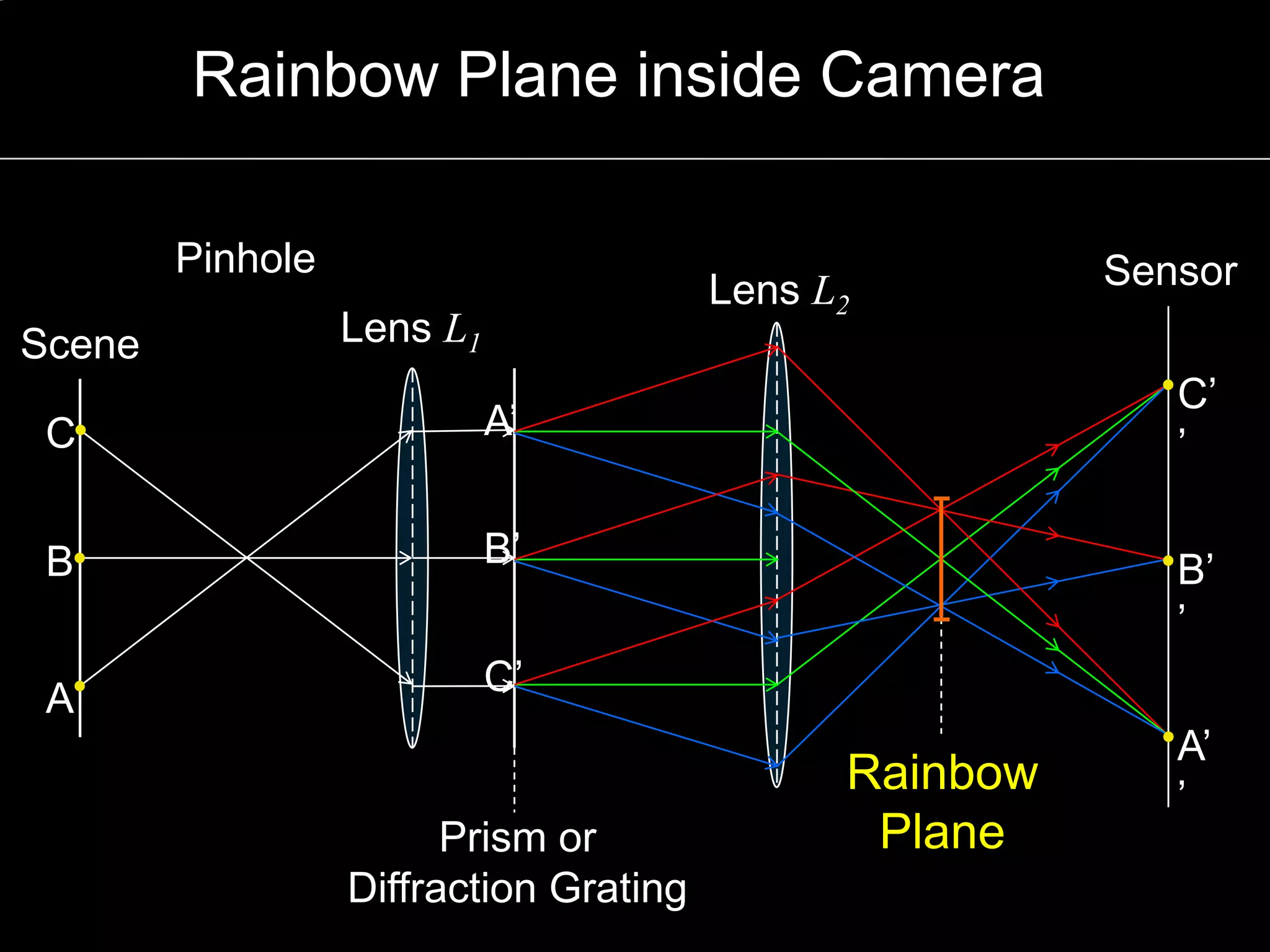
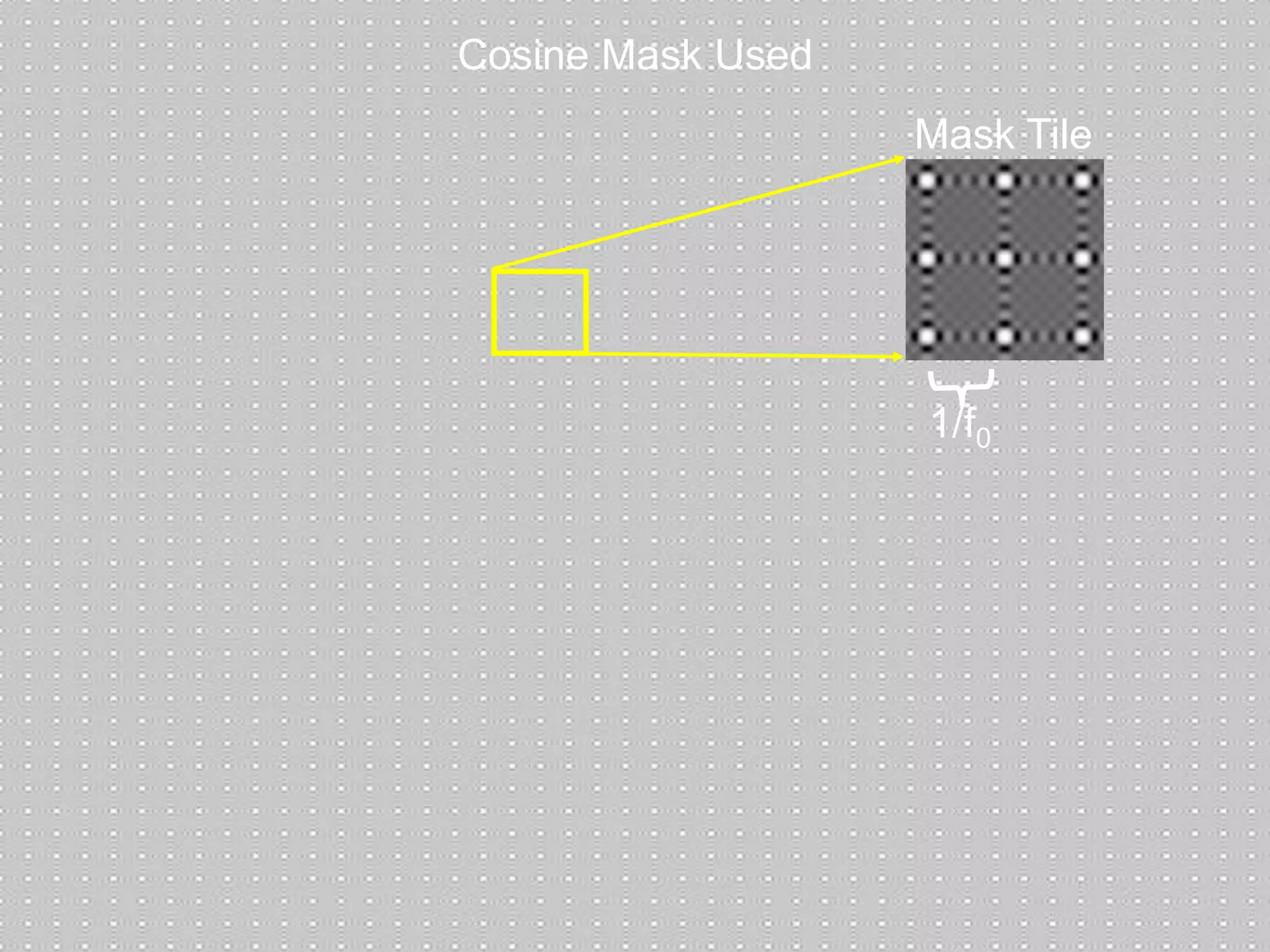
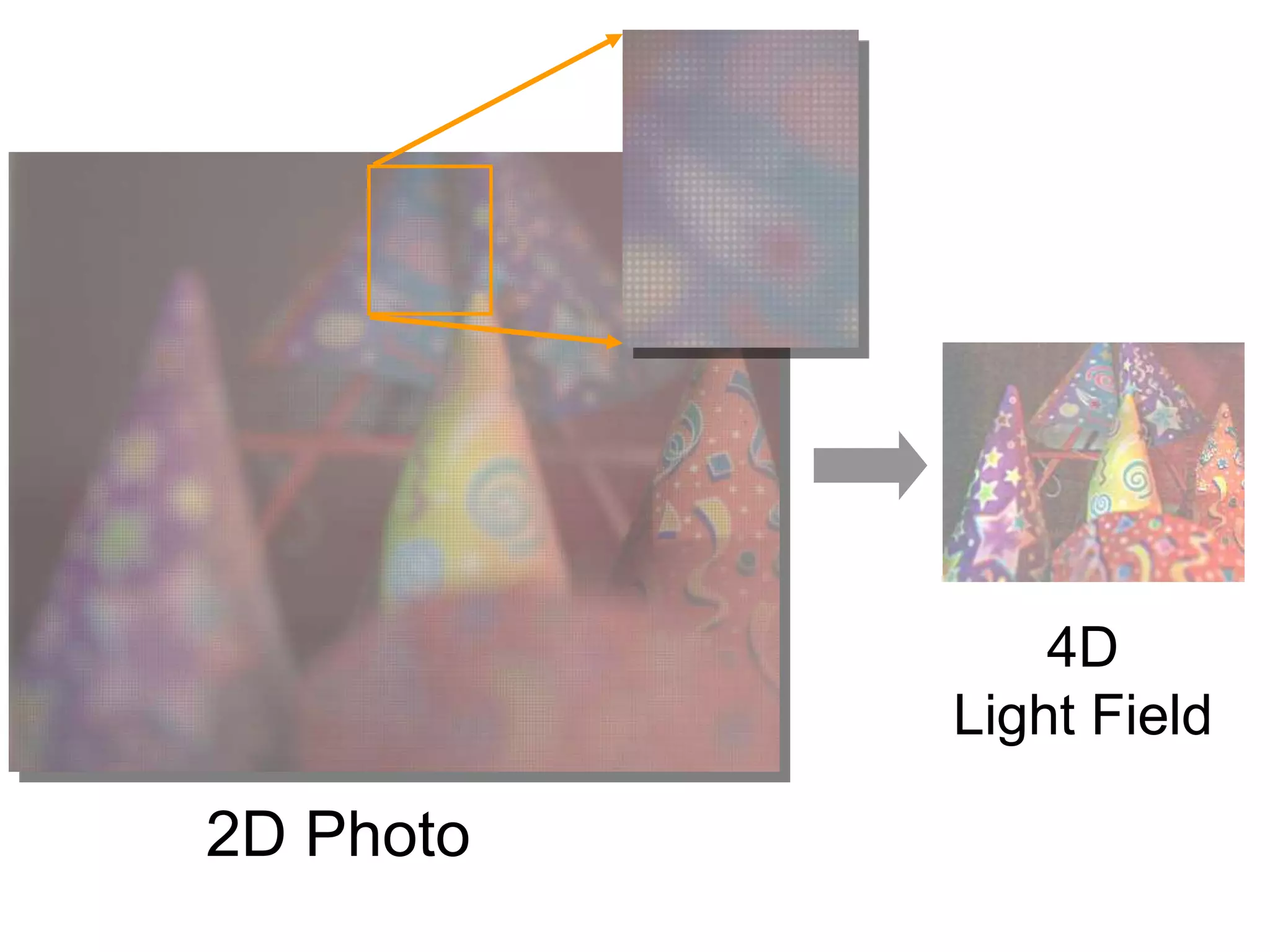
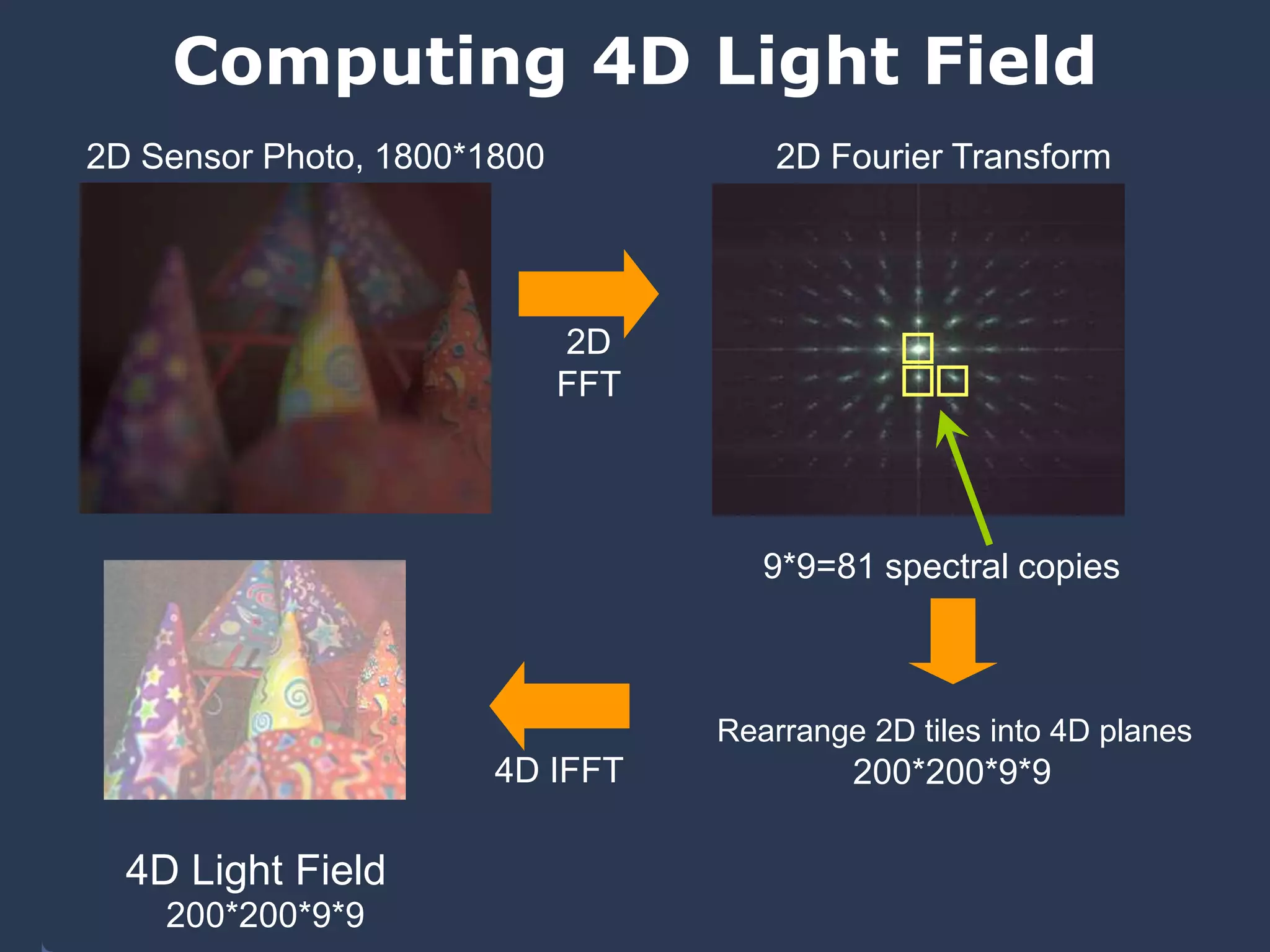
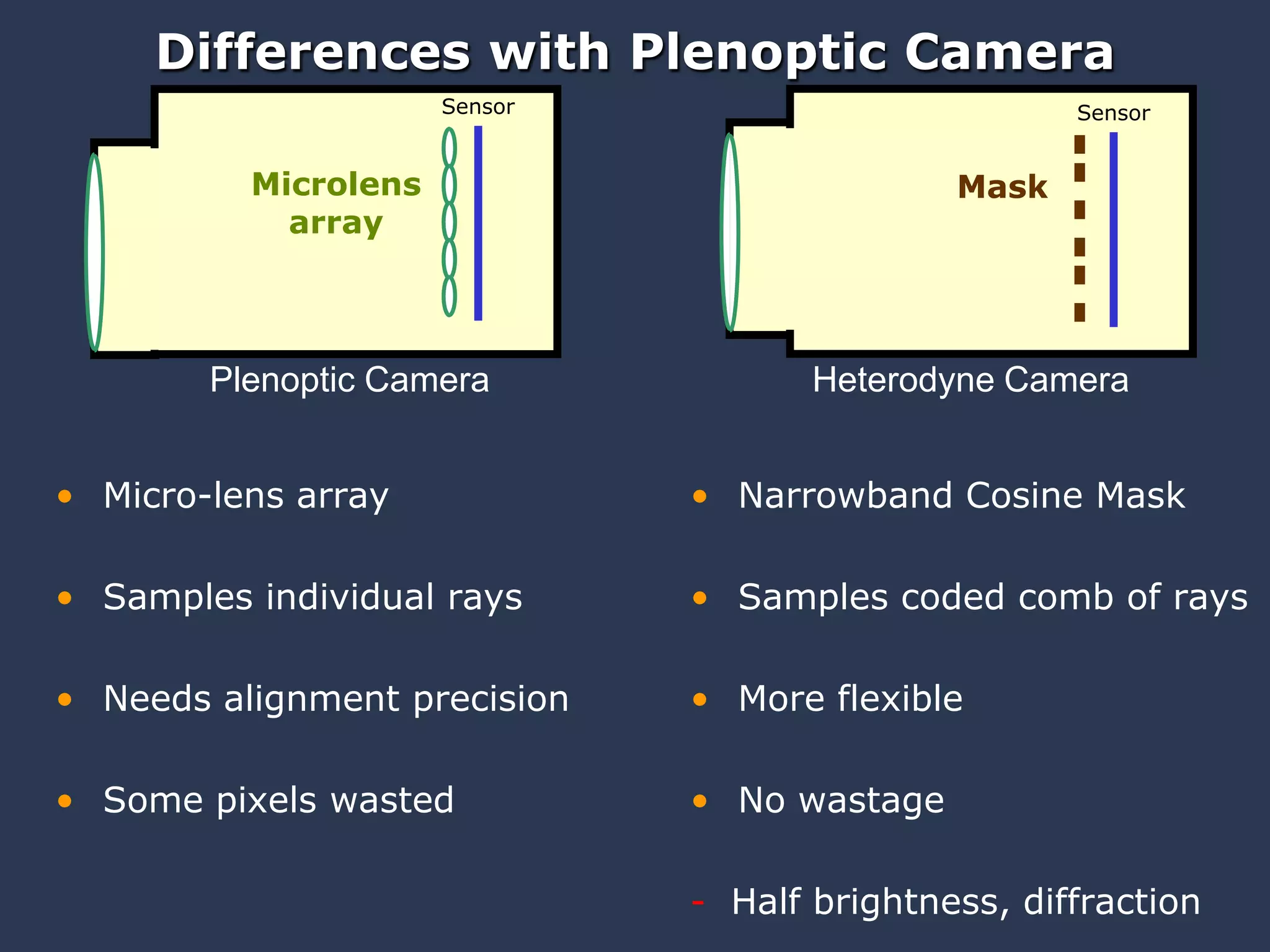
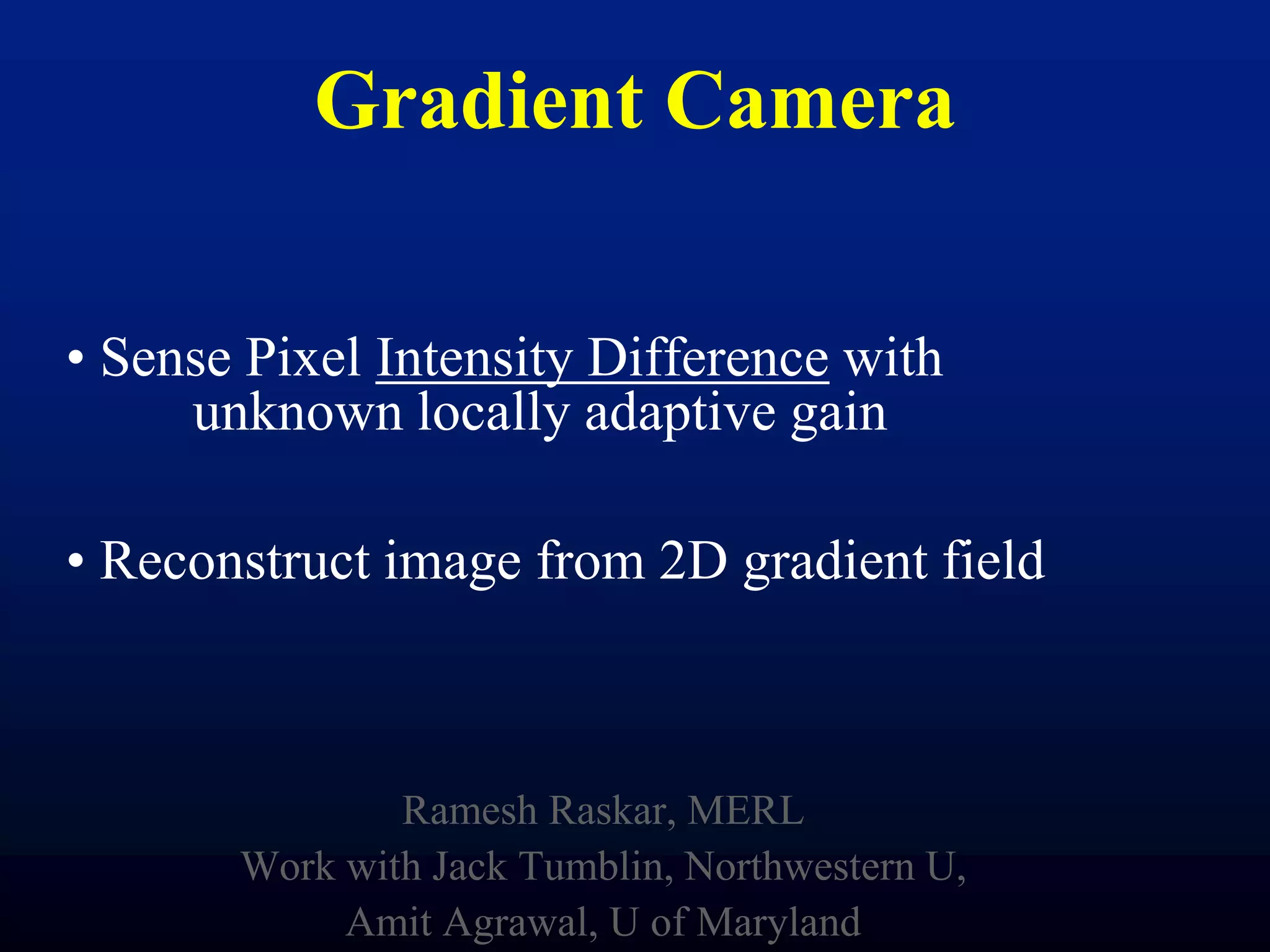
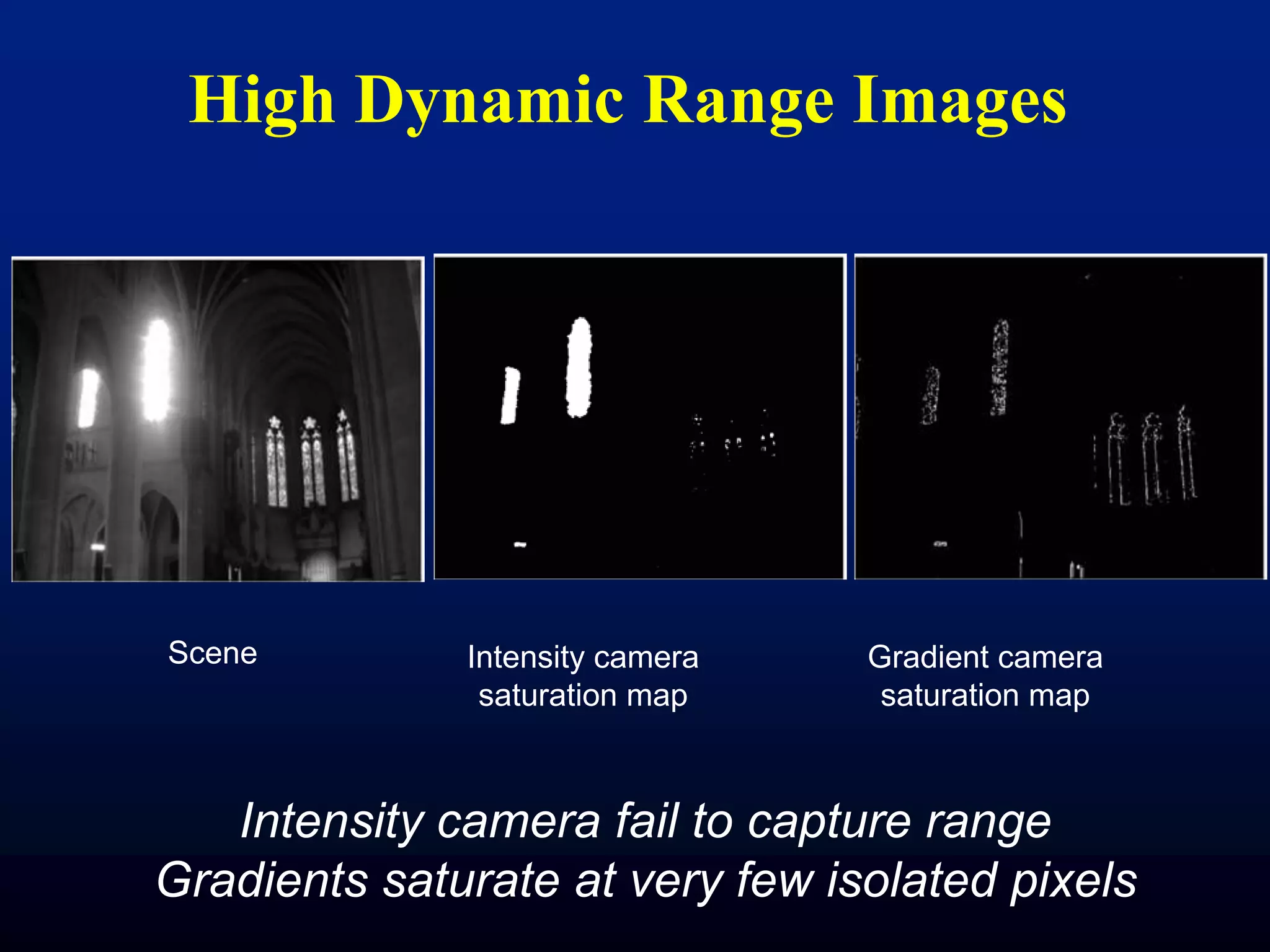
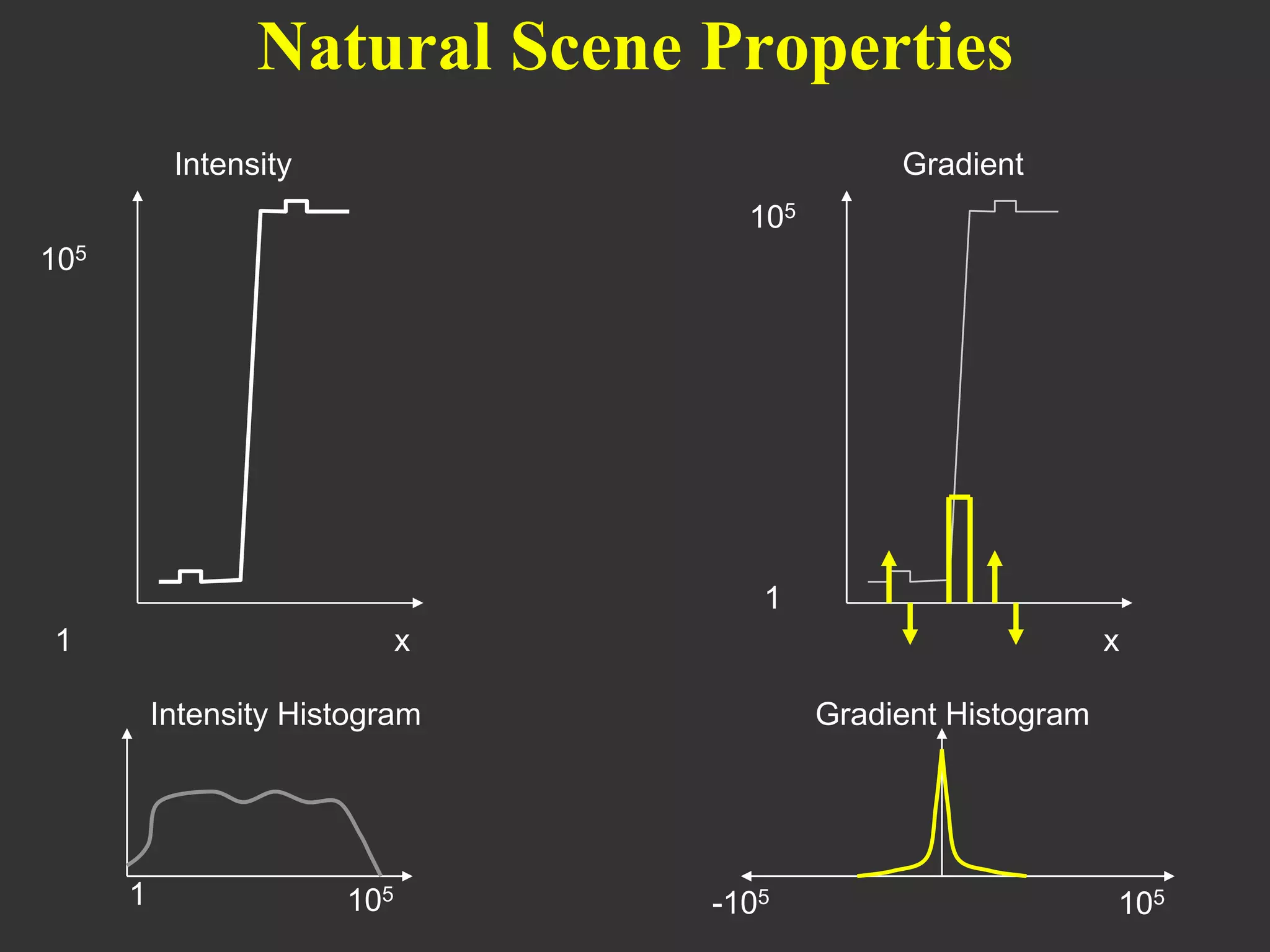
The document discusses light field and coded aperture cameras. It describes the Stanford plenoptic camera which uses a microlens array to sample individual rays of light, capturing 14 pixels per lens. An alternative approach is a mask-based light field camera that uses a narrowband cosine mask to sample a coded combination of rays. This heterodyne approach captures half the brightness but avoids wasting pixels and issues with lens array alignment. The document outlines how such cameras can digitally refocus images and increase depth of field. It also discusses using the Fourier transform to compute a 4D light field from 2D photos captured with a mask.

