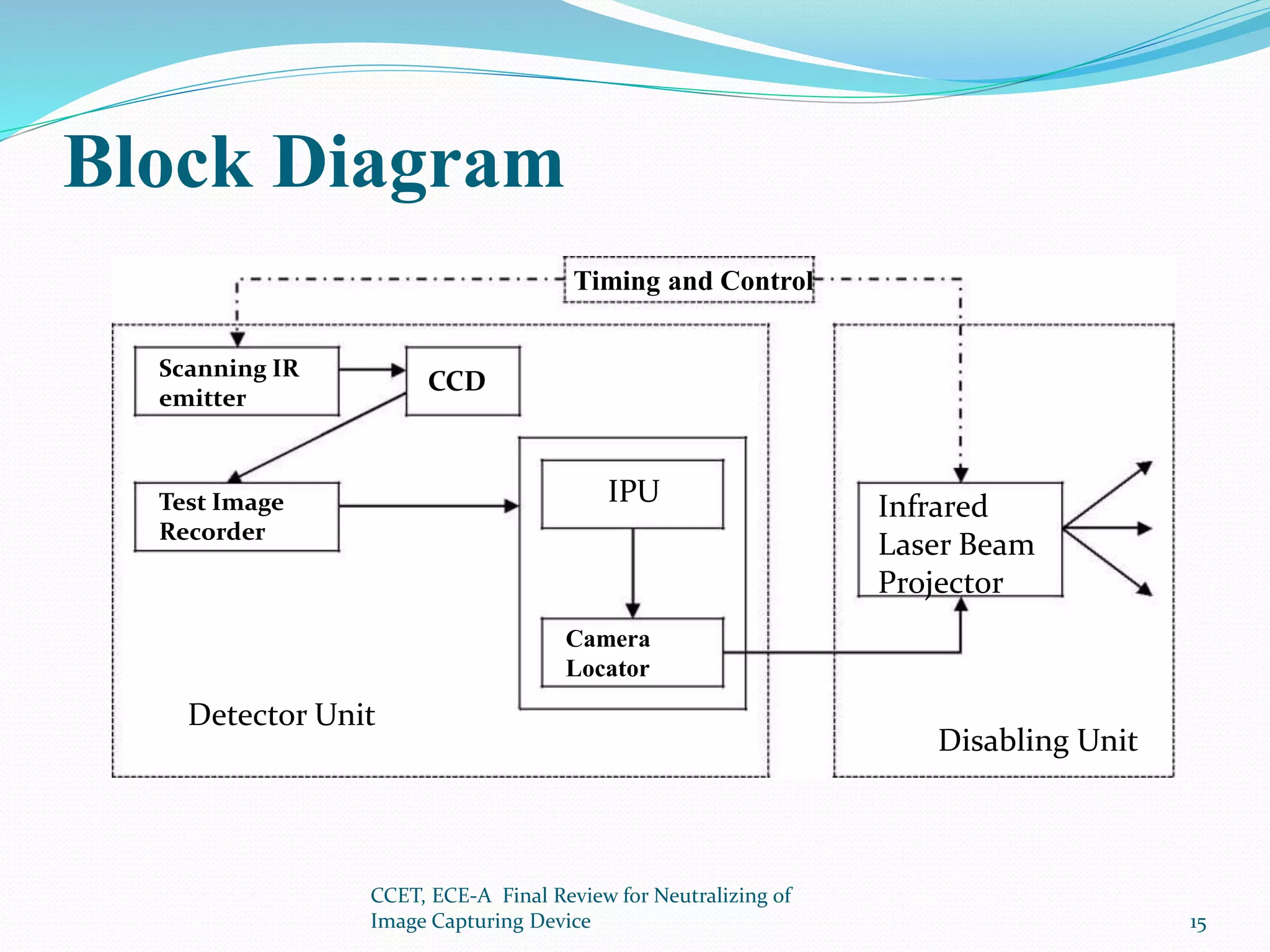
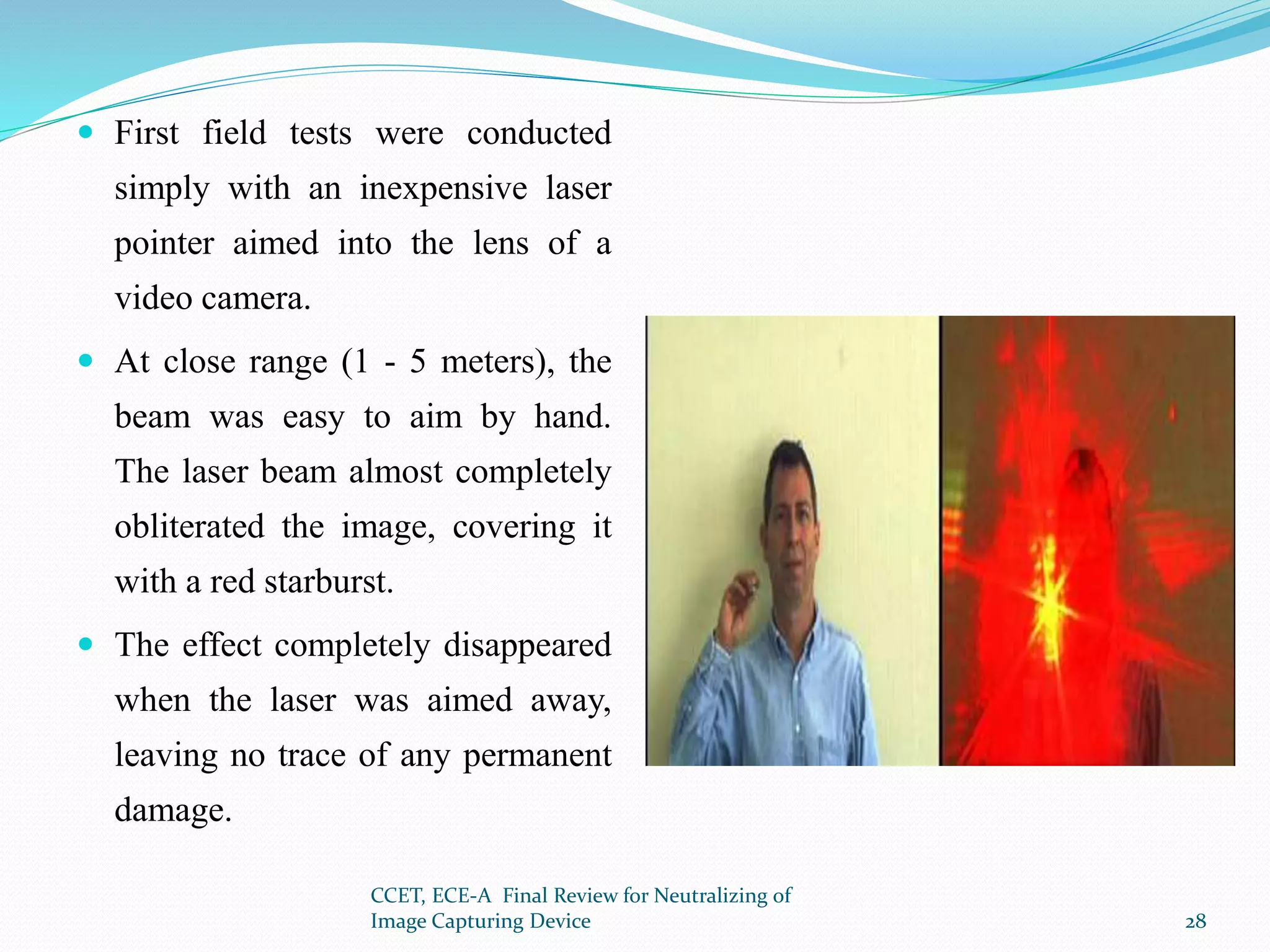
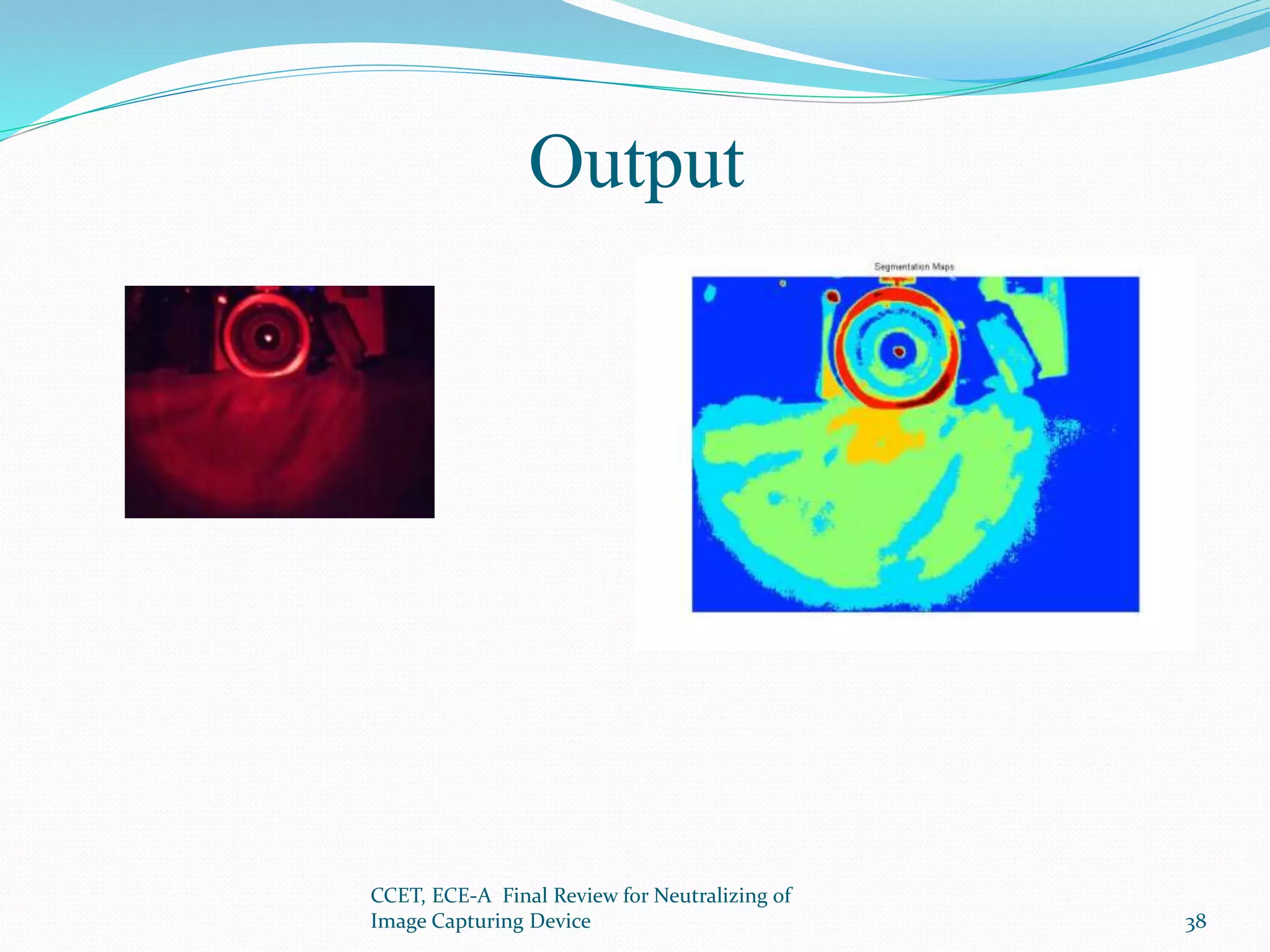
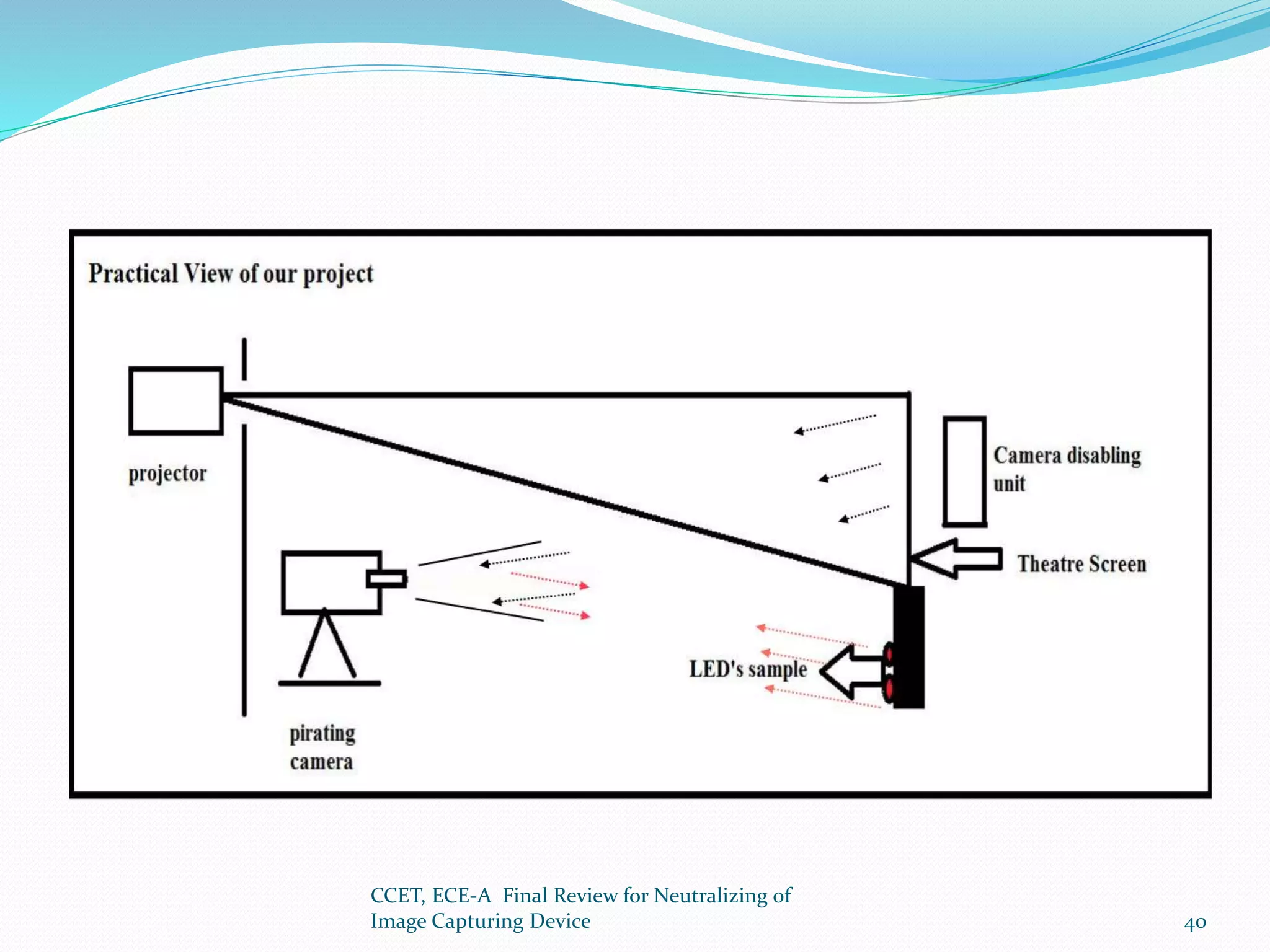
The document presents a project that aims to neutralize image capturing devices. It discusses detecting cameras using LEDs and image processing, then disabling the camera with a laser. The system works by identifying cameras using their CCD sensor properties when exposed to light. Images are processed to locate cameras then a laser is aimed at the camera lens to overexpose the image sensor. The document outlines the system components, working, safety measures and potential for future development.