Nervous System- Comparative account of Brain.pdf
•
0 likes•1,023 views
The document discusses the comparative anatomy of brains across vertebrates. It notes that all vertebrate brains share a common underlying form and early development, with three initial swellings that become the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. Across classes like fish, amphibians, and mammals, the relative sizes of these parts change. In mammals, the forebrain grows much larger and dominates. The functions of different brain regions are also described. The development of brain vesicles and flexures is outlined. Finally, features of the brain in different vertebrates like sharks, frogs, lizards, pigeons, and rabbits are compared.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
Comparision of brain in vertebrates

The vertebrate brain
The vertebrate brain is the main part of the central nervous system. The brain and the spinal cord make up the central nervous system,
In most of the vertebrates the brain is at the front, in the head. It is protected by the skull and close to the main sense organs.
Brains are extremely complex and the part of human and animal body. The brain controls the other organs of the body, either by activating muscles or by causing secretion of chemicals such as hormones and neurotransmitters.
Muscular action allows rapid and coordinated responses to changes in the environment.
The brain of an adult human weights about 1300–1400 grams .
In vertebrates, the spinal cord by itself can cause reflex responses as well as simple movement such as swimming or walking. However, sophisticated control of behaviour requires a centralized brain.
The structure of all vertebrate brains is basically the same.
At the same time, during the course of evolution, the vertebrate brain has undergone changes, and become more effective.
In so-called 'lower' animals, most or all of the brain structure is inherited, and therefore their behaviour is mostly instinctive.
In mammals, and especially in man, the brain is developed further during life by learning. This has the benefit of helping them fit better into their environment. The capacity to learn is seen best in the cerebral cortex.
Three principles
The brain and nervous system is essentially a system which makes connections. It has input from sense organs and output to muscles. It is connected in several ways with the endocrine system, which makes hormones, and the digestive system and sex system. Hormones work slowly, so those changes are gradual.
The brain is a kind of department store. It has, all inter-connected, departments which do different things. They all help each other gather senses.
Much of what the body does is not conscious. Basically, much of the body runs on automatic (breathing, heart beat, hungry, hair growth) adjusted by the autonomic nervous system. The brain, too, does much of its work without a person noticing it. The unconscious mind refers to the brain activities which are hardly ever noticed.
Accessory Respiratory organs in Fishes.pptx

The document discusses accessory respiratory organs in fishes. It describes 7 types of accessory respiratory organs that have developed in some fish species to help them breathe in low oxygen environments. These include the skin, bucco-pharyngeal epithelium, gut epithelium, outgrowths of pelvic fins, and modified gill structures. Examples are given of important modifications seen in the accessory respiratory organs of species like Heteropneustes fossilis, Anabas testudineus, and Clarias batrachus. The swim bladder acts as an accessory respiratory organ in some primitive fish species. Accessory organs allow fish to live in low oxygen water and breathe air when available, and their development is an adaptive response
Parental care in fishes By TANZEEBA AMIN

Parental care is an important behavior for perpetuating fish species. Many fish species care for their eggs and young in various ways. Some fish build different types of nests, such as circular, basin-shaped, or barrel-shaped nests to lay and care for eggs. Other fish deposit eggs in suitable locations or carry them in their mouths or pouches. Some fish are viviparous. Parental care benefits offspring survival but increases costs to parents. There is great diversity in parental care strategies among fish species.
Aortic arches in vertebrates

Vertebrates generally have a ventral aorta and dorsal aorta, with six pairs of aortic arches that branch off and pass through gill arches. In fishes, the six pairs of arches each pass blood through the gills. Over time, some arches reduce or disappear, with sharks having five pairs and most fish having four functional pairs. In land vertebrates like reptiles, amphibians, birds and mammals, the number of arches reduces further to three pairs or less as lungs replace gills and the circulatory system evolves to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
Heart in vetrebrates

Evolutionary change in heart of vertebrates
Heart is situated ventral to the oseophagus in the pericardial section of the coelom.
Heart is a highly muscular pumping organ that pumps blood into arteries and sucks it back through the veins.
In vertebrates it has undergone transformation by twisting from a straight tube to a complex multi-chambered organ.
. There has been an increase in the number of chambers in heart during evolution of vertebrates.
The heart is covered by a transparent protective covering, called pericardium. It is a single layer in fish.
Within pericardium there is a pericardial fluid, protects the heart from the external injury.
The evolution of the heart is based on the separation of oxygenated blood from deoxygenated blood for efficient oxygen transport.
Aortic arches

The basic fundamental plan of the aortic arches is similar in different vertebrates during embryonic stages.
But in adult the condition of the arrangement is changed either being lost or modified considerably.
The number of aortic arches is gradually reduced as the scale of evolution of vertebrates is ascended.
The embryonic aortic arches were basically six pairs.
But with progressive evolution , there has been consequent reduction in numbers of aortic arches.
In the basic pattern the major arterial channels consists of
A ventral aorta emerging from the heart and passing forward beneath the pharynx
A dorsal aorta paired above the pharynx and passing caudal above the digestive tract.
Six pairs of aortic arches connecting ventral aorta to with the dorsal aorta.
1st aortic arch= Mandibular aortic arch
2nd Aortic arch= hyoid aortic arch
3rd ,4th ,5th and 6th aortic arches in case of aquatic animal , known as branchial aortic arches.
Evolution of Heart

The primitive blueprint for the heart and circulatory system emerged with the arrival of the third mesodermal germ layer in bilaterians. Since then, hearts in animals have evolved from a single layered tube to a multiple chambered heart in due course of time.
succession of kidneys in a vertebrate series

1. Kidneys evolve from the primitive archinephros to the pronephros, mesonephros, and finally the metanephros, which is the definitive kidney of amniotes.
2. The pronephros is the first to develop and is functional only in embryonic or larval stages. The mesonephros follows and is functional in embryos and adults of some species.
3. The metanephros is the adult kidney of amniotes and shows greater complexity with millions of nephrons and additional structures like loops of Henle in mammals.
Recommended
Comparision of brain in vertebrates

The vertebrate brain
The vertebrate brain is the main part of the central nervous system. The brain and the spinal cord make up the central nervous system,
In most of the vertebrates the brain is at the front, in the head. It is protected by the skull and close to the main sense organs.
Brains are extremely complex and the part of human and animal body. The brain controls the other organs of the body, either by activating muscles or by causing secretion of chemicals such as hormones and neurotransmitters.
Muscular action allows rapid and coordinated responses to changes in the environment.
The brain of an adult human weights about 1300–1400 grams .
In vertebrates, the spinal cord by itself can cause reflex responses as well as simple movement such as swimming or walking. However, sophisticated control of behaviour requires a centralized brain.
The structure of all vertebrate brains is basically the same.
At the same time, during the course of evolution, the vertebrate brain has undergone changes, and become more effective.
In so-called 'lower' animals, most or all of the brain structure is inherited, and therefore their behaviour is mostly instinctive.
In mammals, and especially in man, the brain is developed further during life by learning. This has the benefit of helping them fit better into their environment. The capacity to learn is seen best in the cerebral cortex.
Three principles
The brain and nervous system is essentially a system which makes connections. It has input from sense organs and output to muscles. It is connected in several ways with the endocrine system, which makes hormones, and the digestive system and sex system. Hormones work slowly, so those changes are gradual.
The brain is a kind of department store. It has, all inter-connected, departments which do different things. They all help each other gather senses.
Much of what the body does is not conscious. Basically, much of the body runs on automatic (breathing, heart beat, hungry, hair growth) adjusted by the autonomic nervous system. The brain, too, does much of its work without a person noticing it. The unconscious mind refers to the brain activities which are hardly ever noticed.
Accessory Respiratory organs in Fishes.pptx

