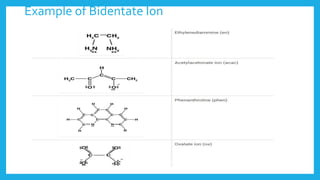
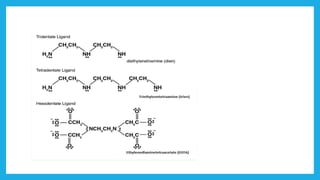
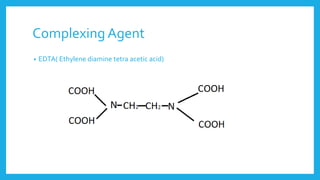
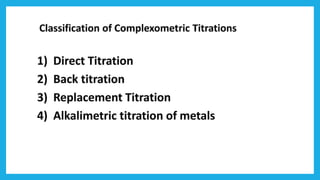
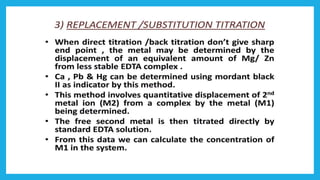
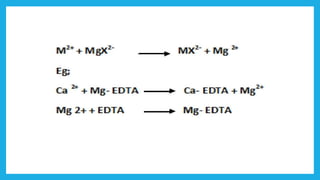
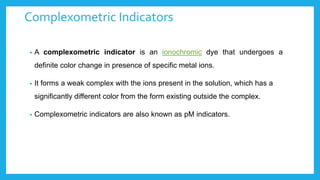
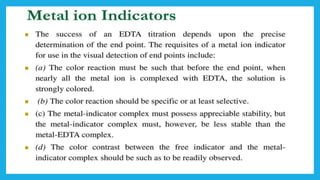
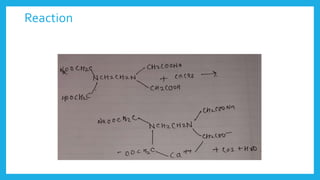
Complexometric titration involves using a ligand such as EDTA that forms stable complexes with metal ions to determine the endpoint of a titration. EDTA is commonly used as the titrant because it forms strong complexes with many metal ions. Complexometric indicators that undergo a color change are used to detect the endpoint when the metal ion is completely bound by EDTA. Common applications include assays to determine the concentration of metal ions like magnesium, calcium, and aluminum in samples.