![Light Field Inside a Camera
Lenslet-based Light Field camera
[Adelson and Wang, 1992, Ng et al. 2005 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codedphotography2013class-131018121619-phpapp01/75/Coded-Photography-Ramesh-Raskar-2-2048.jpg)
![Stanford Plenoptic Camera
[Ng et al 2005]
Contax medium format camera
Kodak 16-megapixel sensor
Adaptive Optics microlens array
125μ square-sided microlenses
4000
4000 pixels
292
292 lenses = 14
14 pixels per lens](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codedphotography2013class-131018121619-phpapp01/75/Coded-Photography-Ramesh-Raskar-3-2048.jpg)
![Digital Refocusing
[Ng et al 2005]
Can we achieve this with a Mask alone?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codedphotography2013class-131018121619-phpapp01/75/Coded-Photography-Ramesh-Raskar-4-2048.jpg)
![Mask based Light Field Camera
Mask
Sensor
[Veeraraghavan, Raskar, Agrawal, Tumblin, Mohan, Siggraph 2007 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codedphotography2013class-131018121619-phpapp01/75/Coded-Photography-Ramesh-Raskar-5-2048.jpg)

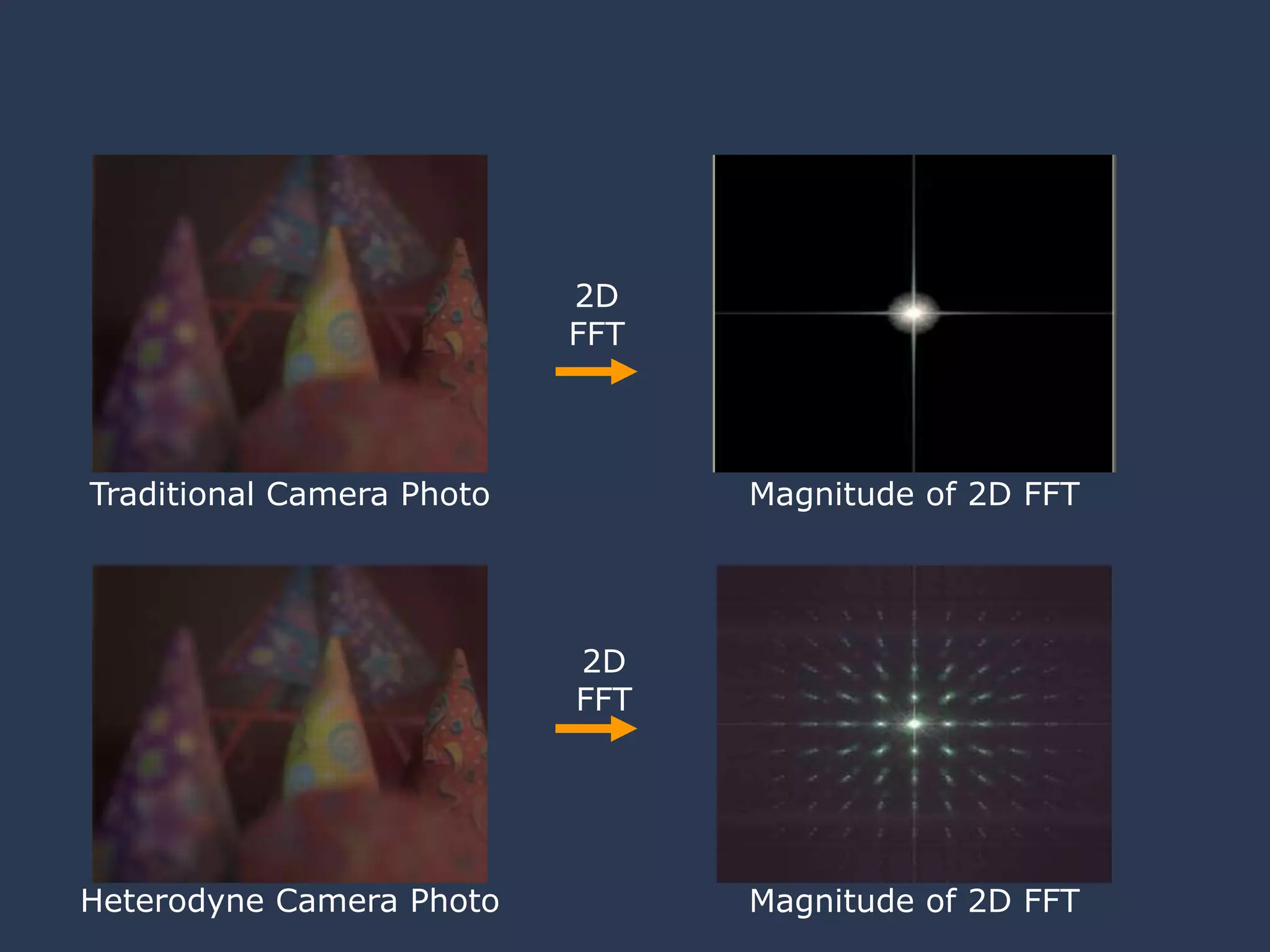
![Captured 2D Photo
Encoding due to
Mask
[Veeraraghavan, Raskar, Agrawal, Tumblin, Mohan, Siggraph 2007 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codedphotography2013class-131018121619-phpapp01/75/Coded-Photography-Ramesh-Raskar-8-2048.jpg)
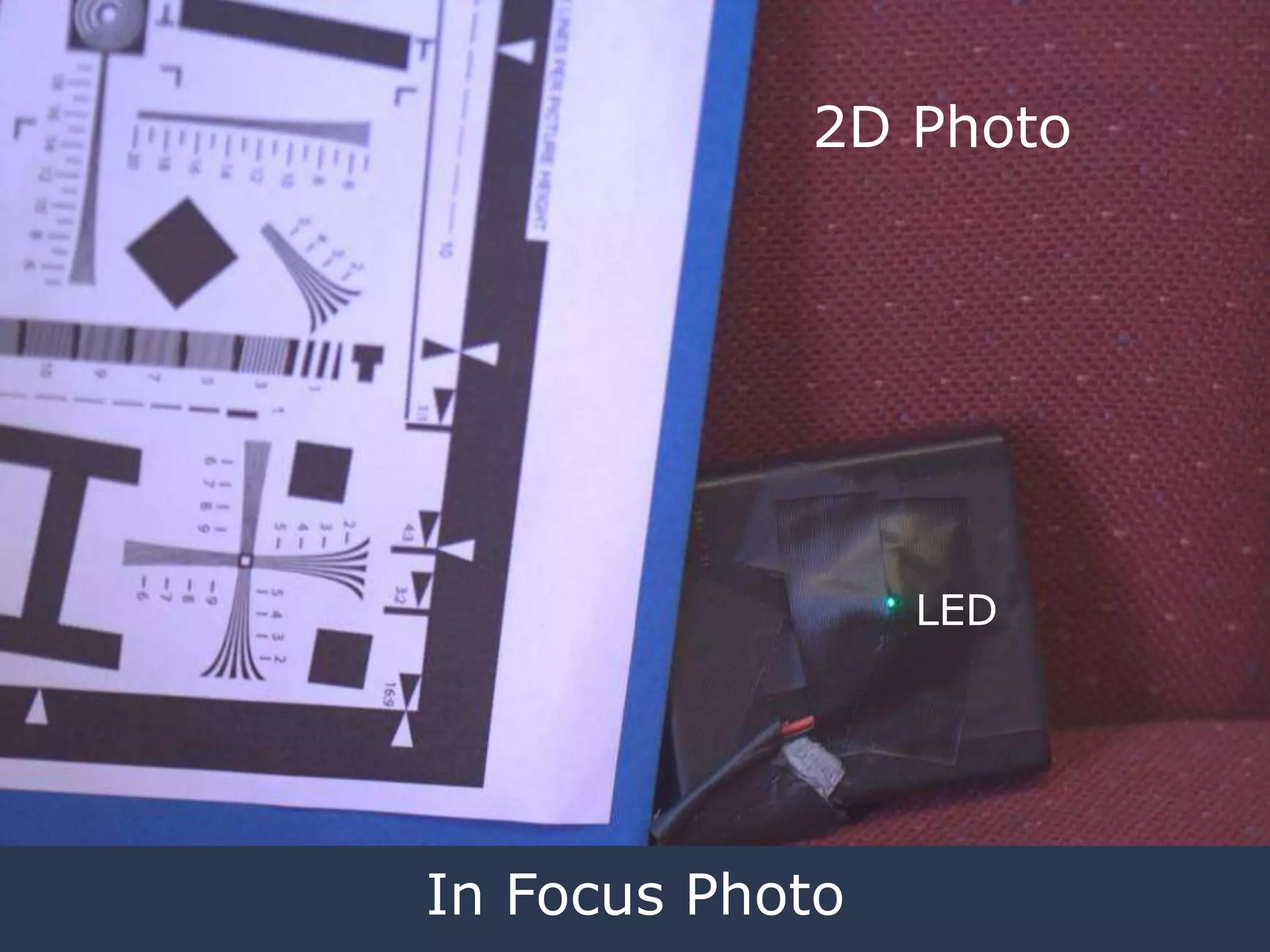


![Captured Blurred
Photo
[Veeraraghavan, Raskar, Agrawal, Tumblin, Mohan, Siggraph 2007 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codedphotography2013class-131018121619-phpapp01/75/Coded-Photography-Ramesh-Raskar-13-2048.jpg)