The document discusses accessory respiratory organs in fishes. It describes 7 types of accessory respiratory organs that have developed in some fish species to help them breathe in low oxygen environments. These include the skin, bucco-pharyngeal epithelium, gut epithelium, outgrowths of pelvic fins, and modified gill structures. Examples are given of important modifications seen in the accessory respiratory organs of species like Heteropneustes fossilis, Anabas testudineus, and Clarias batrachus. The swim bladder acts as an accessory respiratory organ in some primitive fish species. Accessory organs allow fish to live in low oxygen water and breathe air when available, and their development is an adaptive response
Parental care in fishes By TANZEEBA AMIN

Parental care is an important behavior for perpetuating fish species. Many fish species care for their eggs and young in various ways. Some fish build different types of nests, such as circular, basin-shaped, or barrel-shaped nests to lay and care for eggs. Other fish deposit eggs in suitable locations or carry them in their mouths or pouches. Some fish are viviparous. Parental care benefits offspring survival but increases costs to parents. There is great diversity in parental care strategies among fish species.
Aortic arches in vertebrates

Vertebrates generally have a ventral aorta and dorsal aorta, with six pairs of aortic arches that branch off and pass through gill arches. In fishes, the six pairs of arches each pass blood through the gills. Over time, some arches reduce or disappear, with sharks having five pairs and most fish having four functional pairs. In land vertebrates like reptiles, amphibians, birds and mammals, the number of arches reduces further to three pairs or less as lungs replace gills and the circulatory system evolves to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
Heart in vetrebrates

Evolutionary change in heart of vertebrates
Heart is situated ventral to the oseophagus in the pericardial section of the coelom.
Heart is a highly muscular pumping organ that pumps blood into arteries and sucks it back through the veins.
In vertebrates it has undergone transformation by twisting from a straight tube to a complex multi-chambered organ.
. There has been an increase in the number of chambers in heart during evolution of vertebrates.
The heart is covered by a transparent protective covering, called pericardium. It is a single layer in fish.
Within pericardium there is a pericardial fluid, protects the heart from the external injury.
The evolution of the heart is based on the separation of oxygenated blood from deoxygenated blood for efficient oxygen transport.
Aortic arches

The basic fundamental plan of the aortic arches is similar in different vertebrates during embryonic stages.
But in adult the condition of the arrangement is changed either being lost or modified considerably.
The number of aortic arches is gradually reduced as the scale of evolution of vertebrates is ascended.
The embryonic aortic arches were basically six pairs.
But with progressive evolution , there has been consequent reduction in numbers of aortic arches.
In the basic pattern the major arterial channels consists of
A ventral aorta emerging from the heart and passing forward beneath the pharynx
A dorsal aorta paired above the pharynx and passing caudal above the digestive tract.
Six pairs of aortic arches connecting ventral aorta to with the dorsal aorta.
1st aortic arch= Mandibular aortic arch
2nd Aortic arch= hyoid aortic arch
3rd ,4th ,5th and 6th aortic arches in case of aquatic animal , known as branchial aortic arches.
Evolution of Heart

The primitive blueprint for the heart and circulatory system emerged with the arrival of the third mesodermal germ layer in bilaterians. Since then, hearts in animals have evolved from a single layered tube to a multiple chambered heart in due course of time.
succession of kidneys in a vertebrate series

1. Kidneys evolve from the primitive archinephros to the pronephros, mesonephros, and finally the metanephros, which is the definitive kidney of amniotes.
2. The pronephros is the first to develop and is functional only in embryonic or larval stages. The mesonephros follows and is functional in embryos and adults of some species.
3. The metanephros is the adult kidney of amniotes and shows greater complexity with millions of nephrons and additional structures like loops of Henle in mammals.
URINOGENITAL SYSTEM

The urinogenital system includes the urinary and reproductive systems of vertebrates. The urinary system includes kidneys and ducts, while the reproductive system includes gonads and ducts. These two systems are closely related in vertebrates. The kidneys develop from the pronephros, mesonephros and metanephros in embryos. The metanephros contains nephrons, the functional units of vertebrate kidneys. Male gonads are testes that produce sperm, while female gonads are ovaries that produce eggs. Sperm and eggs meet during reproduction and are exchanged via various genital ducts and organs between males and females.
Comparative anatomy of aortic arches

The document discusses the development and modifications of aortic arches across vertebrates. In early embryos, most vertebrates develop 6 pairs of aortic arches that connect the dorsal aorta to the ventral aorta and carry blood to the gills. Over evolution, there is a reduction in arches as respiration moves from gills to lungs. By adulthood, mammals and birds typically have 3 pairs of arches - the third becomes the carotid artery, fourth becomes systemic arteries, and sixth becomes pulmonary arteries.
Malphigian tubules

Malphigian tubules are excretory organs found in insects like cockroaches and crabs. They are located between the foregut and hindgut and excrete waste in the form of uric acid while also helping with osmoregulation. The tubules have a fine, sometimes coiled tubular structure consisting of three regions - a distal region that is small and contractile, a middle region that is the largest and contains two cell types, and a proximal region that drains pre-urine to the hindgut.
Accessory respiratory organ in fishes

Anand. P.P MSc Applied Zoology Calicut University,Kerala .
this works more useful in degree science students.
Integument of vertebrates

The document discusses the integumentary system across different chordate groups. It describes the key features of skin in protochordates, cyclostomes, fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. The integumentary system generally consists of an outer epidermis layer and inner dermis layer, with variations in features like keratinization, glands, scales/feathers/hair, and pigment cells across groups. The skin serves protective, sensory, and excretory functions for chordates.
Neoteny

This document discusses the differences between neoteny and paedogenesis. Neoteny involves slowed somatic growth such that organisms remain in juvenile stages, while paedogenesis involves accelerated sexual maturity even as larvae. Neoteny can be seen in humans while paedogenesis is found in amphibians like salamanders. There are two types of neoteny - total neoteny where larvae become sexually mature but retain larval features, and partial neoteny which involves a postponed metamorphosis beyond normal periods due to environmental or physiological factors. Neoteny is viewed as an adaptive consequence of retaining larval features that may be advantageous in certain environments.
Urino genitial system of vertebrates

The document discusses the urinogenital system in vertebrates. It begins by defining the urinogenital system and its components, which include the kidneys, urinary ducts, gonads, and genital ducts. It then describes the evolution and development of the kidney structures in vertebrates, from the primitive pronephros to the more advanced metanephros. Key points include that the kidney evolves from the intermediate mesoderm and progresses through pronephric, mesonephric, and metanephric stages. The metanephros is the definitive kidney structure in amniotes. The document also discusses kidney structure and blood supply in different vertebrate groups.
Olfactory and gustatory receptors

The document discusses chemoreceptors, which include taste receptors and olfactory receptors. Taste and smell rely on chemical receptors being stimulated by certain molecules. Humans can taste sweet, sour, bitter, salty, and umami; taste and smell are directly related because they use the same types of receptors. Olfactory receptors are located in the nose, while taste receptors are located in the tongue and oral cavity. Both system detect chemicals and transmit signals to the brain.
Brain of vertebrates

The document summarizes the development and comparative anatomy of the vertebrate brain. It describes how the embryonic brain divides into three primary vesicles - the prosencephalon, mesencephalon, and rhombencephalon. It then discusses the specific structures that develop from each of these regions across different vertebrate groups, including differences in brain structure between cyclostomes, fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. Key differences include the size of regions like the cerebrum, cerebellum, and olfactory bulbs across the groups.
Origin of chordata

