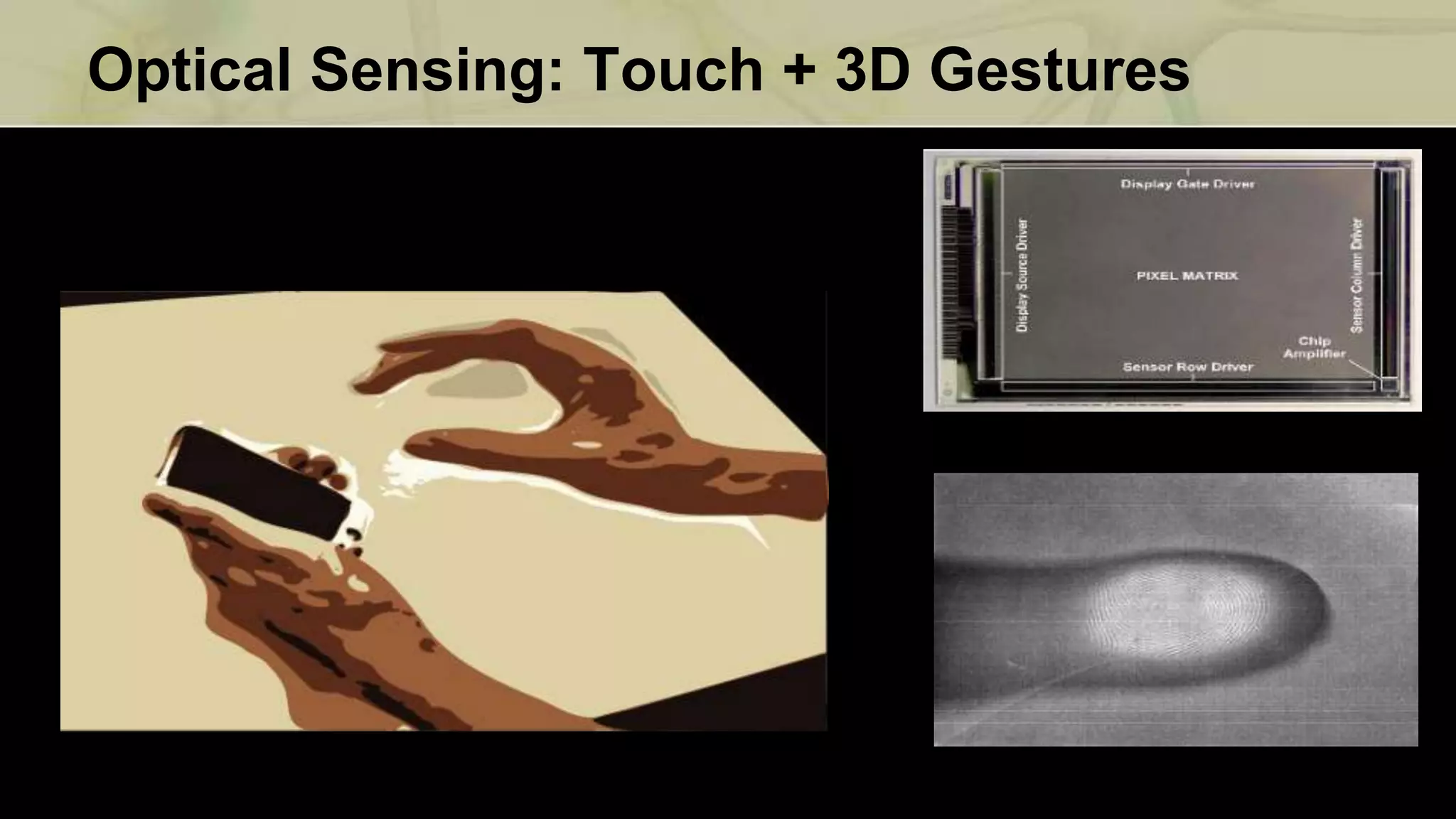
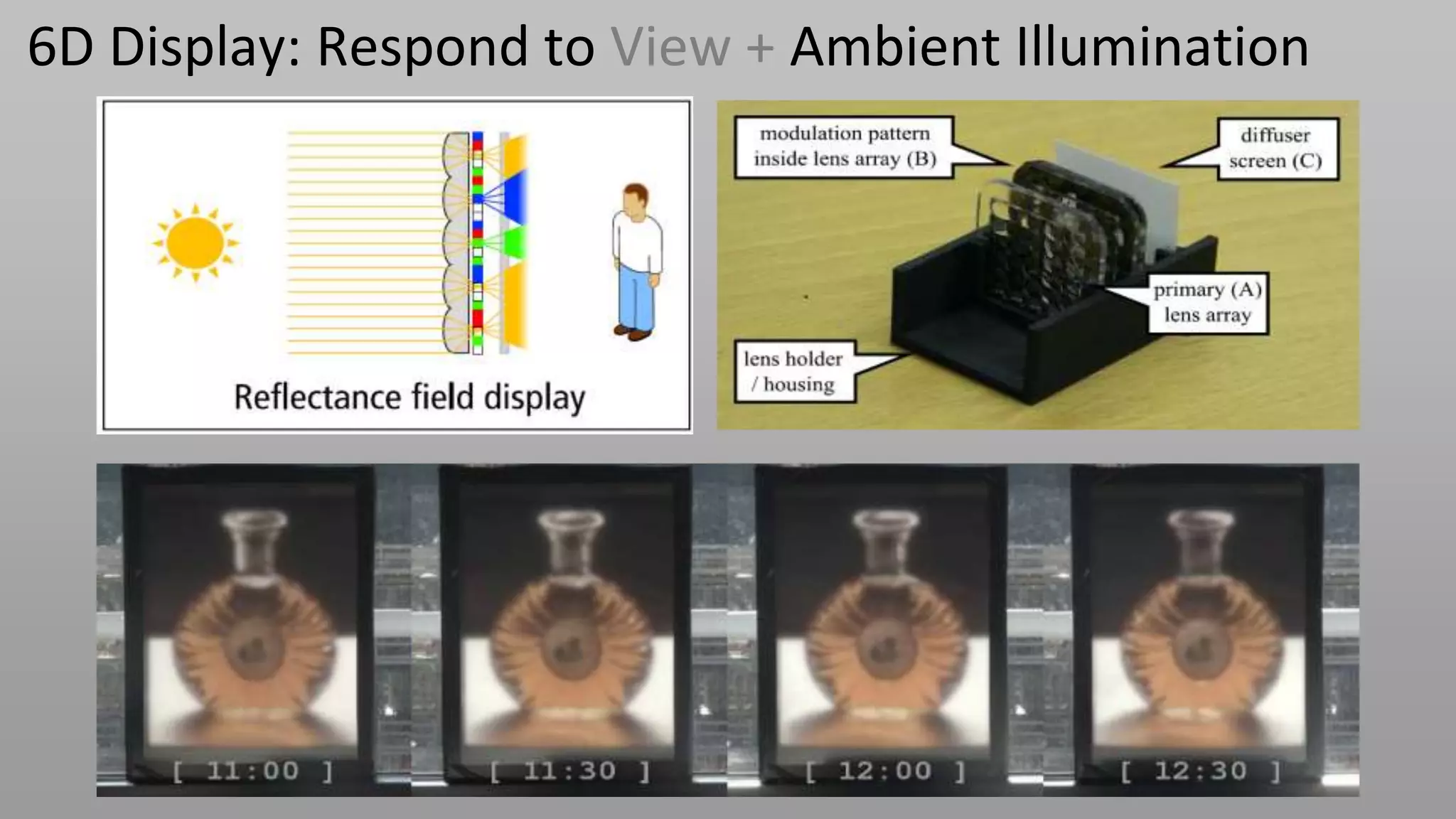
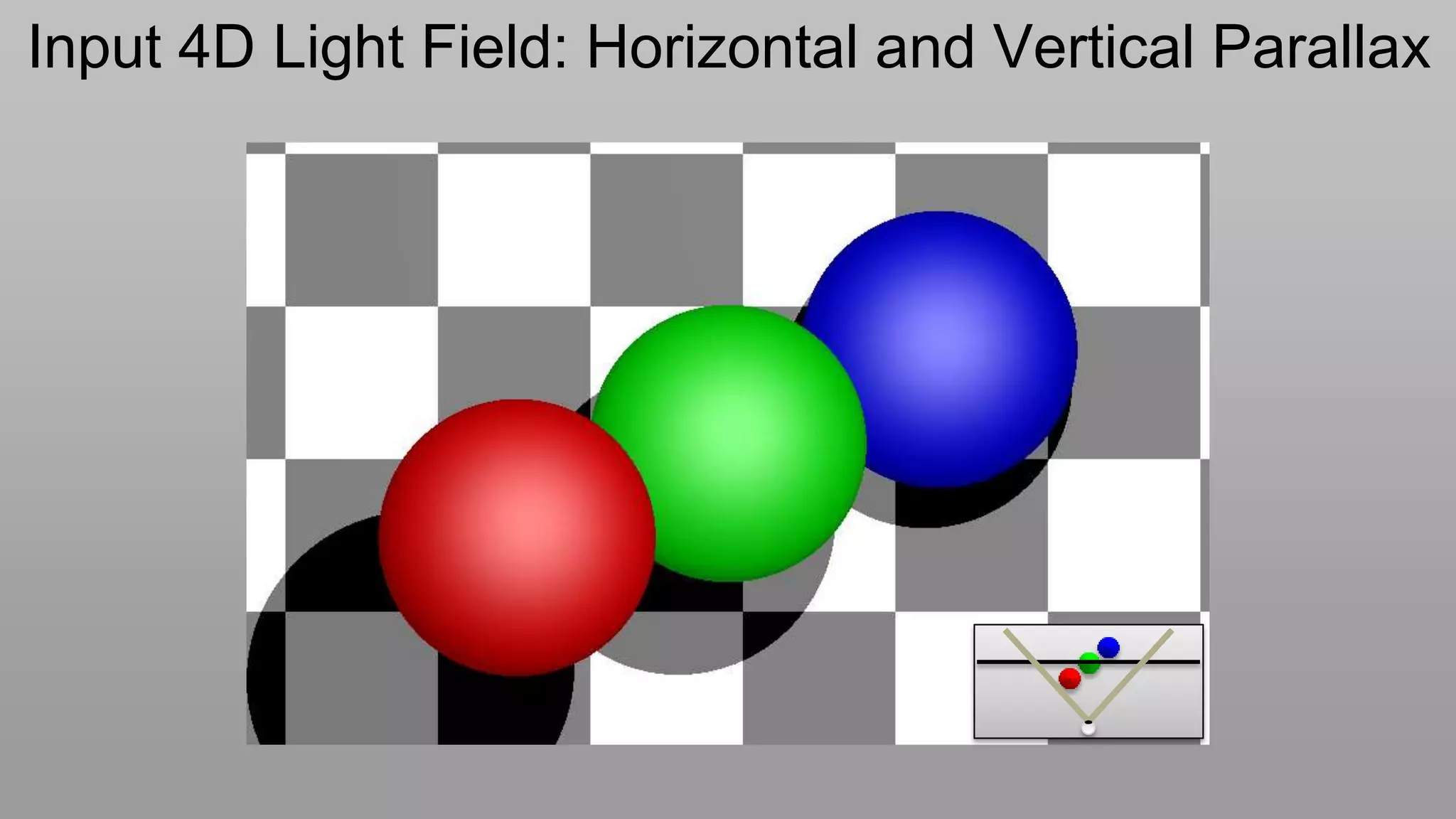
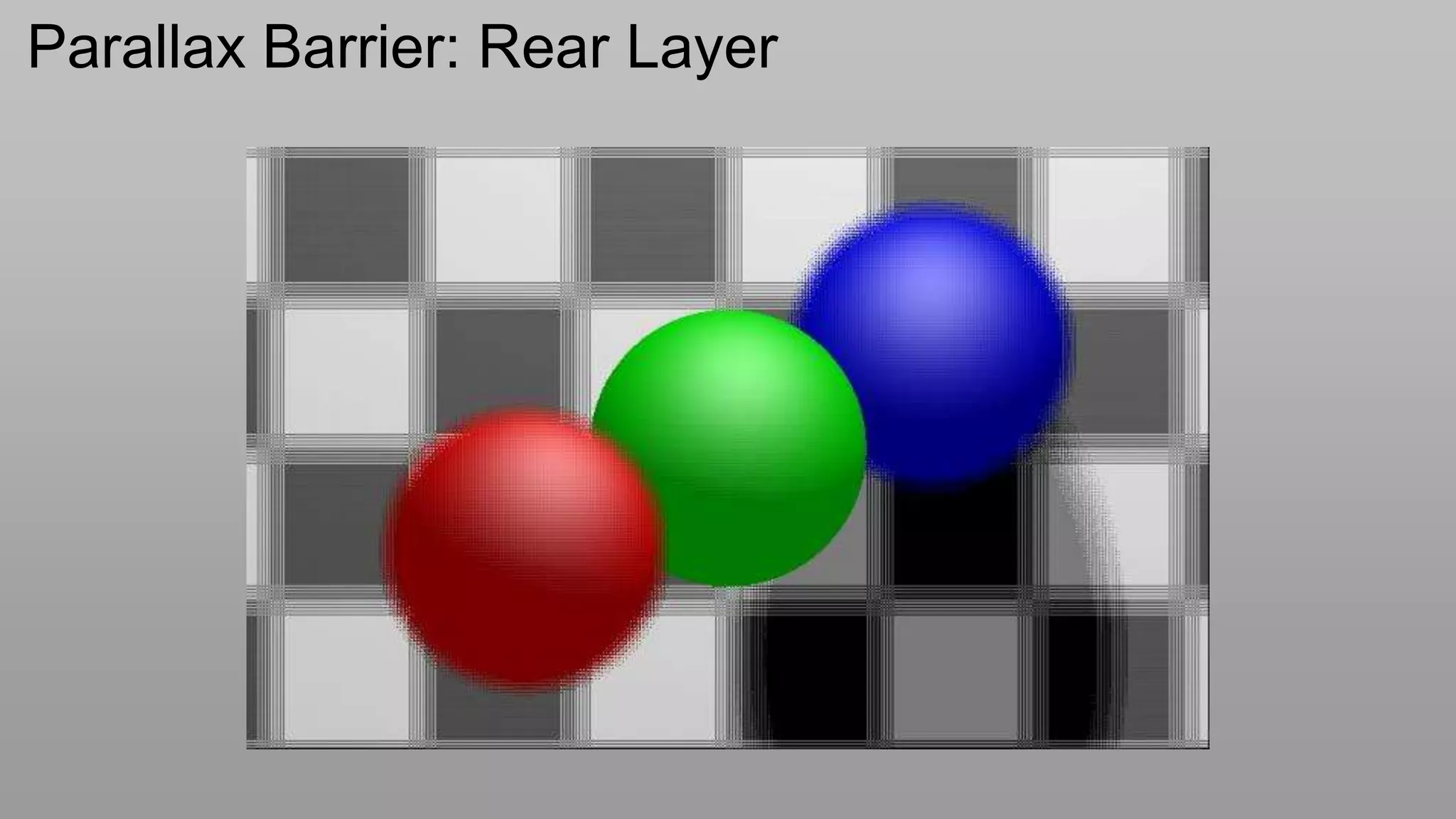
This document discusses compressive displays and related technologies for reducing the bandwidth requirements of multi-view and light field displays. It describes several technologies including layered 3D displays, polarization field displays, and high-rank 3D displays that decompose 4D light fields into lower dimensional representations. It also discusses using mathematical techniques like non-negative matrix factorization for further compressing display data. The document promotes open collaboration through the proposed Compressive Display Consortium to advance next generation displays.








