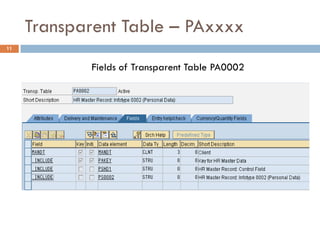
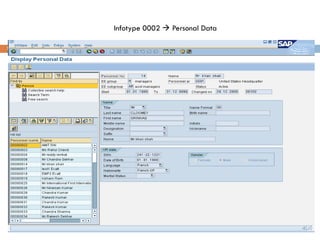
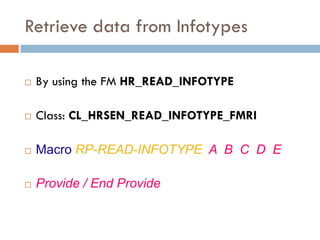
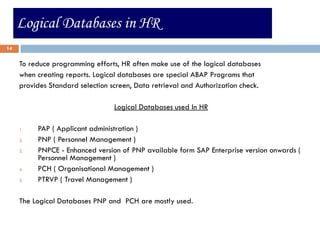
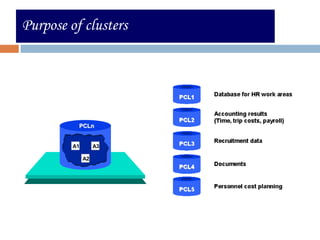
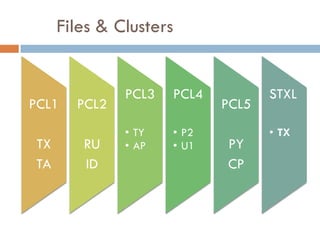
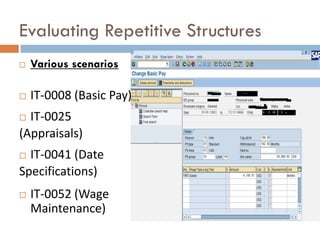
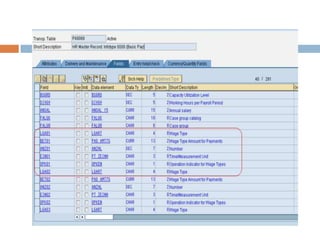
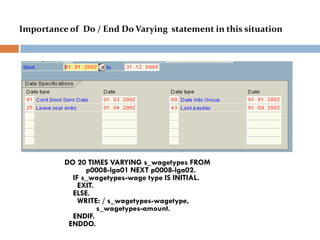
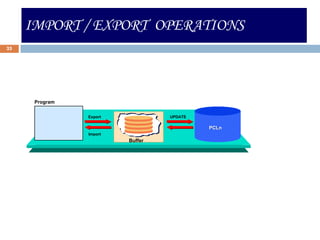
This document compares ABAP and ABAP-HR programming. It introduces basic HR concepts like infotypes and clusters. It then discusses key aspects of ABAP-HR like using logical databases, macros, import/export statements, and repetitive structures. Special ABAP statements for HR like DO/ENDDO VARYING and PROVIDE/ENDPROVIDE are also covered. The document aims to help recap basic ABAP and highlight features specific to ABAP-HR programming.