ORIGIN OF CHORDATES
Animal kingdom is basically divided into two sub kingdoms:
Non-chordata- including animals without notochord.
Chordata- This comprising animals having notochord or chorda dorsalis.
Chordates were evolved sometime 500 million years ago during Cambrian period (invertebrates were also began to evolve in this period) .
Chamberlain (1900) pointed out that all modern chordates possess glomerular kidneys that are designed to remove excess water from body.
It is believed that Chordates have originated from invertebrates.
It is difficult to determine from which invertebrate group the chordates were developed.
Chordate ancestors were soft bodied animals. Hence they were not preserved as Fossils.
However, early fossils of chordates have all been recovered from marine sediments and even modern protochordates are all marine forms.
Also glomerular kidneys are also found in some marine forms such as myxinoids and sharks. That makes the marine origin of chordates more believable.
Chordates evolved from some deuterostome ancestor (echinoderms, hemichordates, pogonophorans etc.) as they have similarities in embryonic development, type of coelom and larval stages.
Many theories infers origin of chordates, hemichordates and echinoderms from a common ancestor.
Jaw suspension in vertebrates [autosaved]![Jaw suspension in vertebrates [autosaved]](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![Jaw suspension in vertebrates [autosaved]](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
INTRODUCTION
The jaw (Upper and lower) is any opposable articulated structure at the entrance of the mouth.
It is typically used for grasping and manipulating food.
Jaw suspension means the fusion of upper jaw and lower jaw or skull for efficient biting.
There are different ways in which these attachments are attained depending upon the modifications in visceral arches in vertebrates.
In most vertebrates, the jaws are bony or cartilaginous and oppose vertically.
The vertebrate jaw is derived from the most anterior two pharyngeal arches supporting the gills, and usually bears numerous teeth.
The vertebrate jaw probably originally evolved in the Silurian period and appeared in the Placoderm fish which further diversified in the Devonian.
It is believed that the hyoid system suspends the jaw from the brain case of the skull, permitting great mobility of the jaws.
The original selective advantage offered by the jaw may not be related to feeding, but rather to increased respiration efficiency.
The jaws were used in the buccal pump (observable in modern fish and amphibians) that pumps water across the gills of fish or air into the lungs in the case of amphibians.
Over evolutionary time the more familiar use of jaws (to humans), in feeding, was selected for and became a very important function in vertebrates. Many teleost fish have substantially modified jaws for suction feeding and jaw protrusion, resulting in highly complex jaws with dozens of bones involved.
Jaw Suspension or Suspensoria:
The method by which the upper and lower jaws are suspended or attached from the chondrocranium is known as jaw suspension or suspensorium.
Amongst the visceral arches, the first (mandibular) arch consists of
= a dorsal palato pterygoquadrate bar forming the upper jaw,
= and ventral Meckel’s cartilage forms the lower jaw.
The second (hyoid) arch consists of = a dorsal hyomandibular supporting and suspending the jaws with the cranium, and a ventral hyoid.
The remaining visceral arches support the gills and are, hence, called branchial arches. Thus, splanchnocranium forms the jaws and suspends them with the chondrocranium.
Receptor organs in vertebrates

Sense organs are the specialized organs composed of sensory neurons, which help us to perceive and respond to our surroundings. There are five sense organs – eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and skin.
External receptors (exteroceptors): sense organs for touch, smell, taste, sight and hearing.
Internal receptors (interocepyors): these sense organs found in the body which detect the temperature, pain, hunger, thirst, fatigue and muscle position.
Comparative anatomy of heart structure

1. All chordates have a circulatory system with blood and lymph traveling through separate yet interconnected vessels.
2. In vertebrates the blood vascular system is closed, with a contractile heart and continuous vessels. The heart pumps oxygenated blood from the veins into the arteries.
3. Over the course of evolution, the structure of the heart has become more complex and compartmentalized. In early vertebrates like sharks the heart had two chambers, while in advanced mammals it is a four-chambered heart that fully separates pulmonary and systemic circulation.
Electric organs in fishes 1

Electric organs are found in about 250 species of fish and are composed of electroplates, which are stacks of electrocytes that discharge electricity. The organs vary in voltage output between species from 4-550 volts and serve functions like catching prey, defense, communication, and territory maintenance. Electric organs are thought to have evolved from muscle tissue, with different fish lineages co-opting different muscle groups for electrocyte differentiation during development.
Social organization and social behaviour in insects

Introduction
Properties of a society
Advantages of a society
Disadvantages of a society
Social organisation and social behaviour in insects:-
1. Termites
2.Honeybees
3.Ants
4.Yellow wasp
Vertebrate respiratory system

Dr. P.B.Reddy provides an overview of the comparative anatomy of the vertebrate respiratory system. The document discusses why animals need to breathe and defines internal and external respiration. It then describes the key characteristics and functions of respiratory organs across different vertebrate groups, including fish, amphibians, reptiles and others. Specific structures are examined such as gills, lungs and the mechanisms of gas exchange that occur.
Comparative pro,mete,& eutheria, features of prototheria to eutheria,& af...

Comparative pro,mete,& eutheria, features of prototheria to eutheria,& affinity to pro,meta &eutheria
Peripheral and autonomic nervous system of vertebrates

Central nervous system: The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. The brain plays a central role in the control of most bodily functions, including awareness, movements, sensations, thoughts, speech, and memory. Some reflex movements can occur via spinal cord pathways without the participation of brain structures. The spinal cord is connected to a section of the brain called the brainstem and runs through the spinal canal.
Peripheral Nervous System: Nerve fibers that exit the brainstem and spinal cord become part of the peripheral nervous system. Cranial nerves exit the brainstem and function as peripheral nervous system mediators of many functions, including eye movements, facial strength and sensation, hearing, and taste.
The autonomic nervous system: The autonomic nervous system is a control system that acts largely unconsciously and regulates bodily functions, such as the heart rate, digestion, respiratory rate, pupillary response, urination, and sexual arousal. This system is the primary mechanism in control of the fight-or-flight response.
The autonomic nervous system comprises two antagonistic sets of nerves, the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The hypothalamus is the key brain site for central control of the autonomic nervous system, and the paraventricular nucleus is the key hypothalamic site for this control.
Divisions of Nervous System:
The vertebrate nervous system has three divisions:
(i) A central nervous system comprising the brain and spinal cord. Its function is to receive the stimulus from the receptors and transmit its response to the effectors. Thus, it coordinates all the functions of the body.
(ii) A peripheral nervous system consisting of cranial and spinal nerves arising from the brain and spinal cord respectively. It forms a connecting link between the receptors, central nervous system (CNS) and effectors.
(iii) An autonomic nervous system made of two ganglionated sympathetic nerves, ganglia in the head and viscera, and their connecting nerves. The autonomic nervous system is often regarded as a part of the peripheral nervous system because the two are connected. But all the three divisions of the nervous system are connected intimately both structurally and functionally.
Primate social organization

Primate social organizations can generally be categorized into two types: 1) solitary foragers or dispersed polygyny where females forage alone and males monopolize access to females, and 2) where females forage together in female-bonded groups that are larger and contain multiple males. Group structures range from one-male harems to multi-male/multi-female groups. The type of social structure adopted depends on factors like the nature of resources and how defendable or monopolizable they are.
Comparative account of axial and appendicular skeleton of amniots

Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy ... Appendicular Skeleton. Appendicular skeleton ... 5 - Tetrapods - tendency for reduction in number of dermal bones ... distal row = 5 distal carplas numbered 1 through 5 (starting on thumb, or radial, side).
Nervous systems in vertebrates: T.Y.B.Sc. Sem VI Notes

Nervous systems in vertebrates: T.Y.B.Sc. Sem VI NotesDr. Sudesh D. Rathod, B N Bandodkar College of Science
The document discusses the development and differentiation of the brain in vertebrates. It begins by explaining how the neural tube develops and differentiates into three primary brain vesicles - the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. These later develop into five vesicles. It then describes the relationships between the early brain structures and the mature nervous system. The document also discusses the flexures of the brain, the evolution of the cerebral hemispheres and cerebellum across different vertebrates, and provides a comparative overview of brain anatomy in key vertebrate groups.More Related Content
What's hot
URINOGENITAL SYSTEM