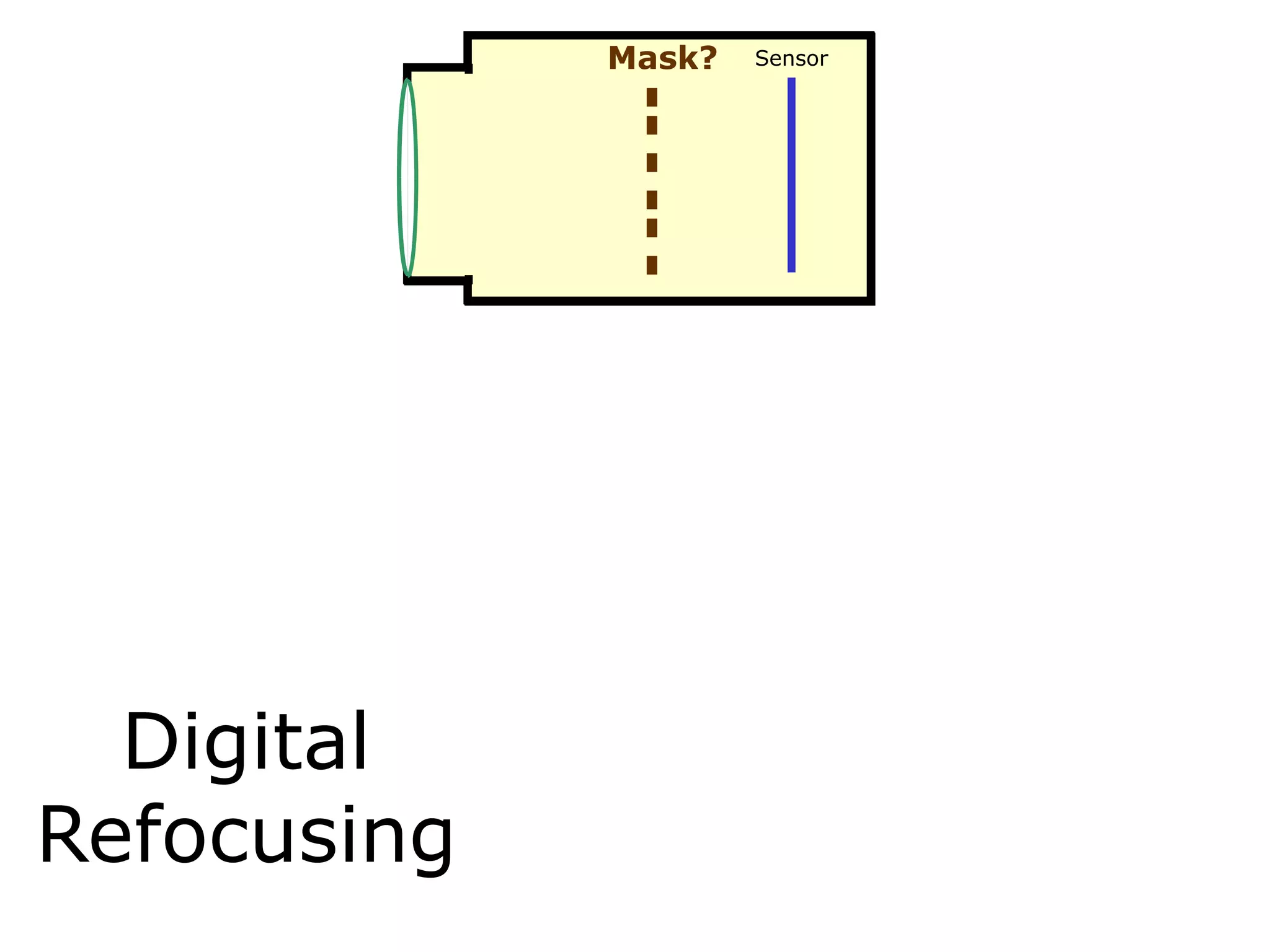
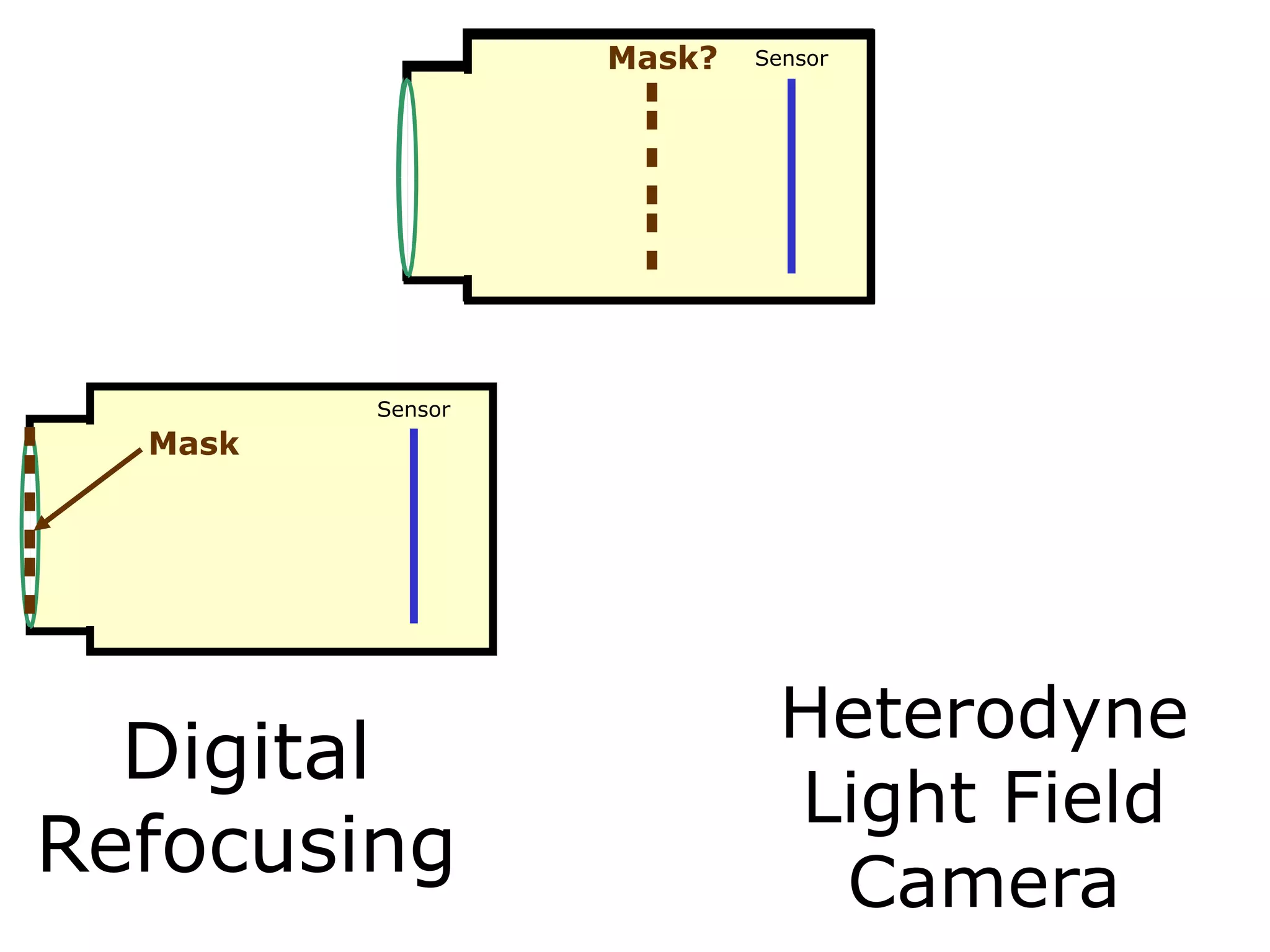
![Mask = more information?
Mask?
Sensor
Sensor
Mask
Digital Refocusing
Sensor
Mask
Heterodyne Light
Field Camera
[Veeraraghavan, Raskar, Agrawal, Tumblin, Mohan], Sig
graph 2007](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codedphotography2013class-131018121619-phpapp01/75/Coded-Photography-Ramesh-Raskar-22-2048.jpg)
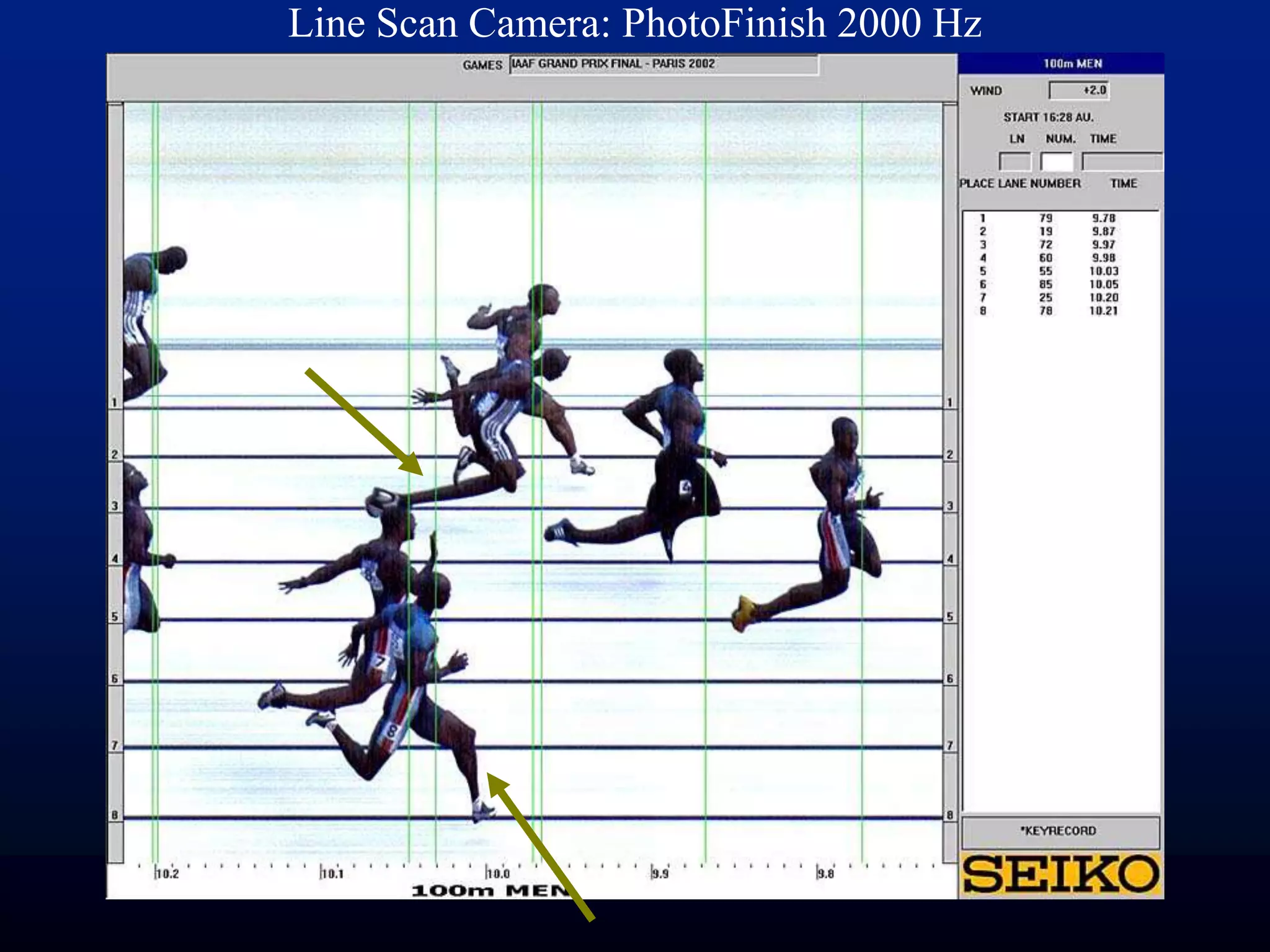
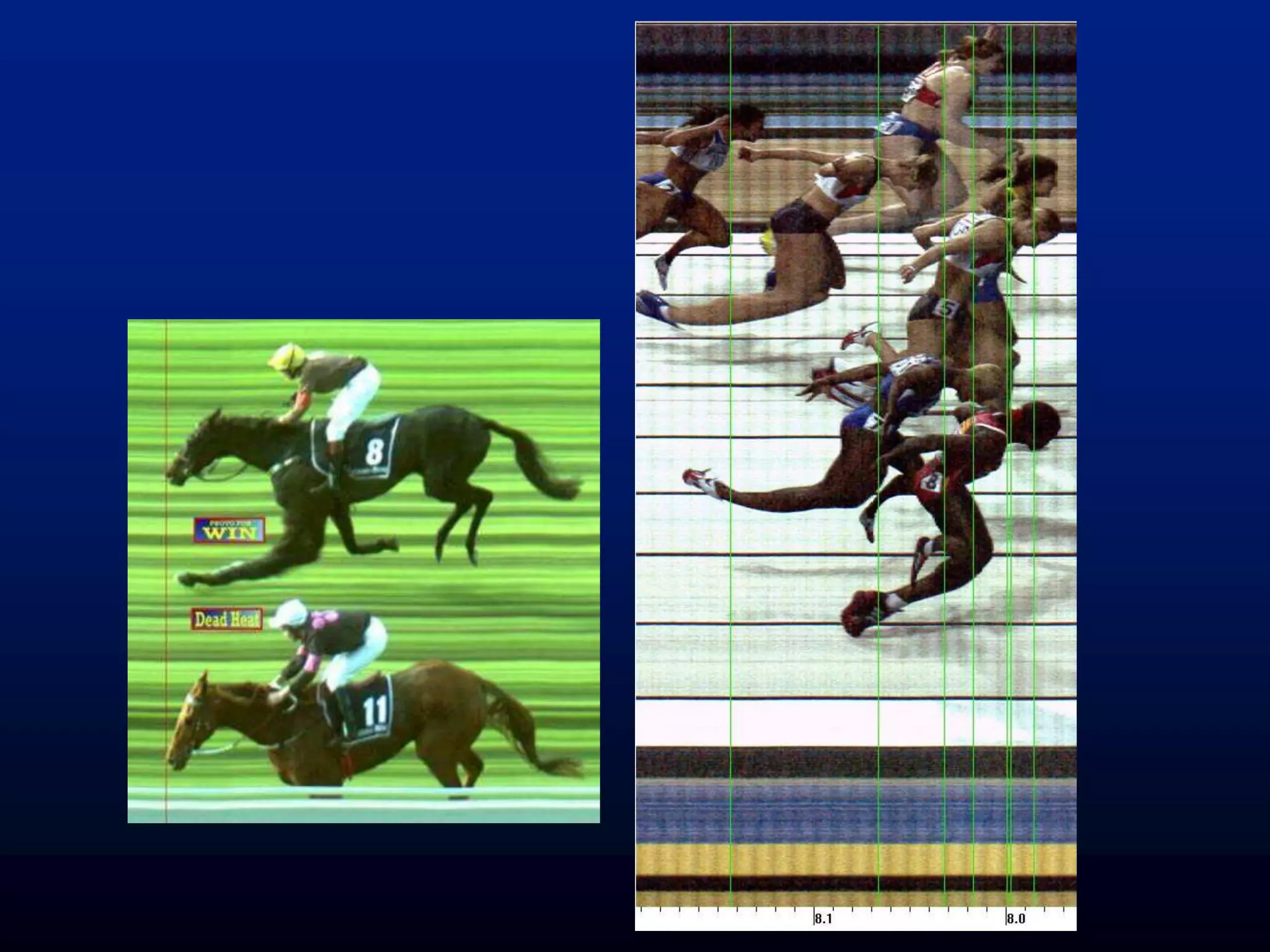



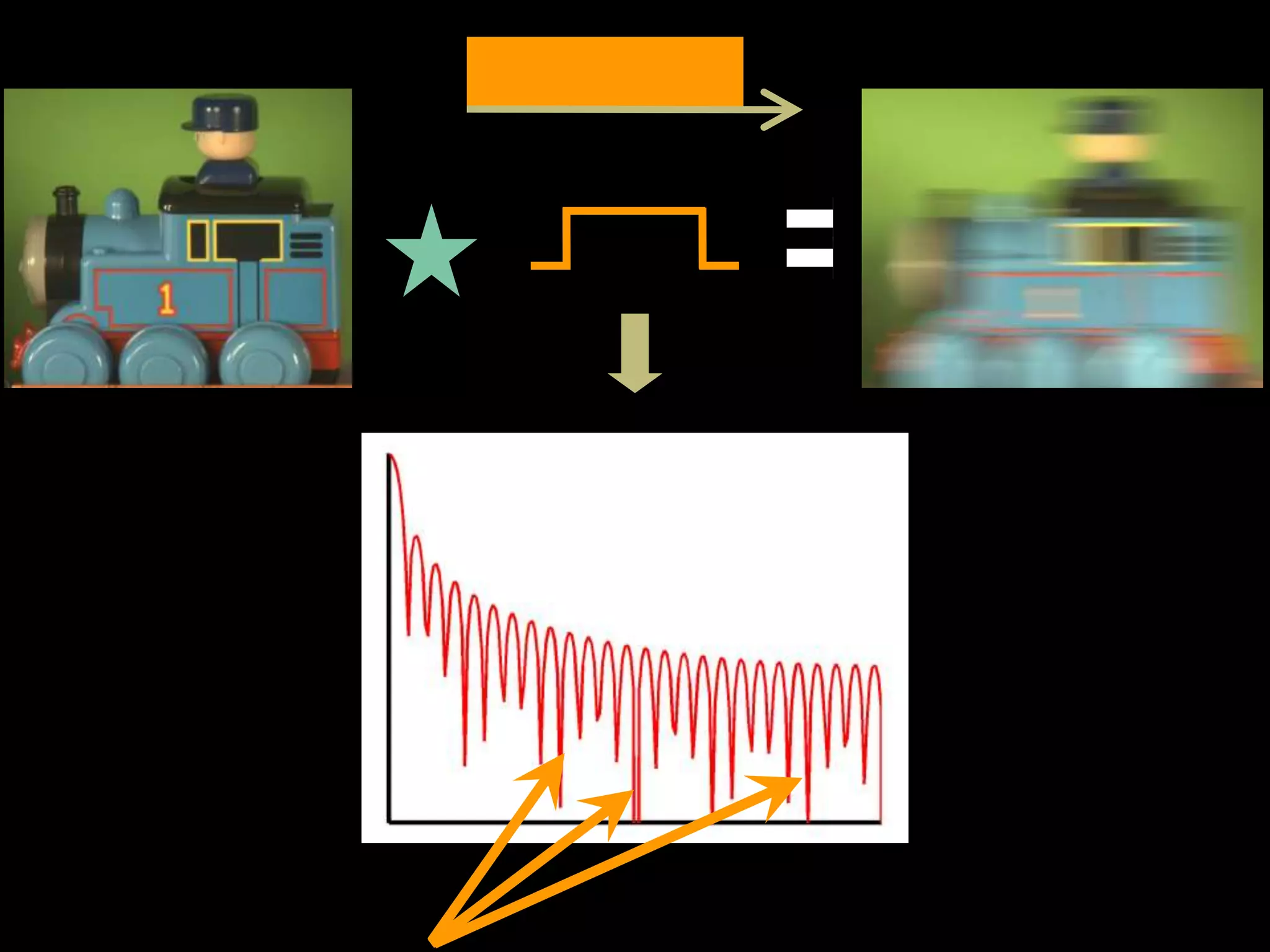
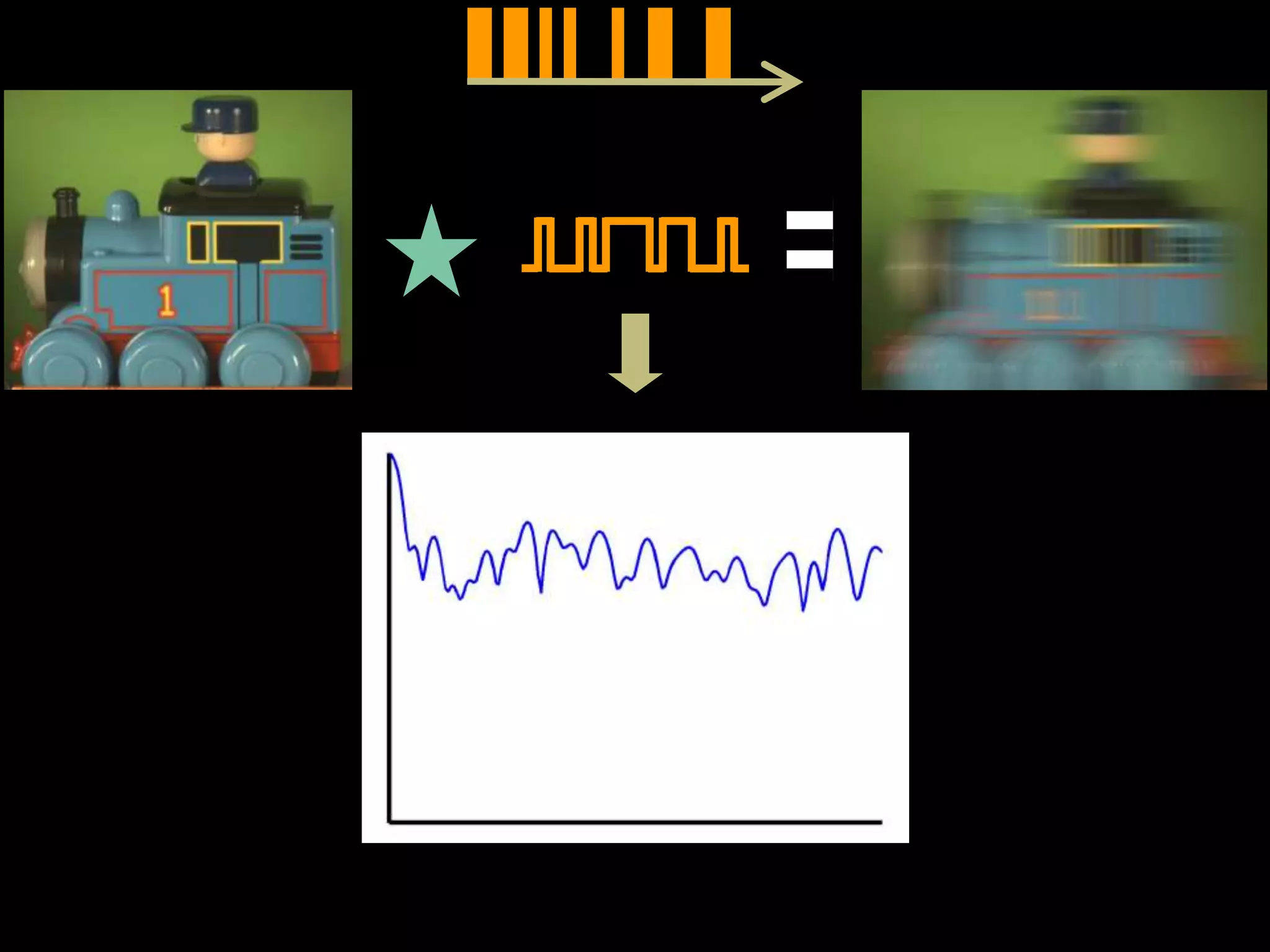
![Fluttered Shutter Camera
[Raskar, Agrawal, Tumblin] Siggraph2006](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codedphotography2013class-131018121619-phpapp01/75/Coded-Photography-Ramesh-Raskar-36-2048.jpg)

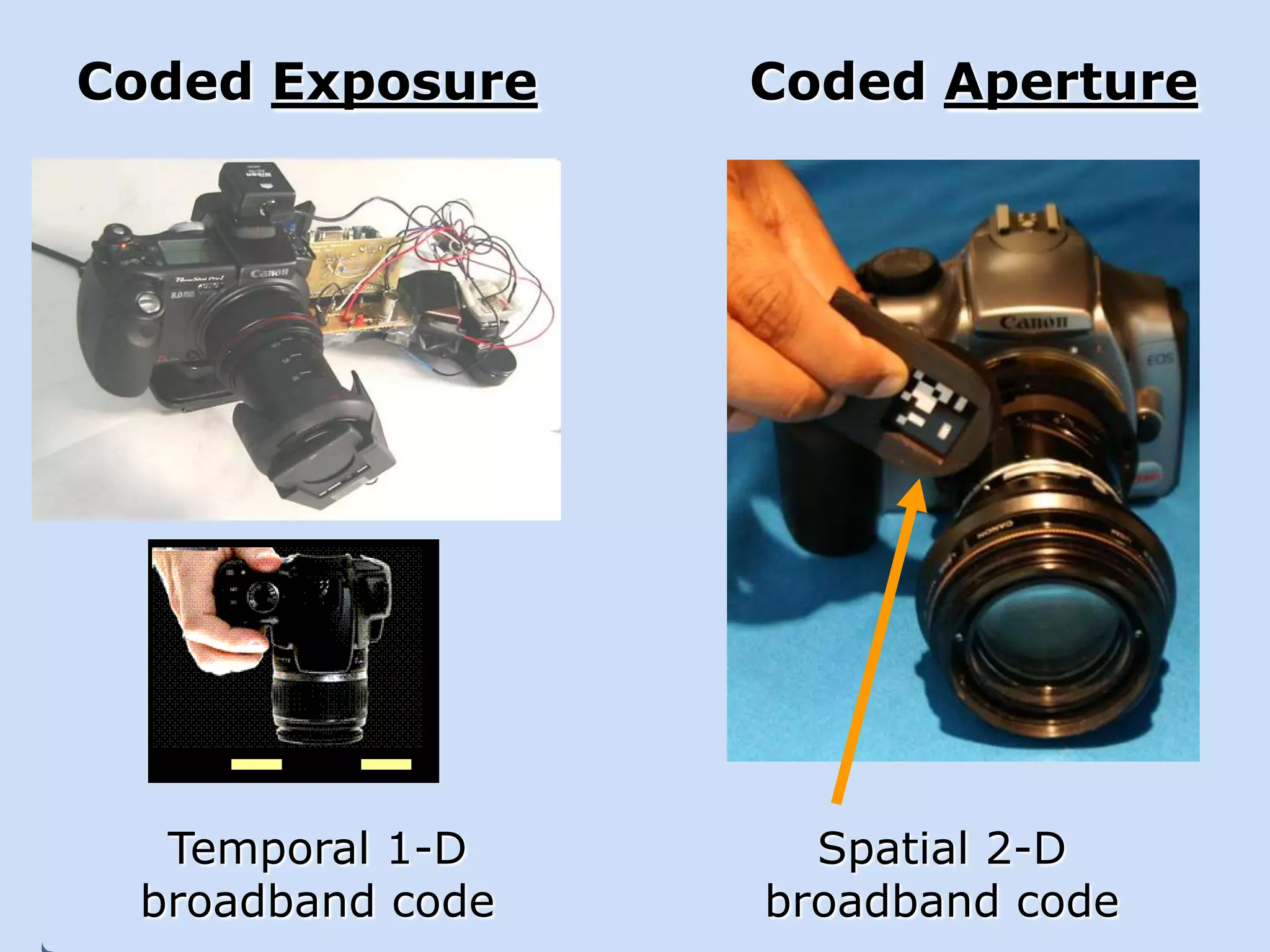

![Multiperspective Camera?
