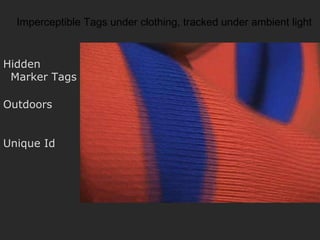
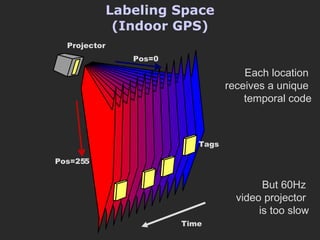
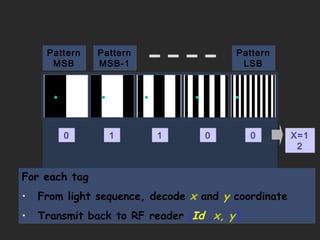
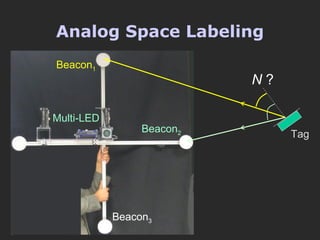
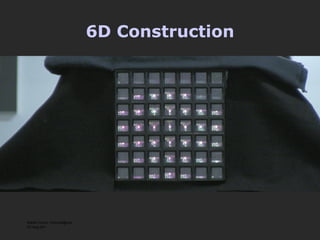
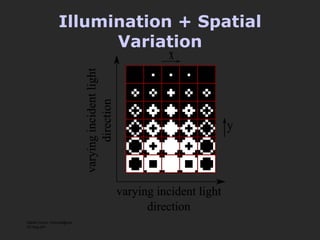
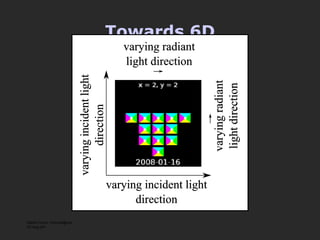
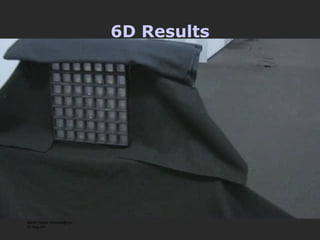
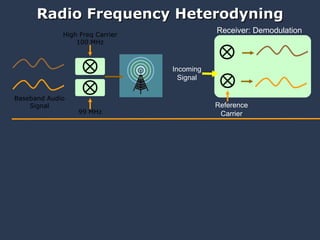
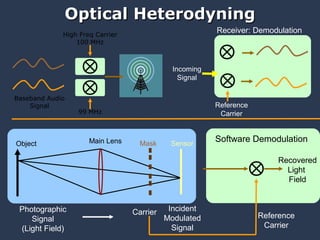
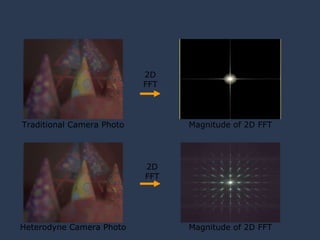
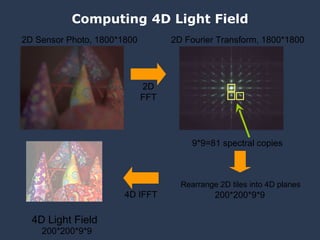
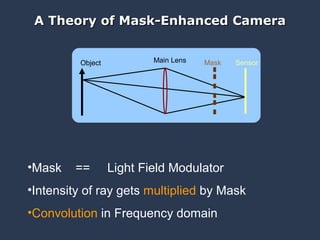
The document discusses using coded masks and modulation techniques to capture light field information and enable digital refocusing and 6D displays with a single 2D sensor. It proposes placing a coded mask in front of the sensor to heterodyne the light field and extract its 4D information. Several applications are mentioned, including coded illumination for motion capture, a 6D display using spatial and illumination variation, and a light field camera that can digitally refocus using a single photograph.