The urinogenital system includes the urinary and reproductive systems of vertebrates. The urinary system includes kidneys and ducts, while the reproductive system includes gonads and ducts. These two systems are closely related in vertebrates. The kidneys develop from the pronephros, mesonephros and metanephros in embryos. The metanephros contains nephrons, the functional units of vertebrate kidneys. Male gonads are testes that produce sperm, while female gonads are ovaries that produce eggs. Sperm and eggs meet during reproduction and are exchanged via various genital ducts and organs between males and females.
Comparative anatomy of aortic arches

The document discusses the development and modifications of aortic arches across vertebrates. In early embryos, most vertebrates develop 6 pairs of aortic arches that connect the dorsal aorta to the ventral aorta and carry blood to the gills. Over evolution, there is a reduction in arches as respiration moves from gills to lungs. By adulthood, mammals and birds typically have 3 pairs of arches - the third becomes the carotid artery, fourth becomes systemic arteries, and sixth becomes pulmonary arteries.
Malphigian tubules

Malphigian tubules are excretory organs found in insects like cockroaches and crabs. They are located between the foregut and hindgut and excrete waste in the form of uric acid while also helping with osmoregulation. The tubules have a fine, sometimes coiled tubular structure consisting of three regions - a distal region that is small and contractile, a middle region that is the largest and contains two cell types, and a proximal region that drains pre-urine to the hindgut.
Accessory respiratory organ in fishes

Anand. P.P MSc Applied Zoology Calicut University,Kerala .
this works more useful in degree science students.
Integument of vertebrates

The document discusses the integumentary system across different chordate groups. It describes the key features of skin in protochordates, cyclostomes, fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. The integumentary system generally consists of an outer epidermis layer and inner dermis layer, with variations in features like keratinization, glands, scales/feathers/hair, and pigment cells across groups. The skin serves protective, sensory, and excretory functions for chordates.
Neoteny

This document discusses the differences between neoteny and paedogenesis. Neoteny involves slowed somatic growth such that organisms remain in juvenile stages, while paedogenesis involves accelerated sexual maturity even as larvae. Neoteny can be seen in humans while paedogenesis is found in amphibians like salamanders. There are two types of neoteny - total neoteny where larvae become sexually mature but retain larval features, and partial neoteny which involves a postponed metamorphosis beyond normal periods due to environmental or physiological factors. Neoteny is viewed as an adaptive consequence of retaining larval features that may be advantageous in certain environments.
Urino genitial system of vertebrates

The document discusses the urinogenital system in vertebrates. It begins by defining the urinogenital system and its components, which include the kidneys, urinary ducts, gonads, and genital ducts. It then describes the evolution and development of the kidney structures in vertebrates, from the primitive pronephros to the more advanced metanephros. Key points include that the kidney evolves from the intermediate mesoderm and progresses through pronephric, mesonephric, and metanephric stages. The metanephros is the definitive kidney structure in amniotes. The document also discusses kidney structure and blood supply in different vertebrate groups.
Olfactory and gustatory receptors

The document discusses chemoreceptors, which include taste receptors and olfactory receptors. Taste and smell rely on chemical receptors being stimulated by certain molecules. Humans can taste sweet, sour, bitter, salty, and umami; taste and smell are directly related because they use the same types of receptors. Olfactory receptors are located in the nose, while taste receptors are located in the tongue and oral cavity. Both system detect chemicals and transmit signals to the brain.
Brain of vertebrates

The document summarizes the development and comparative anatomy of the vertebrate brain. It describes how the embryonic brain divides into three primary vesicles - the prosencephalon, mesencephalon, and rhombencephalon. It then discusses the specific structures that develop from each of these regions across different vertebrate groups, including differences in brain structure between cyclostomes, fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. Key differences include the size of regions like the cerebrum, cerebellum, and olfactory bulbs across the groups.
Origin of chordata

ORIGIN OF CHORDATES
Animal kingdom is basically divided into two sub kingdoms:
Non-chordata- including animals without notochord.
Chordata- This comprising animals having notochord or chorda dorsalis.
Chordates were evolved sometime 500 million years ago during Cambrian period (invertebrates were also began to evolve in this period) .
Chamberlain (1900) pointed out that all modern chordates possess glomerular kidneys that are designed to remove excess water from body.
It is believed that Chordates have originated from invertebrates.
It is difficult to determine from which invertebrate group the chordates were developed.
Chordate ancestors were soft bodied animals. Hence they were not preserved as Fossils.
However, early fossils of chordates have all been recovered from marine sediments and even modern protochordates are all marine forms.
Also glomerular kidneys are also found in some marine forms such as myxinoids and sharks. That makes the marine origin of chordates more believable.
Chordates evolved from some deuterostome ancestor (echinoderms, hemichordates, pogonophorans etc.) as they have similarities in embryonic development, type of coelom and larval stages.
Many theories infers origin of chordates, hemichordates and echinoderms from a common ancestor.
Jaw suspension in vertebrates [autosaved]![Jaw suspension in vertebrates [autosaved]](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![Jaw suspension in vertebrates [autosaved]](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
INTRODUCTION
The jaw (Upper and lower) is any opposable articulated structure at the entrance of the mouth.
It is typically used for grasping and manipulating food.
Jaw suspension means the fusion of upper jaw and lower jaw or skull for efficient biting.
There are different ways in which these attachments are attained depending upon the modifications in visceral arches in vertebrates.
In most vertebrates, the jaws are bony or cartilaginous and oppose vertically.
The vertebrate jaw is derived from the most anterior two pharyngeal arches supporting the gills, and usually bears numerous teeth.
The vertebrate jaw probably originally evolved in the Silurian period and appeared in the Placoderm fish which further diversified in the Devonian.
It is believed that the hyoid system suspends the jaw from the brain case of the skull, permitting great mobility of the jaws.
The original selective advantage offered by the jaw may not be related to feeding, but rather to increased respiration efficiency.
The jaws were used in the buccal pump (observable in modern fish and amphibians) that pumps water across the gills of fish or air into the lungs in the case of amphibians.
Over evolutionary time the more familiar use of jaws (to humans), in feeding, was selected for and became a very important function in vertebrates. Many teleost fish have substantially modified jaws for suction feeding and jaw protrusion, resulting in highly complex jaws with dozens of bones involved.
Jaw Suspension or Suspensoria:
The method by which the upper and lower jaws are suspended or attached from the chondrocranium is known as jaw suspension or suspensorium.
Amongst the visceral arches, the first (mandibular) arch consists of
= a dorsal palato pterygoquadrate bar forming the upper jaw,
= and ventral Meckel’s cartilage forms the lower jaw.
The second (hyoid) arch consists of = a dorsal hyomandibular supporting and suspending the jaws with the cranium, and a ventral hyoid.
The remaining visceral arches support the gills and are, hence, called branchial arches. Thus, splanchnocranium forms the jaws and suspends them with the chondrocranium.
Receptor organs in vertebrates

Sense organs are the specialized organs composed of sensory neurons, which help us to perceive and respond to our surroundings. There are five sense organs – eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and skin.
External receptors (exteroceptors): sense organs for touch, smell, taste, sight and hearing.
Internal receptors (interocepyors): these sense organs found in the body which detect the temperature, pain, hunger, thirst, fatigue and muscle position.
Comparative anatomy of heart structure

1. All chordates have a circulatory system with blood and lymph traveling through separate yet interconnected vessels.
2. In vertebrates the blood vascular system is closed, with a contractile heart and continuous vessels. The heart pumps oxygenated blood from the veins into the arteries.
3. Over the course of evolution, the structure of the heart has become more complex and compartmentalized. In early vertebrates like sharks the heart had two chambers, while in advanced mammals it is a four-chambered heart that fully separates pulmonary and systemic circulation.
Electric organs in fishes 1

Electric organs are found in about 250 species of fish and are composed of electroplates, which are stacks of electrocytes that discharge electricity. The organs vary in voltage output between species from 4-550 volts and serve functions like catching prey, defense, communication, and territory maintenance. Electric organs are thought to have evolved from muscle tissue, with different fish lineages co-opting different muscle groups for electrocyte differentiation during development.
Social organization and social behaviour in insects

Introduction
Properties of a society
Advantages of a society
Disadvantages of a society
Social organisation and social behaviour in insects:-
1. Termites
2.Honeybees
3.Ants
4.Yellow wasp
Vertebrate respiratory system

Dr. P.B.Reddy provides an overview of the comparative anatomy of the vertebrate respiratory system. The document discusses why animals need to breathe and defines internal and external respiration. It then describes the key characteristics and functions of respiratory organs across different vertebrate groups, including fish, amphibians, reptiles and others. Specific structures are examined such as gills, lungs and the mechanisms of gas exchange that occur.
Comparative pro,mete,& eutheria, features of prototheria to eutheria,& af...

