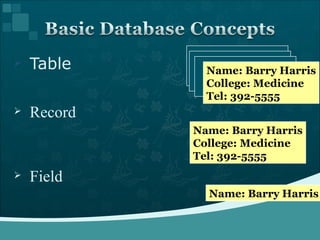
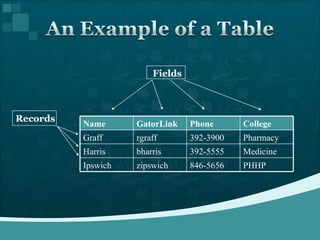
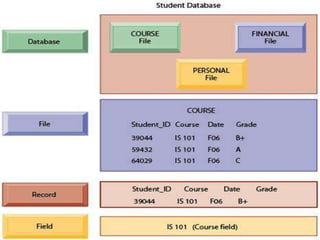
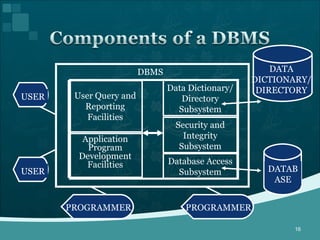
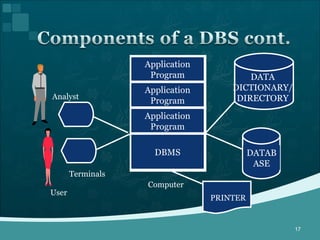
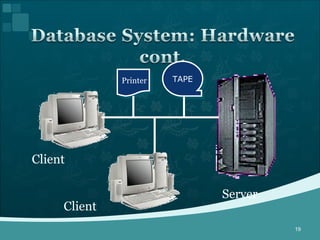
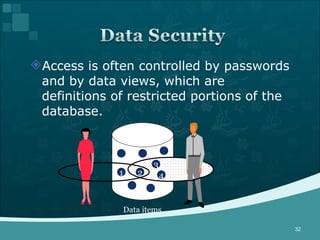
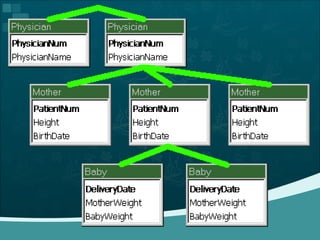
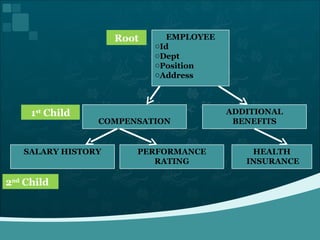
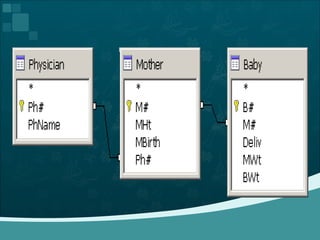
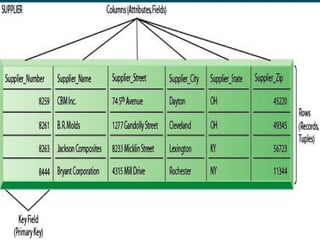
Database management systems (DBMS) help organize data across departments to provide timely, accurate information for better decision-making. A DBMS includes database software, users, and practitioners who design database structures and applications. It defines data through a data dictionary for clear understanding and prevents errors. A DBMS also secures data and maintains integrity through backup and recovery.