![[Lippman 1908] [Nakajima et al. 2001] ... Martin Fuchs <mfuchs@mpi-inf.mpg.de>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/raskarbanff-090428160921-phpapp02/85/Raskar-Banff-21-320.jpg)
![electronic: [Nayar et al. 2004] slit based / different patterns: [Scharstein 1996] Martin Fuchs <mfuchs@mpi-inf.mpg.de>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/raskarbanff-090428160921-phpapp02/85/Raskar-Banff-22-320.jpg)

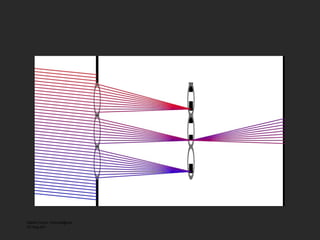

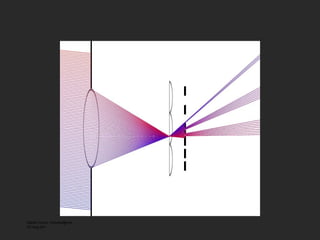
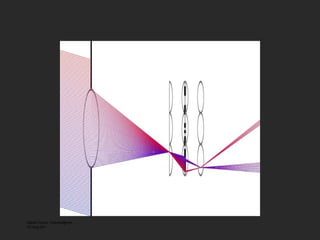









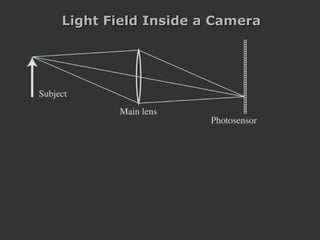
![Lenslet-based Light Field camera [Adelson and Wang, 1992, Ng et al. 2005 ] Light Field Inside a Camera](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/raskarbanff-090428160921-phpapp02/85/Raskar-Banff-47-320.jpg)
![Stanford Plenoptic Camera [Ng et al 2005] 4000 × 4000 pixels ÷ 292 × 292 lenses = 14 × 14 pixels per lens Contax medium format camera Kodak 16-megapixel sensor Adaptive Optics microlens array 125 μ square-sided microlenses](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/raskarbanff-090428160921-phpapp02/85/Raskar-Banff-48-320.jpg)
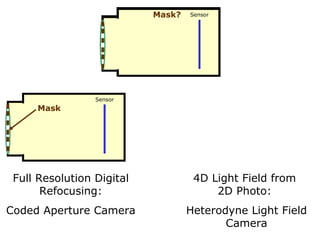
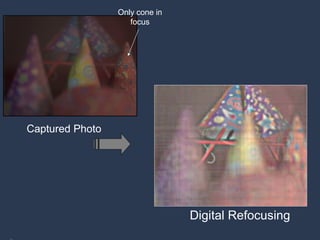
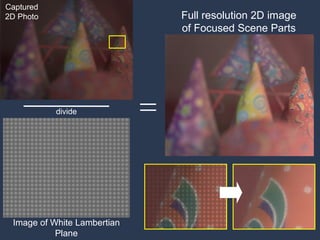
![Digital Refocusing [Ng et al 2005] Can we achieve this with a Mask alone?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/raskarbanff-090428160921-phpapp02/85/Raskar-Banff-49-320.jpg)
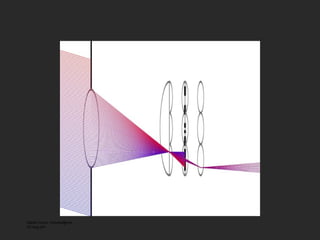
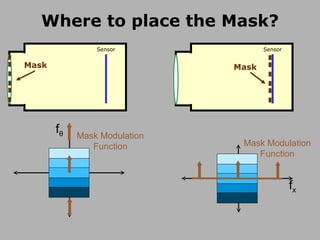
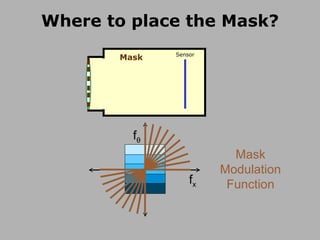
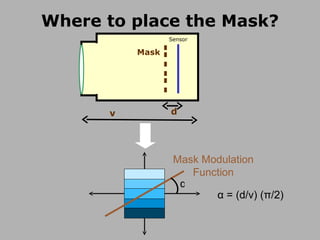
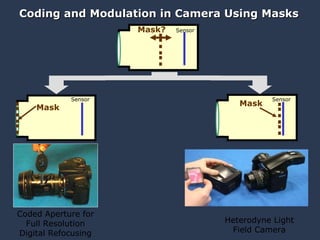
![Mask based Light Field Camera [Veeraraghavan, Raskar, Agrawal, Tumblin, Mohan, Siggraph 2007 ] Mask Sensor](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/raskarbanff-090428160921-phpapp02/85/Raskar-Banff-50-320.jpg)
![Heterodyne Light Field Camera Scanner sensor Mask [Veeraraghavan, Raskar, Agrawal, Tumblin, Mohan, Siggraph 2007 ] Mask Sensor](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/raskarbanff-090428160921-phpapp02/85/Raskar-Banff-51-320.jpg)