Comparative pro,mete,& eutheria, features of prototheria to eutheria,& affinity to pro,meta &eutheria
Peripheral and autonomic nervous system of vertebrates

Central nervous system: The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. The brain plays a central role in the control of most bodily functions, including awareness, movements, sensations, thoughts, speech, and memory. Some reflex movements can occur via spinal cord pathways without the participation of brain structures. The spinal cord is connected to a section of the brain called the brainstem and runs through the spinal canal.
Peripheral Nervous System: Nerve fibers that exit the brainstem and spinal cord become part of the peripheral nervous system. Cranial nerves exit the brainstem and function as peripheral nervous system mediators of many functions, including eye movements, facial strength and sensation, hearing, and taste.
The autonomic nervous system: The autonomic nervous system is a control system that acts largely unconsciously and regulates bodily functions, such as the heart rate, digestion, respiratory rate, pupillary response, urination, and sexual arousal. This system is the primary mechanism in control of the fight-or-flight response.
The autonomic nervous system comprises two antagonistic sets of nerves, the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The hypothalamus is the key brain site for central control of the autonomic nervous system, and the paraventricular nucleus is the key hypothalamic site for this control.
Divisions of Nervous System:
The vertebrate nervous system has three divisions:
(i) A central nervous system comprising the brain and spinal cord. Its function is to receive the stimulus from the receptors and transmit its response to the effectors. Thus, it coordinates all the functions of the body.
(ii) A peripheral nervous system consisting of cranial and spinal nerves arising from the brain and spinal cord respectively. It forms a connecting link between the receptors, central nervous system (CNS) and effectors.
(iii) An autonomic nervous system made of two ganglionated sympathetic nerves, ganglia in the head and viscera, and their connecting nerves. The autonomic nervous system is often regarded as a part of the peripheral nervous system because the two are connected. But all the three divisions of the nervous system are connected intimately both structurally and functionally.
Primate social organization

Primate social organizations can generally be categorized into two types: 1) solitary foragers or dispersed polygyny where females forage alone and males monopolize access to females, and 2) where females forage together in female-bonded groups that are larger and contain multiple males. Group structures range from one-male harems to multi-male/multi-female groups. The type of social structure adopted depends on factors like the nature of resources and how defendable or monopolizable they are.
Comparative account of axial and appendicular skeleton of amniots

Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy ... Appendicular Skeleton. Appendicular skeleton ... 5 - Tetrapods - tendency for reduction in number of dermal bones ... distal row = 5 distal carplas numbered 1 through 5 (starting on thumb, or radial, side).
What's hot (20)
Social organization and social behaviour in insects

Social organization and social behaviour in insects
Comparative pro,mete,& eutheria, features of prototheria to eutheria,& af...

Comparative pro,mete,& eutheria, features of prototheria to eutheria,& af...
Peripheral and autonomic nervous system of vertebrates

Peripheral and autonomic nervous system of vertebrates
Comparative account of axial and appendicular skeleton of amniots

Comparative account of axial and appendicular skeleton of amniots
Similar to Nervous System- Comparative account of Brain.pdf
Nervous systems in vertebrates: T.Y.B.Sc. Sem VI Notes

Nervous systems in vertebrates: T.Y.B.Sc. Sem VI NotesDr. Sudesh D. Rathod, B N Bandodkar College of Science
The document discusses the development and differentiation of the brain in vertebrates. It begins by explaining how the neural tube develops and differentiates into three primary brain vesicles - the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. These later develop into five vesicles. It then describes the relationships between the early brain structures and the mature nervous system. The document also discusses the flexures of the brain, the evolution of the cerebral hemispheres and cerebellum across different vertebrates, and provides a comparative overview of brain anatomy in key vertebrate groups.Cns development

The document discusses the development of the nervous system from the ectoderm germ layer. It describes how the neural plate forms and folds to become the neural tube. The anterior and posterior ends of the neural tube close to form the brain and spinal cord. The neural crest cells go on to form the peripheral nervous system while the neural tube forms the central nervous system. It then details the subdivision and development of the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain regions of the embryonic brain.
The brain

The document summarizes the anatomy and physiology of the brain. It describes the main parts of the brain including the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem. The cerebrum is divided into four lobes that control motor skills, sensation, language, and vision. The cerebellum aids in movement coordination. The brain stem consists of the midbrain, pons, and medulla, and controls vital functions like breathing and heart rate. The document also outlines the structures of the diencephalon including the thalamus, hypothalamus, and pineal gland.
Ch11 eoc

The document describes the structure and function of the central nervous system. It discusses the meninges and cerebrospinal fluid, as well as the ventricles and circulation of CSF. The spinal cord and its ascending and descending tracts are described. Reflex arcs and specific reflexes like withdrawal are explained. The document then covers the structure and function of the brain including the cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem, and their components. Memory, hemispheric dominance and other higher cognitive functions are also summarized.
Cns

The document discusses several topics related to the central nervous system (CNS) including:
1. Astrocytes can be identified using GFAP staining and play a role in blood flow control in the brain.
2. Crossing the blood-brain barrier can be challenging for drug delivery to the brain but is necessary for treating some diseases like Parkinson's.
3. The limbic system including the hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus are involved in memory, emotion, and reward processing.
4. Dopamine pathways in the nucleus accumbens and amygdala are important for motivation and addiction.
Human Brain

The human brain is the most complex organ and is greatly enlarged compared to other mammals. It contains billions of neurons connected by trillions of synapses. While protected by the skull, the brain is susceptible to damage from injuries, diseases, and toxins. The cerebral cortex is the largest part and is highly folded, with specialized regions involved in different functions like vision, motor control, and language. Communication between the left and right hemispheres occurs mainly through the corpus callosum.
comparative_Nervous_Syst_Vertebrate_Life_Sciences_1yr_PDF.pdf

The document discusses the comparative structure of the nervous system across vertebrates from fish to birds. It describes the evolution of the brain from simpler chordates to more complex structures in mammals. Key points include:
1. The brain evolves from a simple nerve cord in cephalochordates to a more subdivided structure in cyclostomes with the addition of ganglia and brain vesicles.
2. Elasmobranch fish brains show the first subdivision into forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain along with developments like the cerebellum for active swimming.
3. Advanced bony fish and amphibian brains have larger optic lobes and corpus striatum suited to their environments while reptiles see further developments
Development of the nervous system

The document summarizes the development of the nervous system from the ectoderm. Key points include:
1) The neural ectoderm differentiates into the central nervous system (neural tube), peripheral nervous system (neural crest cells), and cranial sensory ganglia.
2) Neurulation involves the thickening and folding of the neural plate to form the neural tube, which later divides into the brain and spinal cord.
3) The brain develops from the anterior part of the neural tube and forms ventricles while the spinal cord develops from the posterior part.
4) Common congenital anomalies can occur from incomplete closure of the neural tube, including anencephaly, spina bifida
Brain strom

The document discusses various topics related to the central nervous system including the brain, spinal cord, and brain stem. It provides information on the following:
- The brain is the most complex organ containing billions of neurons.
- The brain stem consists of the medulla oblongata, pons, and midbrain. The medulla and pons contain nuclei that relay signals and control autonomic functions. The midbrain is involved in eye movement, hearing, and posture.
- The cerebellum coordinates movement and balance by comparing motor input and output and relaying adjustments to the cortex through the red nucleus.
- Other parts of the central nervous system discussed include the hypothalamus, th
Presentation1.pptx, radiological anatomy of the brain.