[ Jingyi Yu‟ 2004 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codedphotography2013class-131018121619-phpapp01/75/Coded-Photography-Ramesh-Raskar-43-2048.jpg)

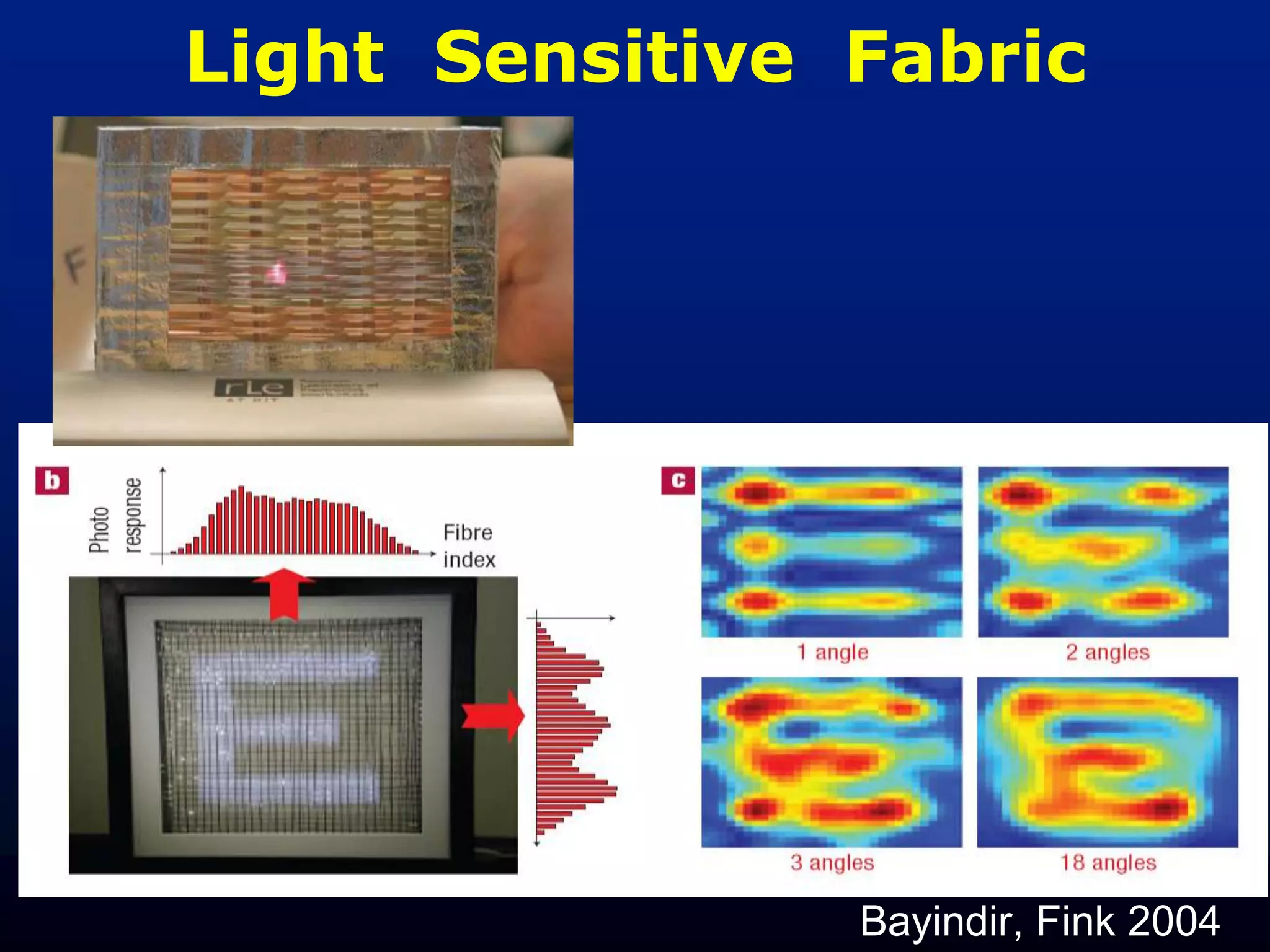
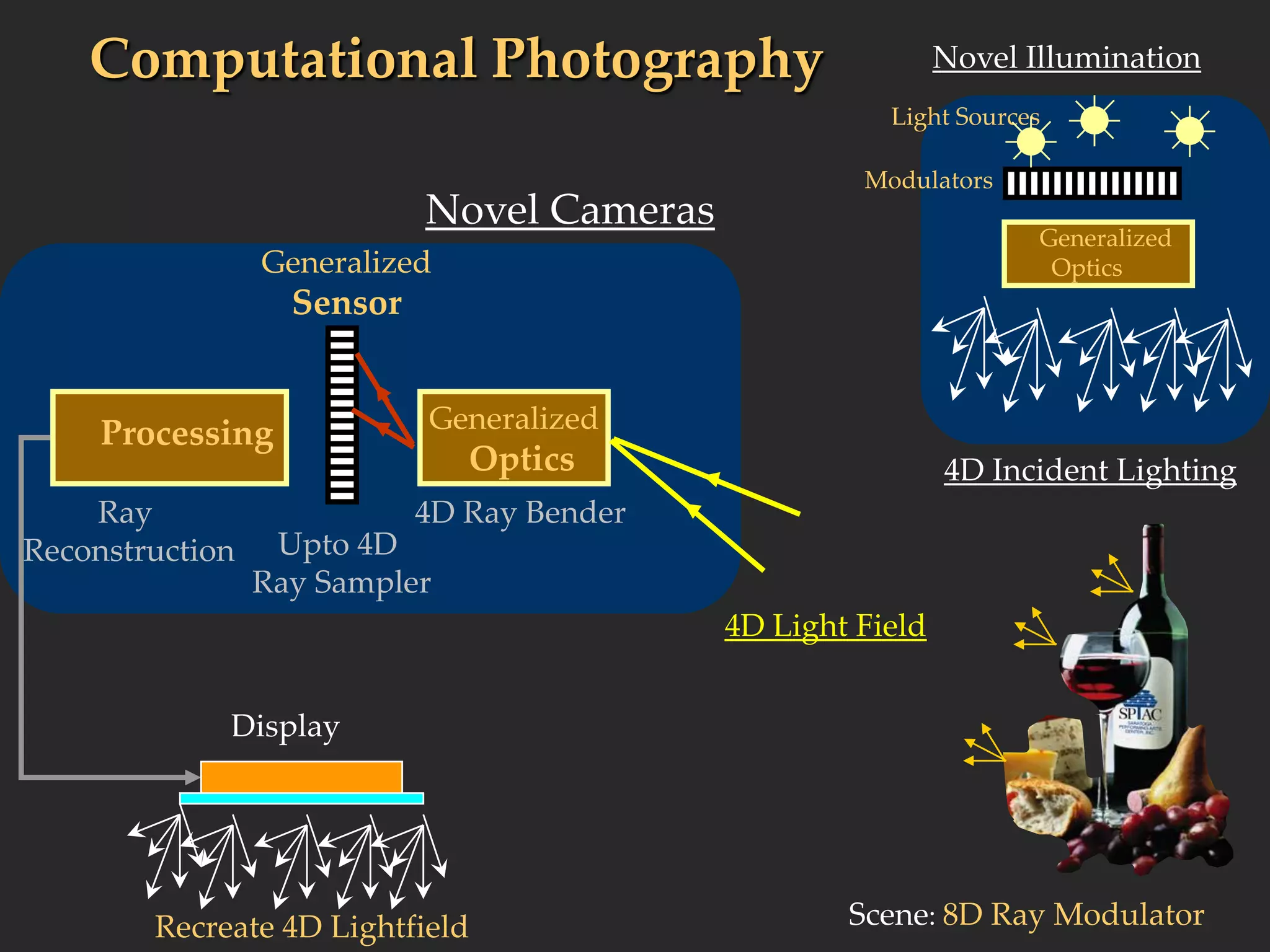
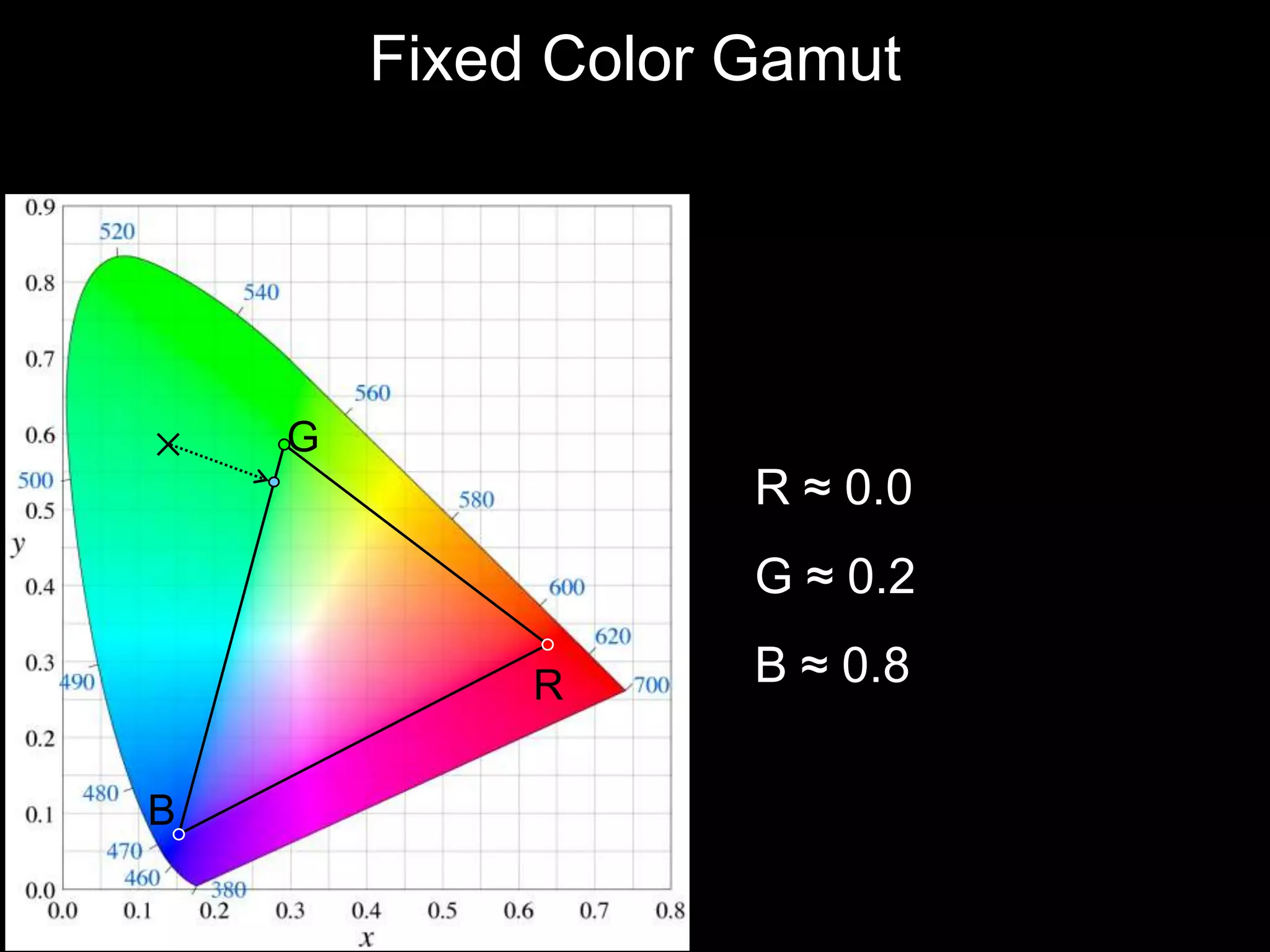