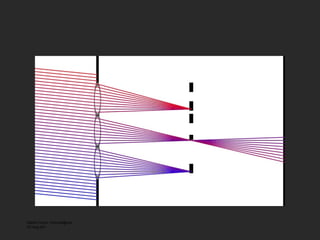
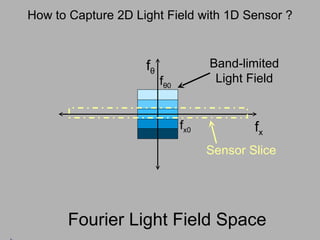
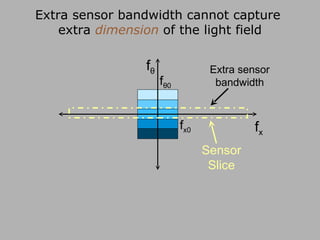
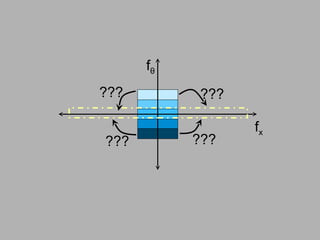
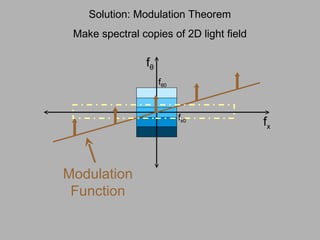
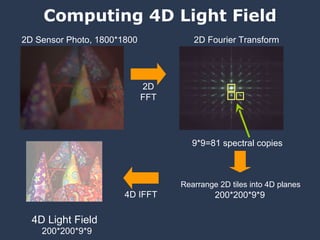
![f θ f x f θ 0 f x0 Band-limited Light Field Sensor Slice – Fourier Slice Theorem Photo = Slice of Light Field in Fourier Domain [Ren Ng, SIGGRAPH 2005]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/raskarbanff-090428160921-phpapp02/85/Raskar-Banff-60-320.jpg)
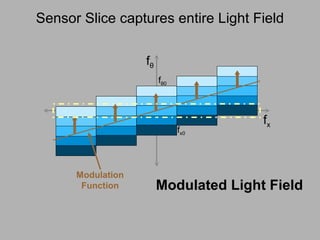
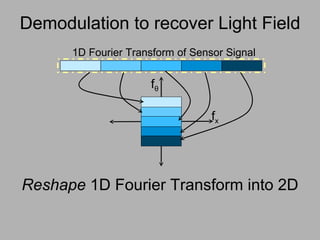
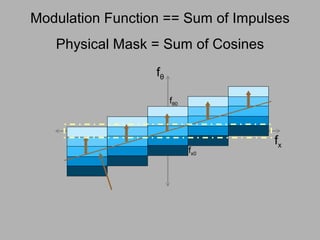
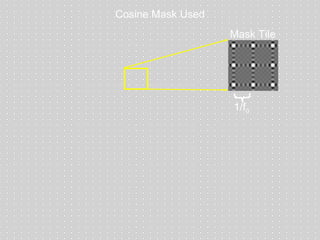


![Mask-based Approaches Coded Illumination Motion Capture [2007] 6D Display Lighting aware [2008] Optical Heterodyning Light Field Capture [2007] http://raskar.info](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/raskarbanff-090428160921-phpapp02/85/Raskar-Banff-78-320.jpg)