This document provides an overview of the radiological anatomy of the brain through computed tomography (CT) imaging. It describes the skull bones and sutures that form the cranial vault, as well as the three cranial fossae that house different brain structures. It also discusses the meningeal layers, including the falx cerebri and tentorium cerebelli, and cerebrospinal fluid spaces within the brain. Key structures like the pituitary fossa and ventricular system are identified. Understanding the normal CT anatomy of the brain provides important context for radiological interpretation.
Embryology development of central nervous system

The document summarizes the embryological development of the central nervous system. It begins with the formation of the neural plate and tube from ectoderm. The neural tube develops three primary brain vesicles - the prosencephalon (forebrain), mesencephalon (midbrain), and rhombencephalon (hindbrain). Neuroepithelial cells form the neural tube wall and generate neuroblasts that migrate inward to form the mantle layer and later differentiate into neurons and glial cells. Neural crest cells emerge along the neural folds and contribute to peripheral ganglia.
Central Nervous system CNS

The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is protected by three layers of tissue called meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. It contains four interconnected ventricles that produce cerebrospinal fluid. The brain is divided into the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. The forebrain contains the cerebrum and limbic system. The cerebrum is made up of grey matter and white matter and is involved in voluntary movement and complex functions. The spinal cord carries signals between the brain and body and contains 31 pairs of spinal nerves.
Overview of the anatomy of the brain and its physiology

The document provides information about the anatomy and structures of the human brain. It discusses the main parts and lobes of the brain including the cerebrum, cerebellum, diencephalon, and brainstem. It describes the ventricles and basal ganglia. Key structures mentioned include the cerebral cortex, motor and sensory areas, Broca's area, thalamus, hypothalamus, pineal gland, lateral ventricles, caudate nucleus, lentiform nucleus, amygdala, and claustrum. The relationships between these structures and their functions are summarized.
The human brain.pptx

The document discusses the anatomy and physiology of the brain. It describes the main parts of the brain as the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem. The cerebrum is the largest part and is divided into four lobes that control functions like movement, sensation, vision, and language. The cerebellum aids in movement coordination and balance. The brain stem consists of the midbrain, pons, and medulla, and controls vital functions like breathing and heart rate. Other parts discussed include the thalamus and hypothalamus, which regulate sensation and autonomic body processes respectively.
CNS PART 2.pptx

The document summarizes key information about the structure and function of the brain and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). It describes the four ventricles that produce CSF and how it circulates through the brain and spinal cord. It discusses the formation of CSF by the choroid plexus and its absorption. The structure and functions of structures like the basal ganglia, thalamus, and blood-brain barrier are also summarized briefly.
The brain

The hippocampus is located deep in the brain and plays an important role in memory formation and spatial navigation. It is involved in fear conditioning and damage to the hippocampus has been linked to anxiety disorders like PTSD. The hippocampus contains anxiety cells that respond to unfamiliar places, and suppressing these cells reduces anxiety in mice. CBD may help reduce activity in the amygdala and aid signaling in the endocannabinoid system involving the hippocampus to help treat anxiety symptoms.
Brain

The brain is the center of the nervous system in vertebrates and some invertebrates. It is located in the head and protected by the skull. Brains can vary greatly in complexity across species. The human brain is the most complex known biological structure and is larger relative to body size than in other primates. Despite scientific progress, much about how brains work remains unknown.
Anatomy of the brain

The document provides an overview of the main anatomical divisions and structures of the human brain. It discusses that the brain can be divided into three main divisions - the forebrain (cerebrum), midbrain, and hindbrain. The cerebrum is the largest part and can be further divided into four lobes. The brain stem connects the forebrain and hindbrain and contains the midbrain, pons, and medulla. The cerebellum is located beneath the tentorium cerebelli and coordinates muscle movements and balance.
Brain

The document summarizes the major parts and functions of the human brain. It describes how the brain is made up of distinct evolutionary parts, including the brain stem which controls basic functions, and the more developed cerebellum and cerebrum. It then provides details on the specific regions and lobes of the cerebrum, including the frontal lobe which governs cognitive thought, and the structures of the limbic system involved in emotion. The document emphasizes the brain's remarkable plasticity and ability to relearn even after injury like stroke.
Similar to Nervous System- Comparative account of Brain.pdf (20)
Nervous systems in vertebrates: T.Y.B.Sc. Sem VI Notes

Nervous systems in vertebrates: T.Y.B.Sc. Sem VI Notes
comparative_Nervous_Syst_Vertebrate_Life_Sciences_1yr_PDF.pdf

comparative_Nervous_Syst_Vertebrate_Life_Sciences_1yr_PDF.pdf
Presentation1.pptx, radiological anatomy of the brain.

Presentation1.pptx, radiological anatomy of the brain.
Overview of the anatomy of the brain and its physiology

Overview of the anatomy of the brain and its physiology
Recently uploaded
Gender and Mental Health - Counselling and Family Therapy Applications and In...

A proprietary approach developed by bringing together the best of learning theories from Psychology, design principles from the world of visualization, and pedagogical methods from over a decade of training experience, that enables you to: Learn better, faster!
Stack Memory Organization of 8086 Microprocessor

The stack memory organization of 8086 microprocessor.
BÀI TẬP BỔ TRỢ TIẾNG ANH 8 CẢ NĂM - GLOBAL SUCCESS - NĂM HỌC 2023-2024 (CÓ FI...

BÀI TẬP BỔ TRỢ TIẾNG ANH 8 CẢ NĂM - GLOBAL SUCCESS - NĂM HỌC 2023-2024 (CÓ FI...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
https://app.box.com/s/y977uz6bpd3af4qsebv7r9b7s21935vdBeyond Degrees - Empowering the Workforce in the Context of Skills-First.pptx

Iván Bornacelly, Policy Analyst at the OECD Centre for Skills, OECD, presents at the webinar 'Tackling job market gaps with a skills-first approach' on 12 June 2024
LAND USE LAND COVER AND NDVI OF MIRZAPUR DISTRICT, UP

This Dissertation explores the particular circumstances of Mirzapur, a region located in the
core of India. Mirzapur, with its varied terrains and abundant biodiversity, offers an optimal
environment for investigating the changes in vegetation cover dynamics. Our study utilizes
advanced technologies such as GIS (Geographic Information Systems) and Remote sensing to
analyze the transformations that have taken place over the course of a decade.
The complex relationship between human activities and the environment has been the focus
of extensive research and worry. As the global community grapples with swift urbanization,
population expansion, and economic progress, the effects on natural ecosystems are becoming
more evident. A crucial element of this impact is the alteration of vegetation cover, which plays a
significant role in maintaining the ecological equilibrium of our planet.Land serves as the foundation for all human activities and provides the necessary materials for
these activities. As the most crucial natural resource, its utilization by humans results in different
'Land uses,' which are determined by both human activities and the physical characteristics of the
land.
The utilization of land is impacted by human needs and environmental factors. In countries
like India, rapid population growth and the emphasis on extensive resource exploitation can lead
to significant land degradation, adversely affecting the region's land cover.
Therefore, human intervention has significantly influenced land use patterns over many
centuries, evolving its structure over time and space. In the present era, these changes have
accelerated due to factors such as agriculture and urbanization. Information regarding land use and
cover is essential for various planning and management tasks related to the Earth's surface,
providing crucial environmental data for scientific, resource management, policy purposes, and
diverse human activities.
Accurate understanding of land use and cover is imperative for the development planning
of any area. Consequently, a wide range of professionals, including earth system scientists, land
and water managers, and urban planners, are interested in obtaining data on land use and cover
changes, conversion trends, and other related patterns. The spatial dimensions of land use and
cover support policymakers and scientists in making well-informed decisions, as alterations in
these patterns indicate shifts in economic and social conditions. Monitoring such changes with the
help of Advanced technologies like Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Systems is
crucial for coordinated efforts across different administrative levels. Advanced technologies like
Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Systems
9
Changes in vegetation cover refer to variations in the distribution, composition, and overall
structure of plant communities across different temporal and spatial scales. These changes can
occur natural.
HYPERTENSION - SLIDE SHARE PRESENTATION.

