This document discusses semantic segmentation using fully convolutional networks (FCNs).
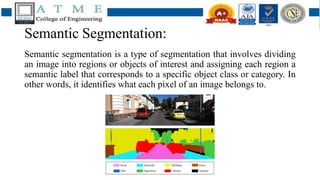
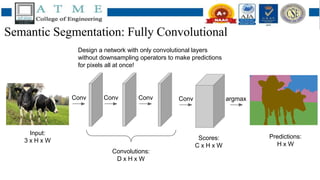
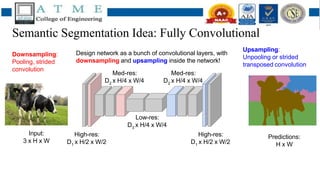
1. Semantic segmentation involves assigning each pixel in an image a class label, such as identifying objects. FCNs can perform pixel-wise segmentation by learning features at different scales through downsampling and then upsampling to generate predictions.
2. Experimental results found that FCNs with downsampling and upsampling improve segmentation accuracy by capturing features at different scales. Downsampling allows learning of more abstract features while upsampling restores resolution for precise predictions.
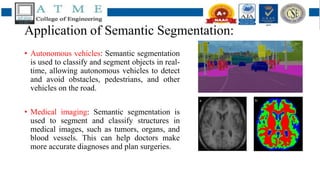
3. In conclusion, FCNs have become a highly effective approach for semantic segmentation tasks in various domains like medical imaging and autonomous driving due to learning multi-scale features and pixel-
![“SEMANTIC SEGMENTATION USING FULLY CONVOLUTIONAL NETWORK”
Co-ordinator
Mrs Kavyashree E D
Asst. Prof.
Dept. of CSE
ATMECE, Mysuru
Presenting By
Ankush Manjunath Naik[4AD19CS008]
Under the Guidance of
Dr. Nasreen Fathima
Associate Prof.
Dept. of CSE
ATMECE, Mysuru](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aaseminartemplate-230301164539-eff81a3e/85/AaSeminar_Template-pptx-1-320.jpg)










![Reference:
• Image Semantic Segmentation using Deep Convolutional Nets, Fully Connected
Conditional Random Fields, and Dilated Convolution. Degui Xiao, Pei Zhong.
[2019]
• Road Segmentation using Point Cloud BEV based on Fully Convolution Network.
Yin Zhang, Guoquan Ren, Guojie Kong, Hui Xie. [2020]
• Guided Co-Segmentation Network for Fast Video Object Segmentation. Weide
Liu, Guosheng Lin, Tianyi Zhang, Zichuan Liu. [2020]
• Real-Time Semantic Segmentation Network Based on Lite Reduced Atrous
Spatial Pyramid Pooling Module Group. Yangsheng Tian, Fangyuan Chen. [2020]
• Deep Guidance Network for Biomedical Image Segmentation. Pengshuai Yin, Rui
Yuan, Yiming Cheng, Qinguao Wu. [2020]
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aaseminartemplate-230301164539-eff81a3e/85/AaSeminar_Template-pptx-16-320.jpg)
![Reference:
• An Image Segmentation Algorithm for LED Bracket's Detection. Xinjia Fang,
Fupei Wu, Zhichao Zeng, Jintian Li. [2016]
• Two-Stream Deep Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Fully Automatic Video
Object Segmentation. Jingwei Xu, Li Song, Rong Xie. [2017]
• A Sonar Image Segmentation Algorithm based on Two-Dimensional Spatio-
Temporal Fuzzy Entropy. Lu Zhen, Chen Yuchao, Zhang Tiedong, Yu Jun. [2018]
• Skin Segmentation based on Improved Thresholding Method. Novira Dwina, Fitri
Arnia, Khairul Munadi. [2018]
• Image Segmentation Based on Superpixel Boundary Movement. Yueting Fang,
Deqiang Yang, JianHou Gan. [2019]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aaseminartemplate-230301164539-eff81a3e/85/AaSeminar_Template-pptx-17-320.jpg)
