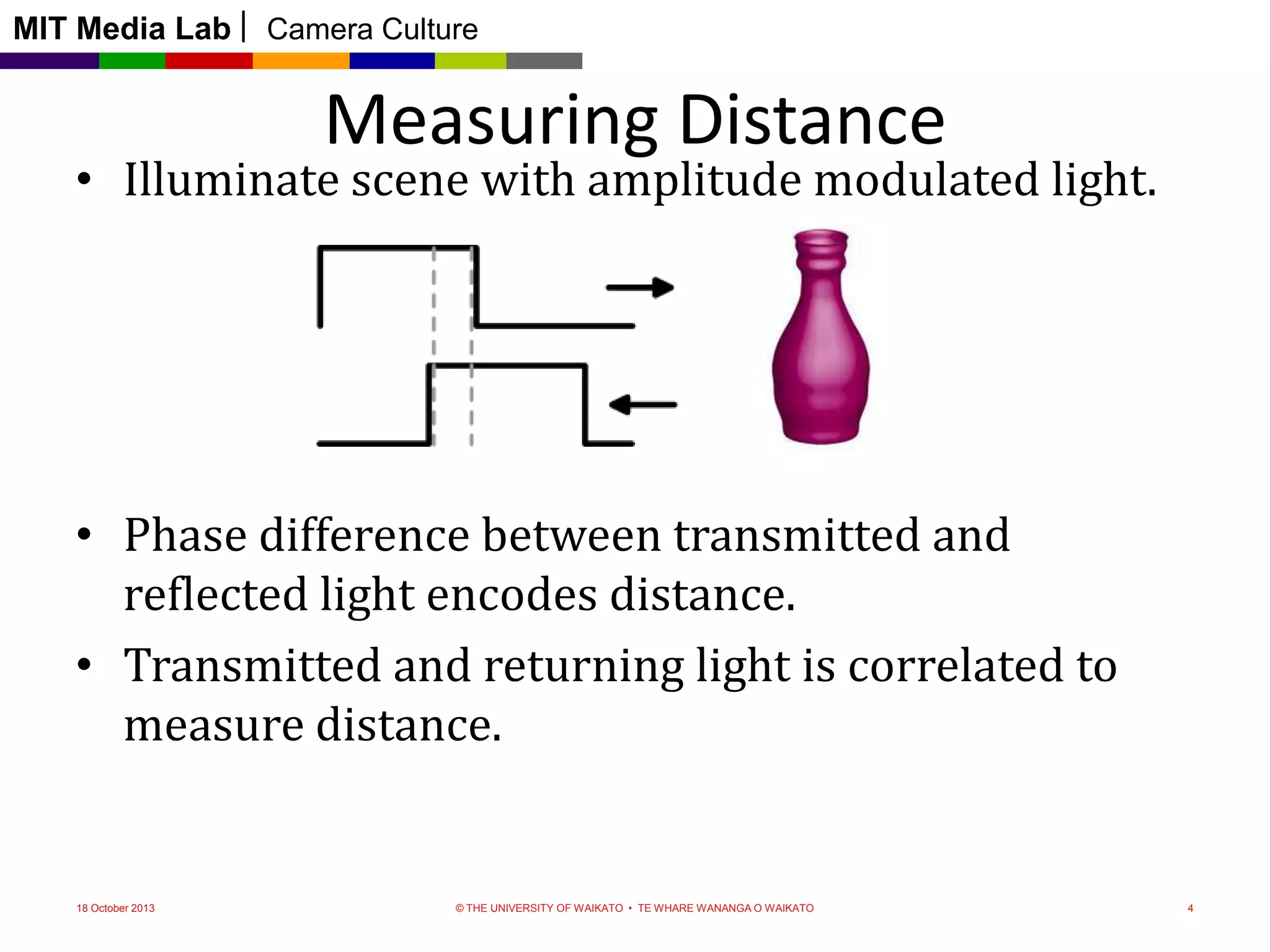
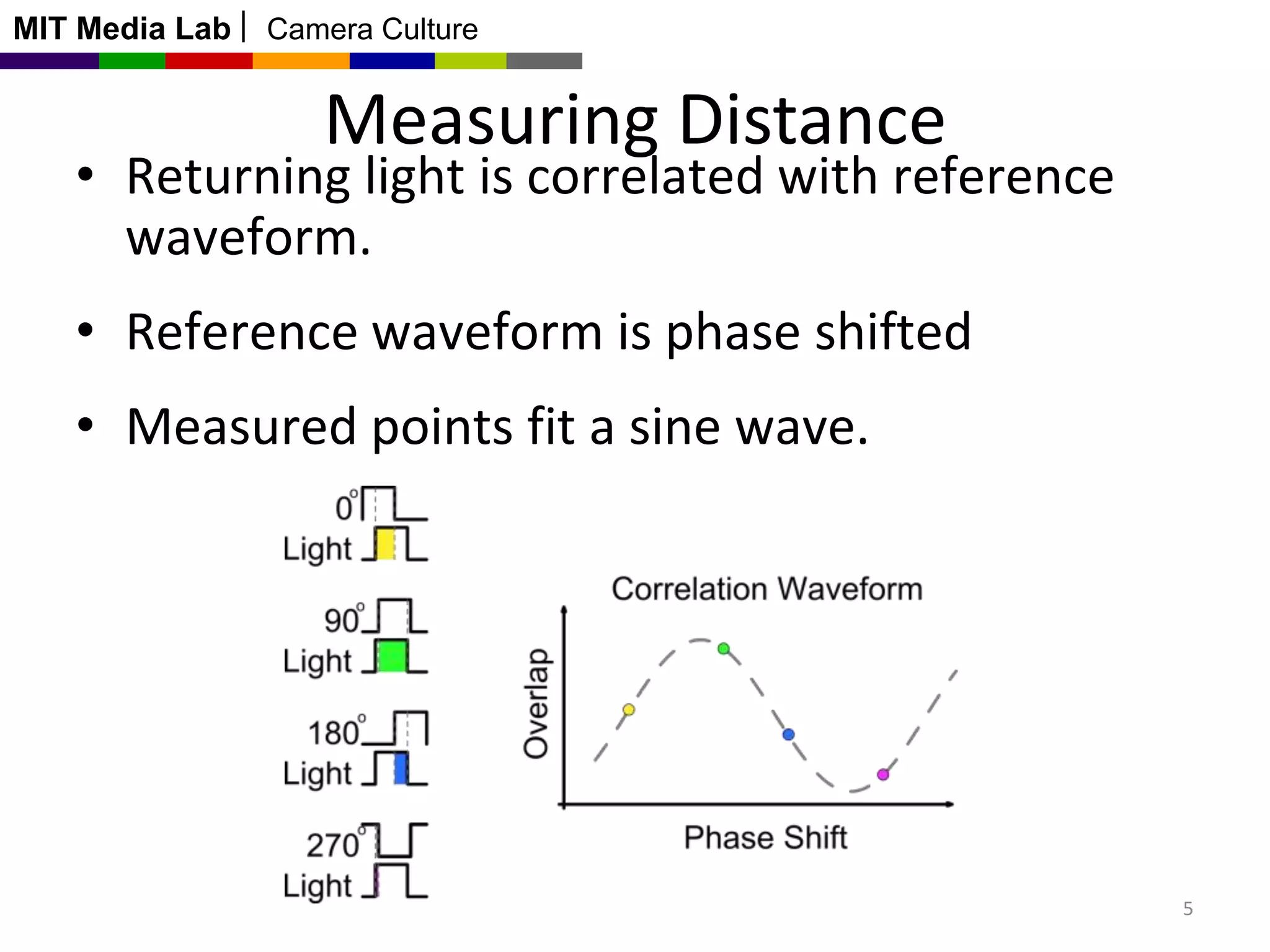
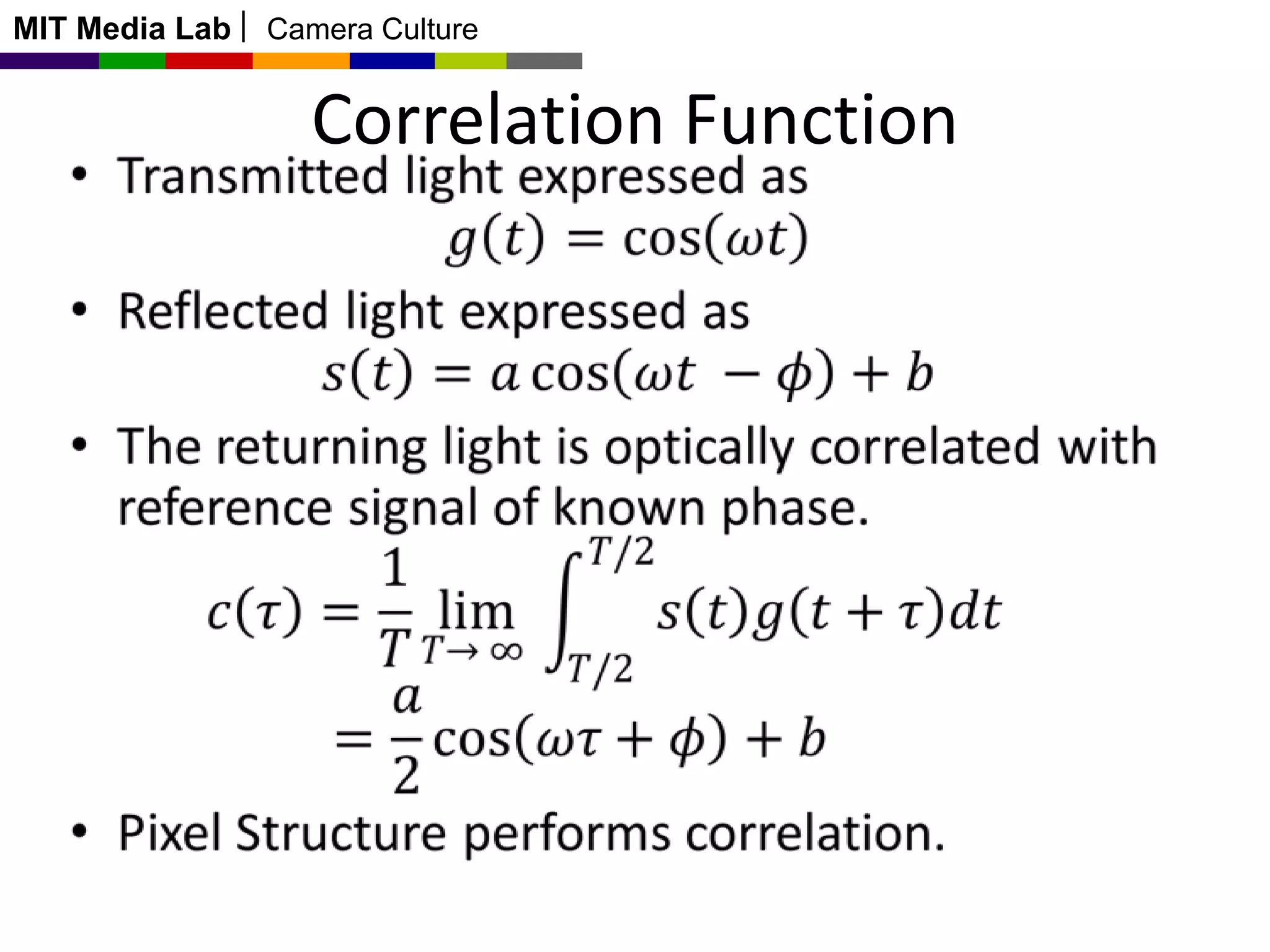