IT WILL BE HELPFULL FOR THE NUSING STUDENTS
IT FOCUSED ON MEDICAL MANAGEMENT AND NURSING MANAGEMENT.
HIGHLIGHTS ON HEALTH EDUCATION.
A Visual Guide to 1 Samuel | A Tale of Two Hearts

These slides walk through the story of 1 Samuel. Samuel is the last judge of Israel. The people reject God and want a king. Saul is anointed as the first king, but he is not a good king. David, the shepherd boy is anointed and Saul is envious of him. David shows honor while Saul continues to self destruct.
BIOLOGY NATIONAL EXAMINATION COUNCIL (NECO) 2024 PRACTICAL MANUAL.pptx

Practical manual for National Examination Council, Nigeria.
Contains guides on answering questions on the specimens provided
Philippine Edukasyong Pantahanan at Pangkabuhayan (EPP) Curriculum

(𝐓𝐋𝐄 𝟏𝟎𝟎) (𝐋𝐞𝐬𝐬𝐨𝐧 𝟏)-𝐏𝐫𝐞𝐥𝐢𝐦𝐬
𝐃𝐢𝐬𝐜𝐮𝐬𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐄𝐏𝐏 𝐂𝐮𝐫𝐫𝐢𝐜𝐮𝐥𝐮𝐦 𝐢𝐧 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐏𝐡𝐢𝐥𝐢𝐩𝐩𝐢𝐧𝐞𝐬:
- Understand the goals and objectives of the Edukasyong Pantahanan at Pangkabuhayan (EPP) curriculum, recognizing its importance in fostering practical life skills and values among students. Students will also be able to identify the key components and subjects covered, such as agriculture, home economics, industrial arts, and information and communication technology.
𝐄𝐱𝐩𝐥𝐚𝐢𝐧 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐍𝐚𝐭𝐮𝐫𝐞 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐒𝐜𝐨𝐩𝐞 𝐨𝐟 𝐚𝐧 𝐄𝐧𝐭𝐫𝐞𝐩𝐫𝐞𝐧𝐞𝐮𝐫:
-Define entrepreneurship, distinguishing it from general business activities by emphasizing its focus on innovation, risk-taking, and value creation. Students will describe the characteristics and traits of successful entrepreneurs, including their roles and responsibilities, and discuss the broader economic and social impacts of entrepreneurial activities on both local and global scales.
Mule event processing models | MuleSoft Mysore Meetup #47

Mule event processing models | MuleSoft Mysore Meetup #47
Event Link:- https://meetups.mulesoft.com/events/details/mulesoft-mysore-presents-mule-event-processing-models/
Agenda
● What is event processing in MuleSoft?
● Types of event processing models in Mule 4
● Distinction between the reactive, parallel, blocking & non-blocking processing
For Upcoming Meetups Join Mysore Meetup Group - https://meetups.mulesoft.com/mysore/YouTube:- youtube.com/@mulesoftmysore
Mysore WhatsApp group:- https://chat.whatsapp.com/EhqtHtCC75vCAX7gaO842N
Speaker:-
Shivani Yasaswi - https://www.linkedin.com/in/shivaniyasaswi/
Organizers:-
Shubham Chaurasia - https://www.linkedin.com/in/shubhamchaurasia1/
Giridhar Meka - https://www.linkedin.com/in/giridharmeka
Priya Shaw - https://www.linkedin.com/in/priya-shaw
How to Setup Warehouse & Location in Odoo 17 Inventory

In this slide, we'll explore how to set up warehouses and locations in Odoo 17 Inventory. This will help us manage our stock effectively, track inventory levels, and streamline warehouse operations.
Recently uploaded (20)
NEWSPAPERS - QUESTION 1 - REVISION POWERPOINT.pptx

NEWSPAPERS - QUESTION 1 - REVISION POWERPOINT.pptx
Gender and Mental Health - Counselling and Family Therapy Applications and In...

Gender and Mental Health - Counselling and Family Therapy Applications and In...
spot a liar (Haiqa 146).pptx Technical writhing and presentation skills

spot a liar (Haiqa 146).pptx Technical writhing and presentation skills
BÀI TẬP BỔ TRỢ TIẾNG ANH 8 CẢ NĂM - GLOBAL SUCCESS - NĂM HỌC 2023-2024 (CÓ FI...

BÀI TẬP BỔ TRỢ TIẾNG ANH 8 CẢ NĂM - GLOBAL SUCCESS - NĂM HỌC 2023-2024 (CÓ FI...
Beyond Degrees - Empowering the Workforce in the Context of Skills-First.pptx

Beyond Degrees - Empowering the Workforce in the Context of Skills-First.pptx
LAND USE LAND COVER AND NDVI OF MIRZAPUR DISTRICT, UP

LAND USE LAND COVER AND NDVI OF MIRZAPUR DISTRICT, UP
BIOLOGY NATIONAL EXAMINATION COUNCIL (NECO) 2024 PRACTICAL MANUAL.pptx

BIOLOGY NATIONAL EXAMINATION COUNCIL (NECO) 2024 PRACTICAL MANUAL.pptx
Philippine Edukasyong Pantahanan at Pangkabuhayan (EPP) Curriculum

Philippine Edukasyong Pantahanan at Pangkabuhayan (EPP) Curriculum
Mule event processing models | MuleSoft Mysore Meetup #47

Mule event processing models | MuleSoft Mysore Meetup #47
How to Setup Warehouse & Location in Odoo 17 Inventory