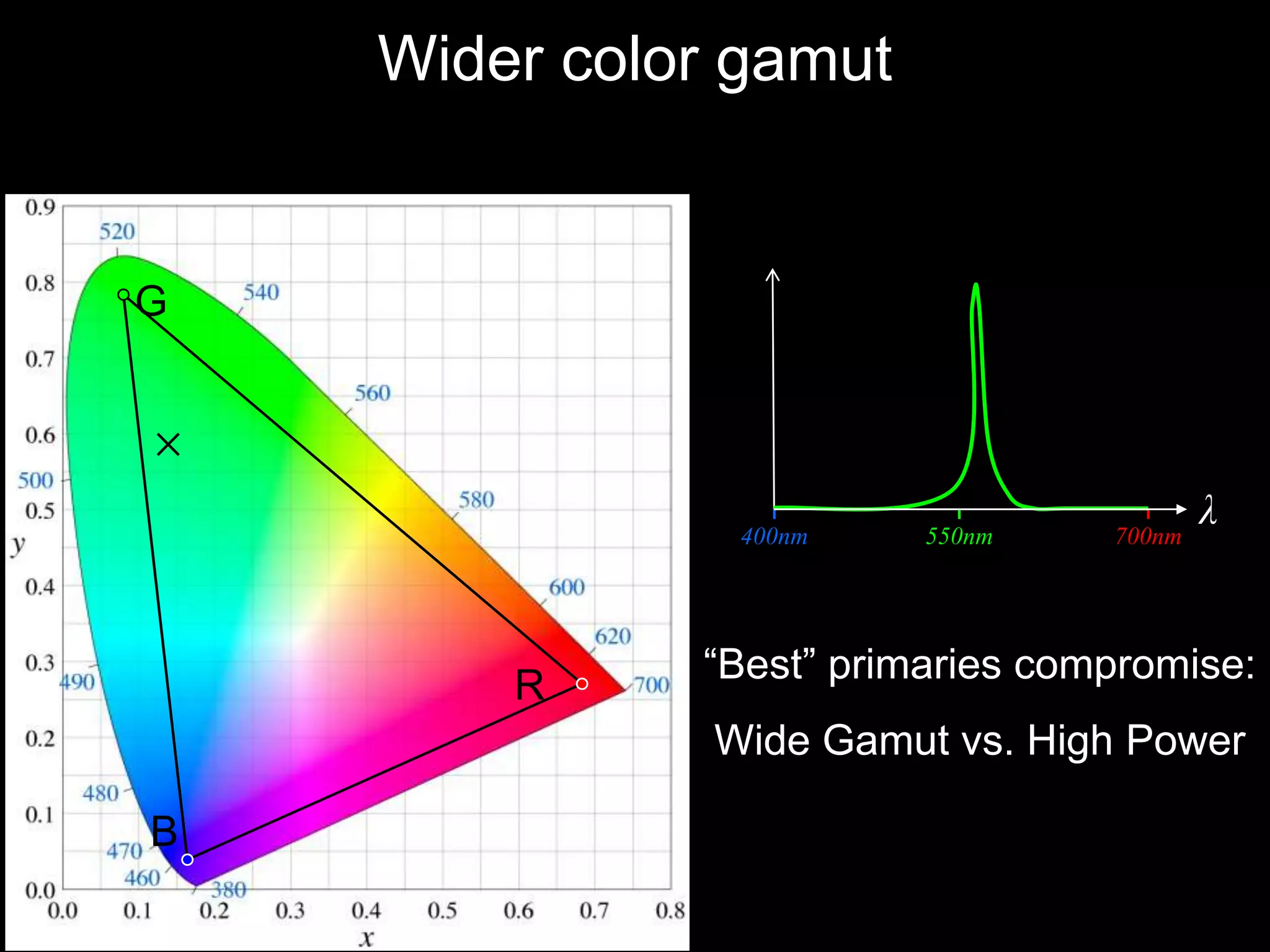
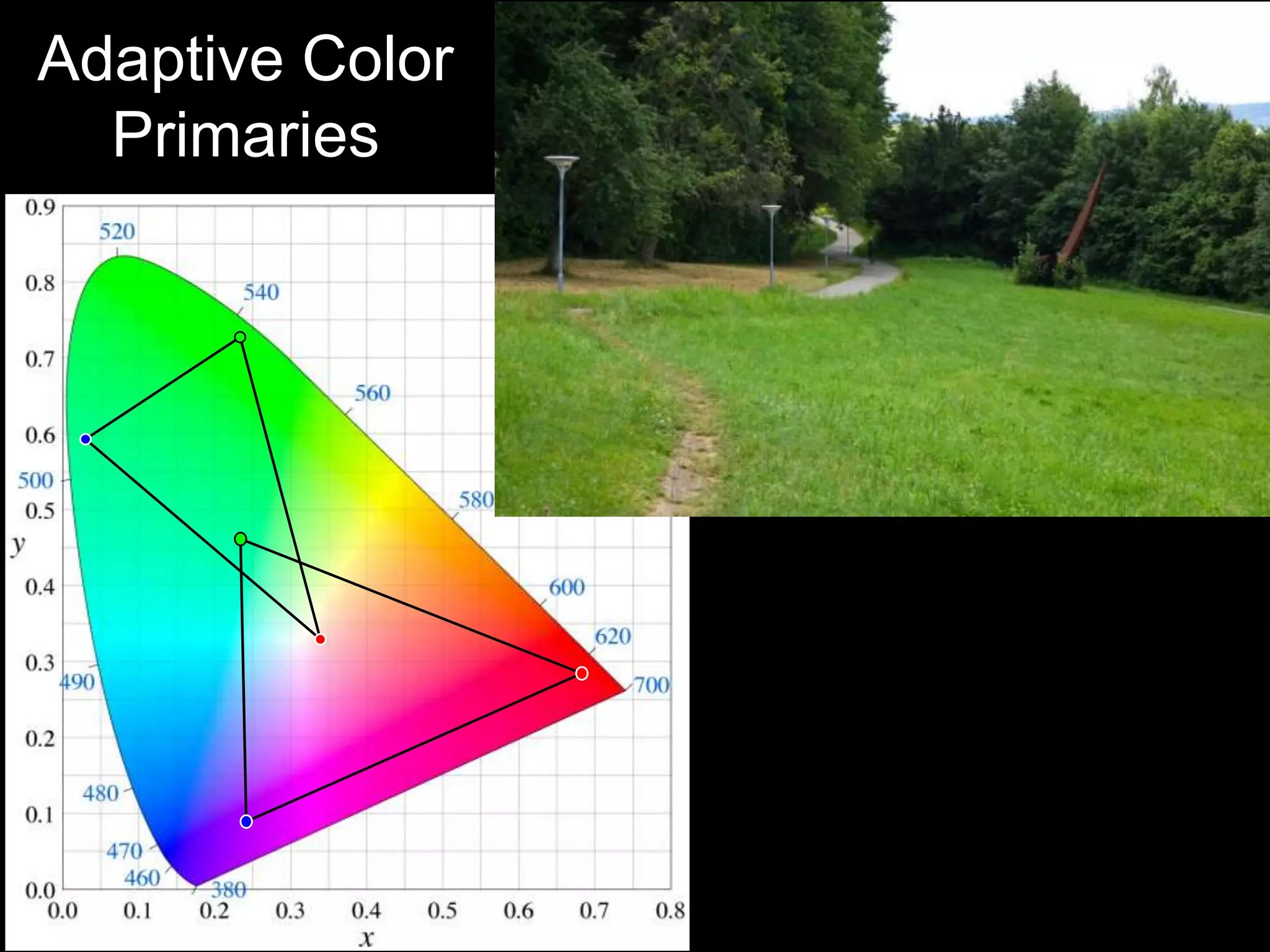
![Agile Spectrum Imaging
With Ankit Mohan, Jack Tumblin [Eurographics 2008]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codedphotography2013class-131018121619-phpapp01/75/Coded-Photography-Ramesh-Raskar-50-2048.jpg)