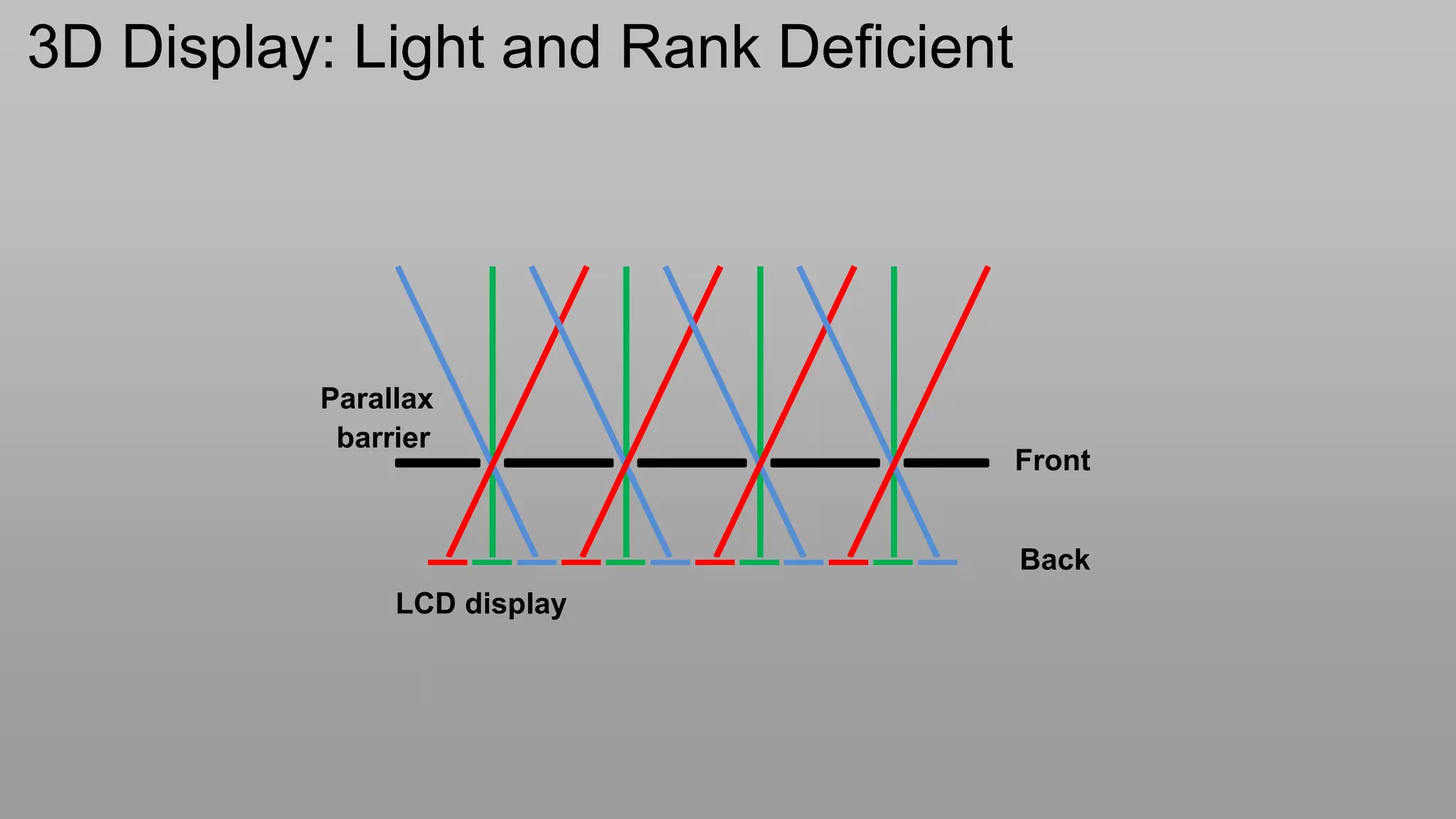

![Light Field of Parallax Barriers: Rank 1
k
L[i,k]
i
k
g[k]
i `
f[i]
light box
L[i, k ] f [i] g[k ] L f g](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ramesheditsraskarsid2012v6compressed-120605084344-phpapp02/75/Compressive-DIsplays-SID-Keynote-by-Ramesh-Raskar-24-2048.jpg)
![Dual LCD: Content-Adaptive Parallax Barriers
G
L[i,k]
k
g[k]
~
i F L`
f[i]
light box
~
L FG](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ramesheditsraskarsid2012v6compressed-120605084344-phpapp02/75/Compressive-DIsplays-SID-Keynote-by-Ramesh-Raskar-25-2048.jpg)
![Dual LCD: Content-Adaptive Parallax Barriers
G
L[i,k]
k
g[k]
i F ~
f[i] L`
light box
~
L FG
Lanman, Hirsch, Kim, Raskar Siggraph Asia 2010](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ramesheditsraskarsid2012v6compressed-120605084344-phpapp02/75/Compressive-DIsplays-SID-Keynote-by-Ramesh-Raskar-26-2048.jpg)