How to Setup Warehouse & Location in Odoo 17 Inventory
Nervous System- Comparative account of Brain.pdf
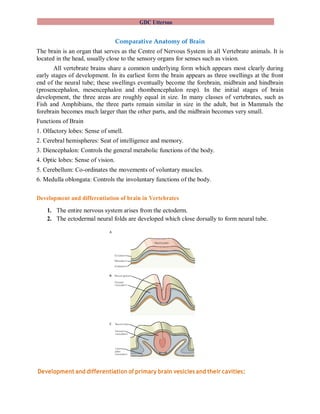
- 1. GDC Uttersoo Comparative Anatomy of Brain The brain is an organ that serves as the Centre of Nervous System in all Vertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. All vertebrate brains share a common underlying form which appears most clearly during early stages of development. In its earliest form the brain appears as three swellings at the front end of the neural tube; these swellings eventually become the forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain (prosencephalon, mesencephalon and rhombencephalon resp). In the initial stages of brain development, the three areas are roughly equal in size. In many classes of vertebrates, such as Fish and Amphibians, the three parts remain similar in size in the adult, but in Mammals the forebrain becomes much larger than the other parts, and the midbrain becomes very small. Functions of Brain 1. Olfactory lobes: Sense of smell. 2. Cerebral hemispheres: Seat of intelligence and memory. 3. Diencephalon: Controls the general metabolic functions of the body. 4. Optic lobes: Sense of vision. 5. Cerebellum: Co-ordinates the movements of voluntary muscles. 6. Medulla oblongata: Controls the involuntary functions of the body. Development and differentiation of brain in Vertebrates 1. The entire nervous system arises from the ectoderm. 2. The ectodermal neural folds are developed which close dorsally to form neural tube. Development and differentiation of primary brain vesicles and their cavities:
- 2. GDC Uttersoo The vesicles of vertebrate brain: 1. Anterior part of neural tube is slightly swollen which initially differentiated in to three primary vesicles of brain namely first prosencephalon (forebrain), second mesencephalon (midbrain) and third rhombencephalon (hindbrain) containing cavities. 2. At later stages two secondary vesicles form in the area of the prosencephalon, 1a and 1b (see fig. below) developing into telencephalon and diencephalon respectively. 3. The diencephalon gives rise to sac like lateral outgrowths called the optic vesicles. The optic vesicles are pushed downward by two large processes growing forward from the anterior vesicle (the primitive cerebral hemispheres). These ultimately develop into the retina, and other nervous parts of the eye. 4. The other secondary vesicles are developed in the rhombencephalon namely 3a and 3b (see fig. below) developing into metencephalon and myelencephalon respectively. 5. Mesencephalon reduces to form a narrow commissure known as cerebral aqueduct (see fig. below). The cavities of vertebrate brain: 1. The cavities of brain are referred as ventricles. There are four ventricles in vertebrate brain namely 1. Olfactory ventricle. 2. Lateral ventricle. 3. Third ventricle. 4. Fourth ventricle 2. The olfactory lobes carry cavities known as olfactory ventricles arising from the anterior part of the cerebral hemispheres. These grow forward, and soon lose olfactory ventricles. 3. The telencephalic vesicles become the cerebral hemispheres, and their cavities become the paired lateral ventricles (lateral telocoeles) of the adult brain.
- 3. GDC Uttersoo 4. The third ventricle lies in the diencephalon (diocoele). Later in development the lateral walls of the diencephalon become greatly thickened to form the thalami, thus reducing the size and changing the shape of the diocoele, which is known in adult anatomy as the third brain ventricle. 5. The fourth ventricle lies in metencephalon. The anterior part of the fourth ventricle is known as metacoele and the posterior part as myelocoele. Flexures of brain: 1. As the result of unequal growth of these different parts of brain, three flexures are formed and the embryonic brain becomes bent on itself in a somewhat zigzag fashion; the two earliest flexures are concave ventrally and are associated with corresponding flexures of the whole head. 2. The first flexure appears in the region of the mid-brain, and is named the ventral cephalic flexure. By means of it the fore-brain is bent in a ventral direction around the anterior end of the notochord and fore-gut, with the result that the floor of the fore-brain comes to lie almost parallel with that of the hind-brain. This flexure causes the mid-brain to become, for a time, the most prominent part of the brain, since its dorsal surface corresponds with the convexity of the curve. 3. The second bend appears at the junction of the hind-brain and medulla spinalis. This is termed the cervical flexure, and increases from the third to the end of the fifth week, when the hind-brain forms nearly a right angle with the medulla spinalis; after the fifth week erection of the head takes place and the cervical flexure diminishes and disappears. 4. The third bend is named the pontine flexure, because it is found in the region of the future pons Varoli. 5. Both the cervical and the pontine flexures eventually straighten out, but the cephalic flexure remains prominent throughout development.
- 4. GDC Uttersoo Evolutionofcerebral hemispheres & cerebellum with reference to shark,frog,lizard, pigeon & rabbit: 1. Telencephalon, called lamina terminalis and the roof of the cerebrum is called cortex or pallium. The telencephalon then appears to be composed of two divisions, the anterior of which is subsequently developed into the cerebral hemispheres, corpora striata, and the olfactory lobes. The hemispheres undergo enormous enlargement in their later development and extend dorsally and posteriorly as well as anteriorly, eventually covering the entire diencephalon and mesencephalon under their posterior lobes. 2. Posterior part of forebrain, the diencephalon, consisting of the thalamus and hypothalamus, representing the anterior vesicle. The median evagination in the roof of the diencephalon develops into epiphysis. 3. The mesencephalon becomes specialized as the optic lobes, visual centers associated with the optic nerves. The dorsal and lateral walls of the mesencephalon later increase rapidly in thickness and become the optic lobes (copora quadrigemina) of the adult brain. . It serves as the main pathway of the fiber tracts which connect the cerebral hemispheres with the posterior part of the brain and the spinal cord. 4. The hindbrain became divided into anterior metencephalon and posterior myelencephalon. The metencephalon shows ventrally and laterally an extensive ingrowth of fiber tracts giving rise to the pons and to the cerebellar peduncles of the adult metencephalon. The roof of the metencephalon undergoes extensive enlargement and becomes the cerebellum of the adult brain. The ventro-lateral wall of the cerebrum becomes thick and called corpus striatum. The ventral and lateral walls of the myelencephalon become the floor and side-walls of the medulla of the adult brain. The medulla becomes specialized as a control center for some autonomic and somatic pathways concerned with vital functions (such as breathing, blood pressure, and heartbeat). The dorsal wall of myelencephalon is thin and receives rich blood vessels thus forming posterior choroid plexus. The pons is above the medulla and also acts as a connecting tract. The cerebellum enlarged and became a structure concerned with balance, equilibrium, and muscular coordination.
- 5. GDC Uttersoo Comparativeanatomyofbraininvertebrates Brain of all vertebrates, from fish to man, is built in accordance with the same architectural plan. However, form of brain differs in different vertebrates in accordance with the habits and behavior of the animals. 1. Elasmobranches: Olfactory lobes are correspondingly large. Optic lobes and pallium are relatively moderate in size. Saccus vasculosus, thin-walled vascular sensory organ, is attached to pituitary and connected with cerebellum. Pineal apparatus is well-developed. Cerebellum is especially large due to active swimming habit. Ruffle-like restiform bodies are present. 2. Amphibians: Olfactory lobes are smaller than optic lobes. Corpus striatum receives greater number of sensory fibres. Cerebral hemispheres are more developed than in fishes. Less-developed cerebellum. Medulla is also small. Pineal body is small. 3. Reptilians: Telencephalon becomes the largest region of brain. Olfactory lobes are larger than in amphibians. A pair of auditory lobes is found posterior to optic lobes. The third ventricle is reduced to a narrow cerebral aqueduct. Cerebellum is somewhat pear-shaped and larger than in amphibians. Modern reptiles show a great development in the basal parts of the forebrain. There are large numbers of nervous connections between the thalamus and the hemispheres. The latter are larger than the optic lobes, showing the increased importance of the former. The walls of the thalamus are very thick and many of the optic nerve paths end there as well as many in the midbrain. 4. Birds: Brain is proportionately larger than that of a reptile. Olfactory lobes are small. Two cerebral hemispheres are larger, smooth and projected posteriorly over the
- 6. GDC Uttersoo diencephalon to meet the cerebellum. Pallium is thin but corpus striatum is greatly enlarged. Optic lobes are conspicuously developed. The cerebellum is greatly enlarged with several superficial folds. 5. Mammals: Brain is proportionately larger than in other vertebrates. Cerebral hemispheres of Prototheria, Metatheria & Eutheria are smaller & smooth, larger & smooth, greatly enlarged & divided into lobes respectively. The two hemispheres are jointed internally by transverse band-like fibres called corpus callosum. Olfactory lobes are relatively small but well defined. Four almost solid optic lobes are present. The mammalian brain is completely dominated by the cerebral hemispheres. The roof has developed enormously and spread out forming the cerebral cortex which in humans is thrown into a number of elaborate folds and almost covers the rest of the brain. The cortex is made up millions of cells. The more folded the surface, the more cells it can contain. These cells make up the gray matter. Their axons, which make up the tracts or pathways in the brain, form the white matter underneath the cortex. The white matter of the spinal cord is also made up of nerve axons, surrounding the central gray matter. Conclusion: Discussing the evolution of brain in these vertebrate groups, it is clear that they are originated from a common ancestral stock.