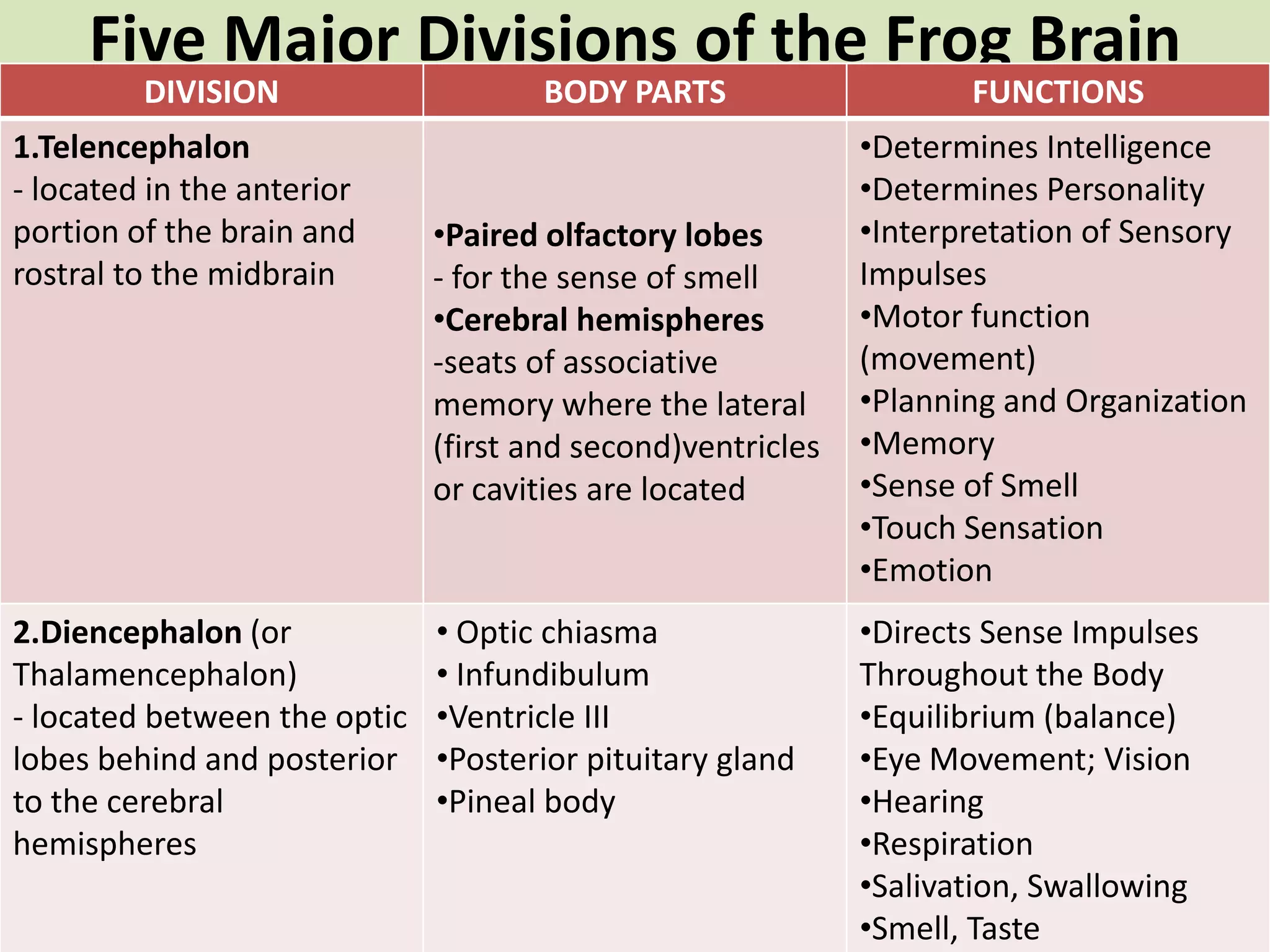
