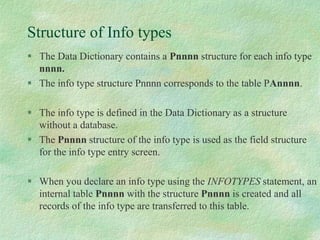
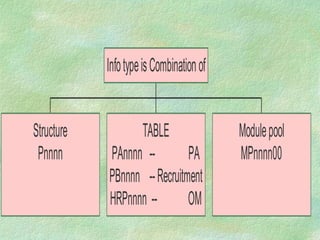
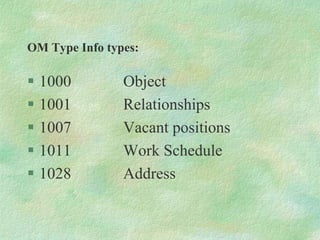
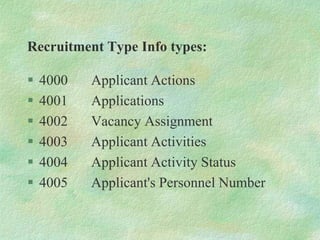
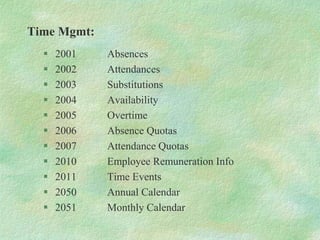
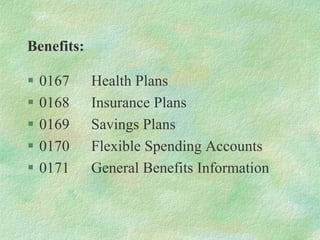
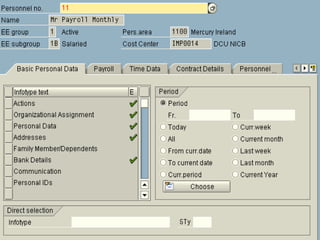
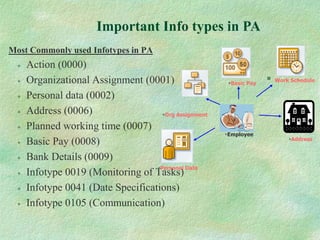
The document discusses SAP HR modules and ABAP HR. It provides an overview of HR-ABAP and the differences between ABAP and ABAP HR. Key aspects covered include info types, their structure and common info types. It describes the three time constraints and provides examples. Personnel Administration is discussed as the central repository for employee data that integrates with other HR modules. Steps for creating a custom info type and enhancements are also summarized.