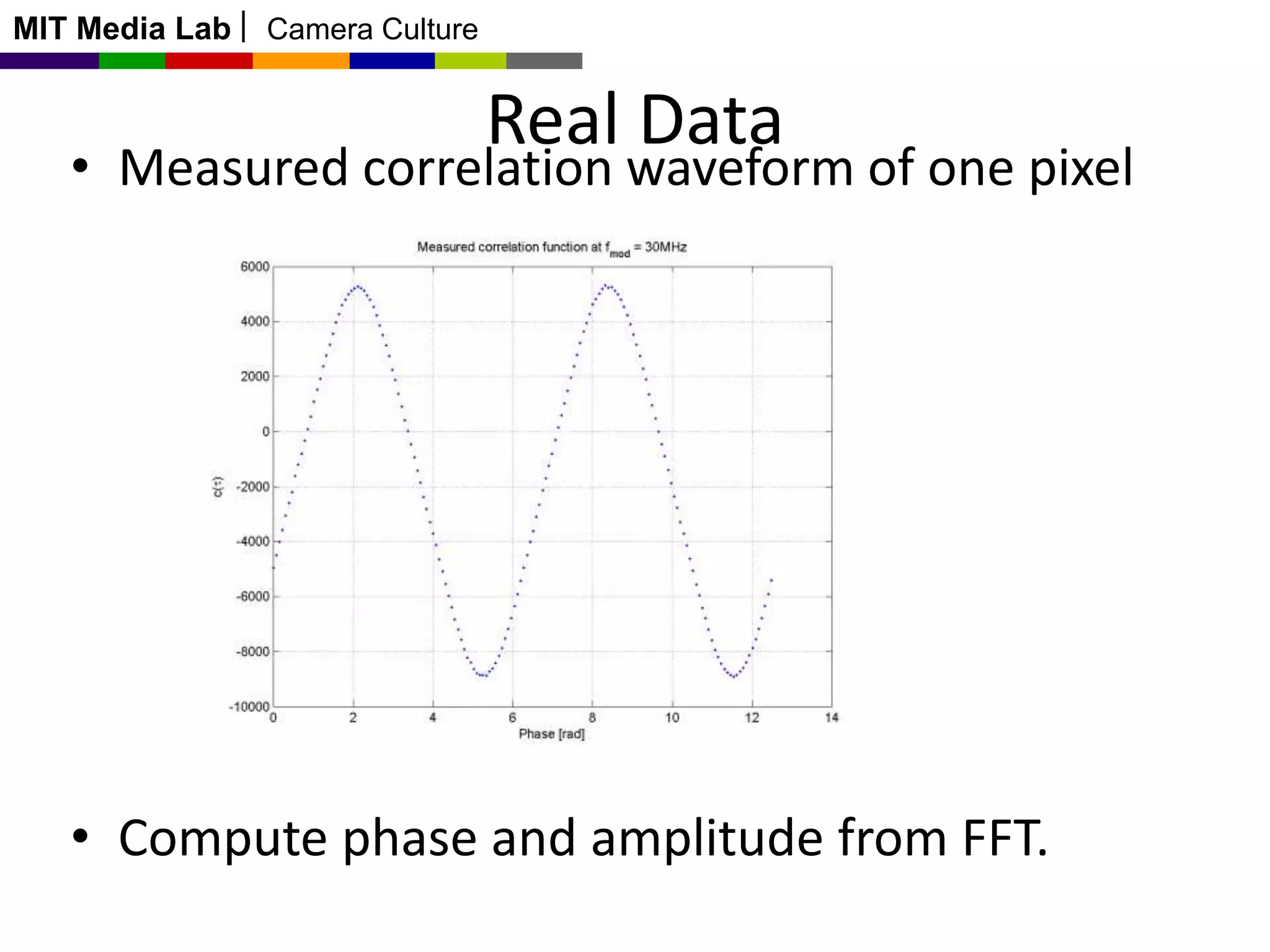
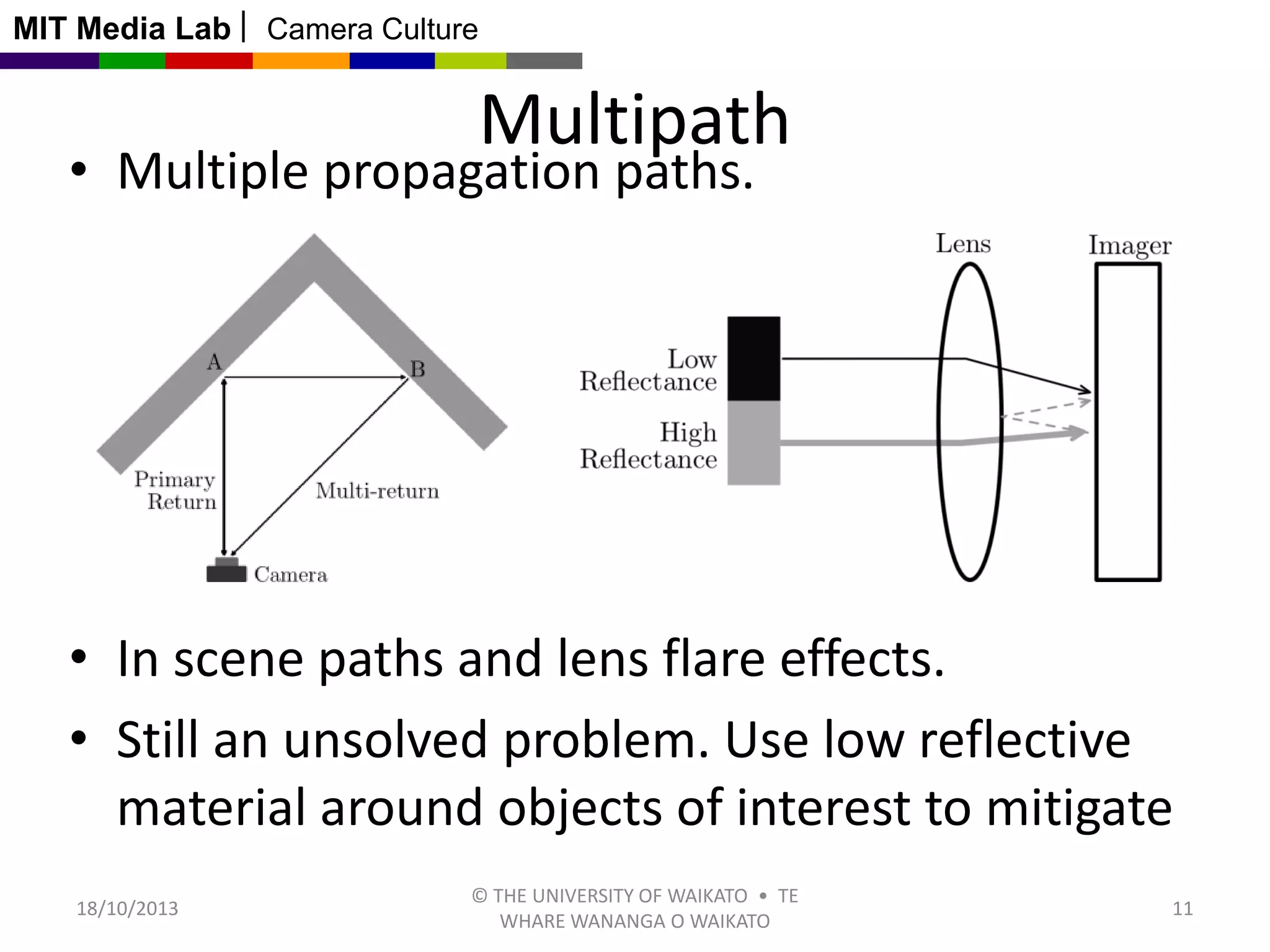
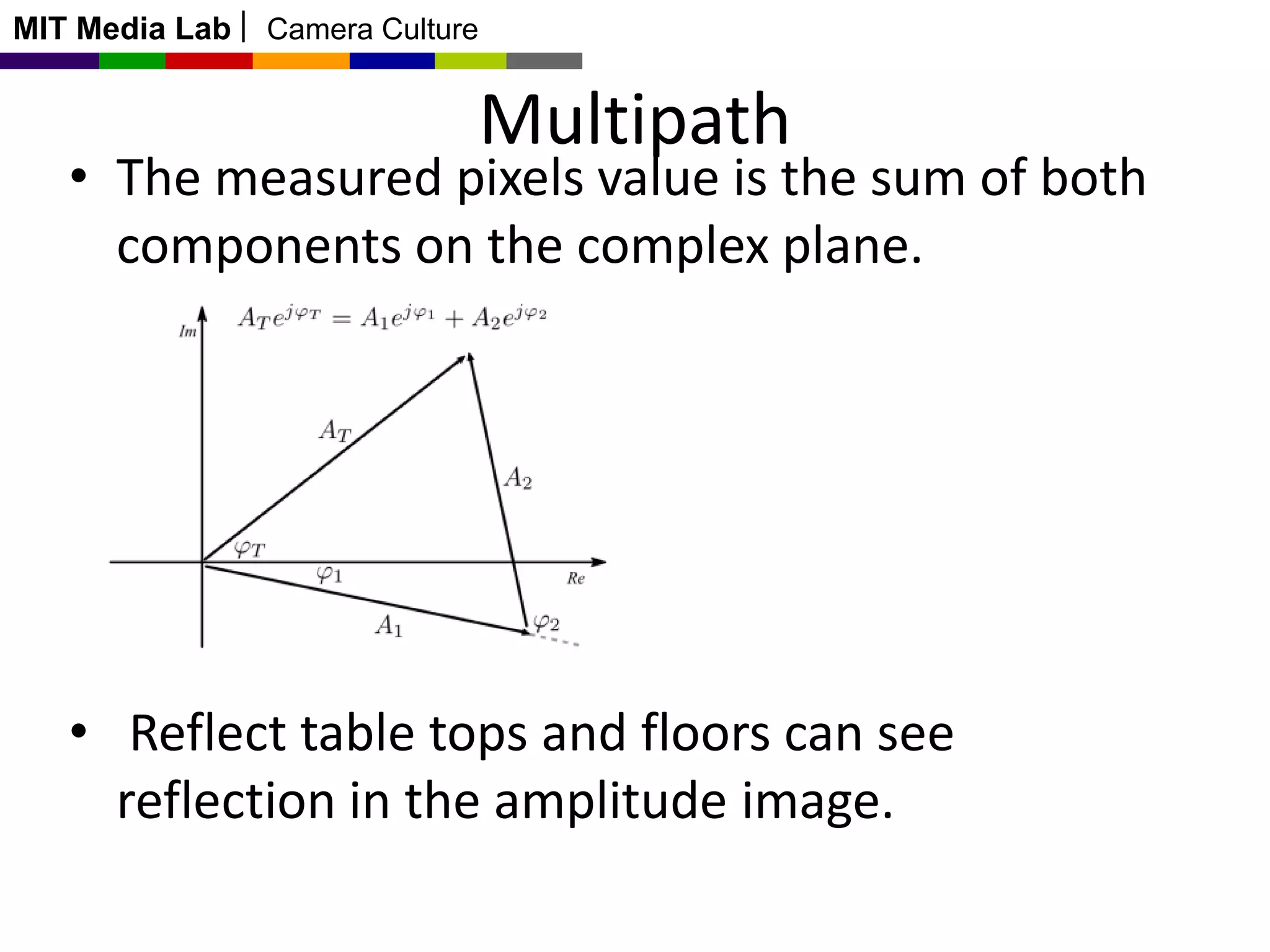
This document discusses time-of-flight cameras and range imaging. It explains that time-of-flight cameras work by illuminating a scene with amplitude modulated light and measuring the phase difference between the transmitted and reflected light, which encodes distance information. It describes the correlation process used to measure distance at each pixel and discusses sources of error such as multipath interference and temperature drift. Real data examples from a 120x160 sensor are shown. Applications discussed include uses in the Kinect, 3D scanning, and potential future uses in mobile phones.