This document provides an overview of high performance thin layer chromatography (HPTLC). It describes the principles, methodology, and applications of HPTLC. Some key points include:
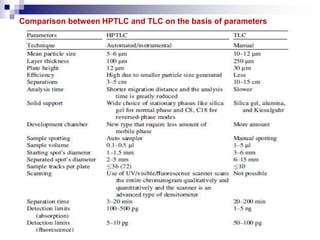
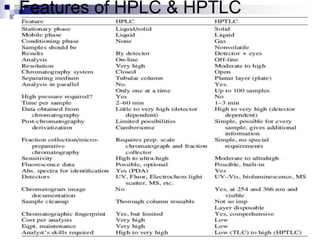
- HPTLC is an improved version of thin layer chromatography (TLC) that allows for more optimized separation of analytes.
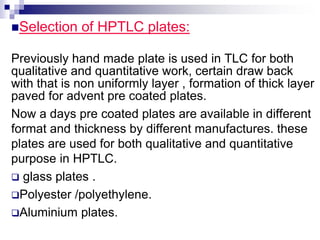
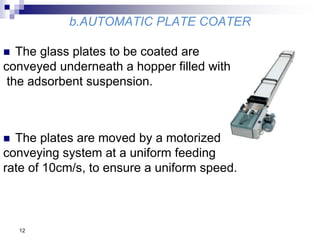
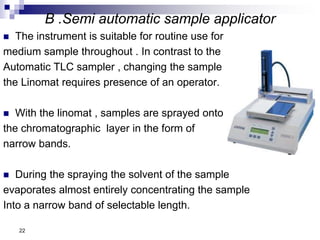
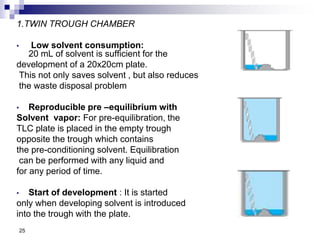
- Samples are applied to HPTLC plates manually or automatically and developed in a chamber using a mobile phase solvent.
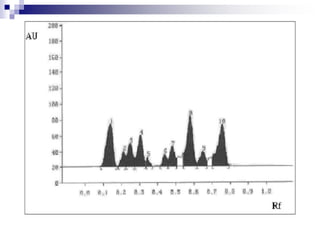
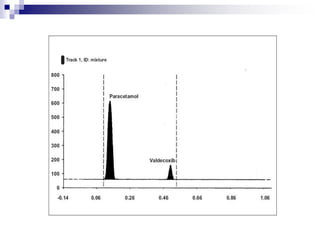
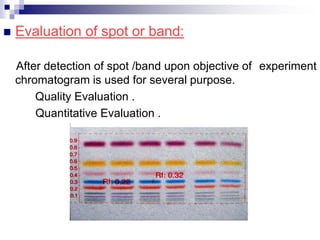
- Separated components are detected visually or using a densitometer, and may require derivatization for improved detection.
- HPTLC is used in pharmaceutical analysis, clinical testing, food testing, and other applications due to its high resolution, sensitivity, accuracy and reproducibility.



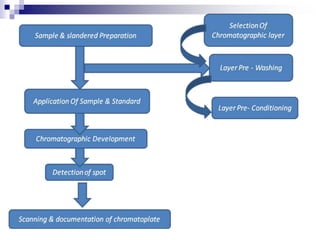
![ Principle:
HPTLC take place in high speed capillary flow range of
the mobile phase, There are three main step in HPTLC
1] sample to analyzed to chromatogram layer volume
precision and suitable position are achieved by use of
suitable instrument.
2] solvent (mobile phase) migrates the planned distance in
layer (stationary) by capillary action in this process sample
separated in its components.
3] separation tracks are scanned in densitometer with light
beam in visible or uv region](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hptlc-231209120716-7065267d/85/HIGH-PERFORMANCE-THIN-LAYER-CHROMATOGRAPHY-5-320.jpg)