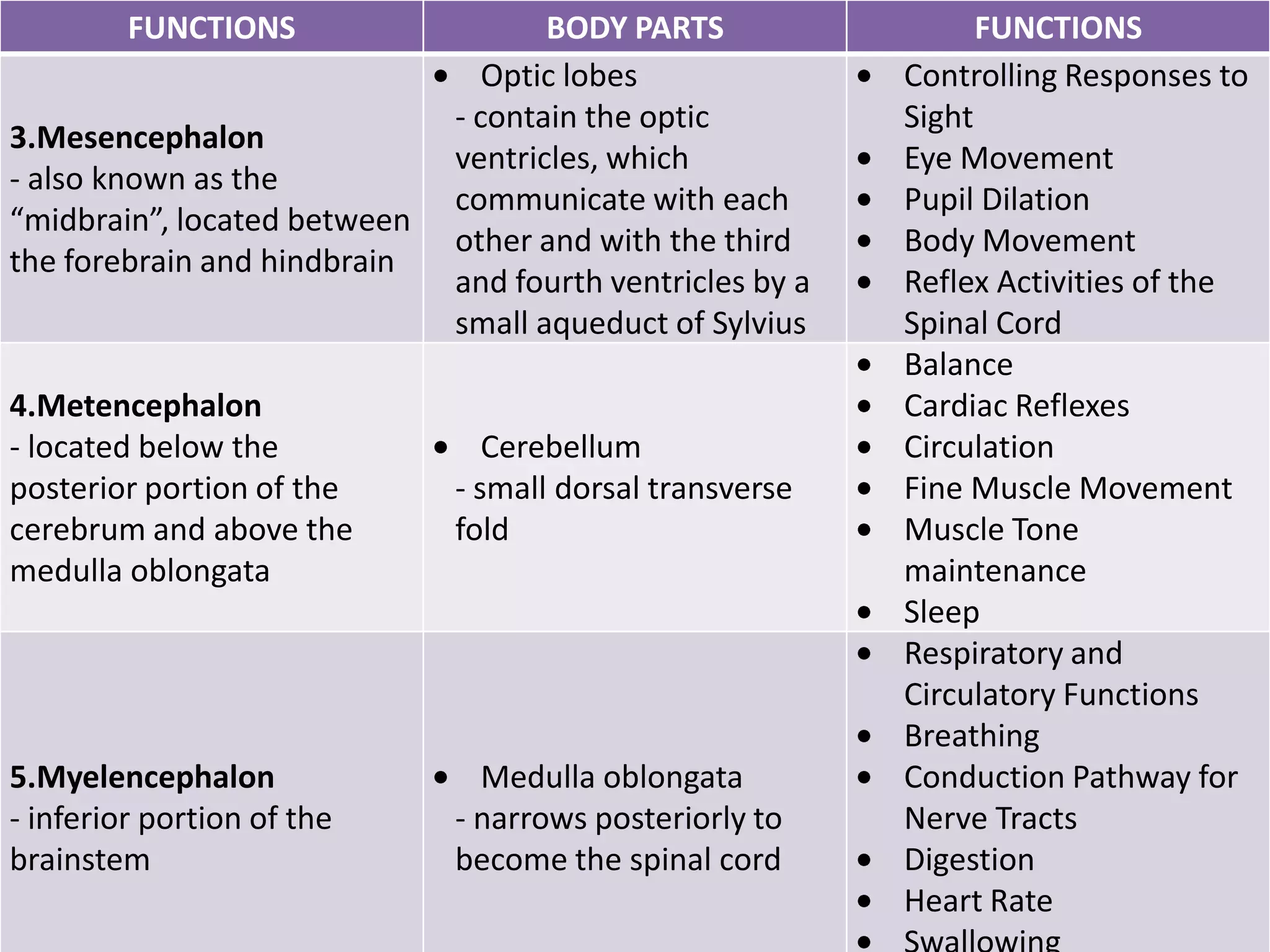
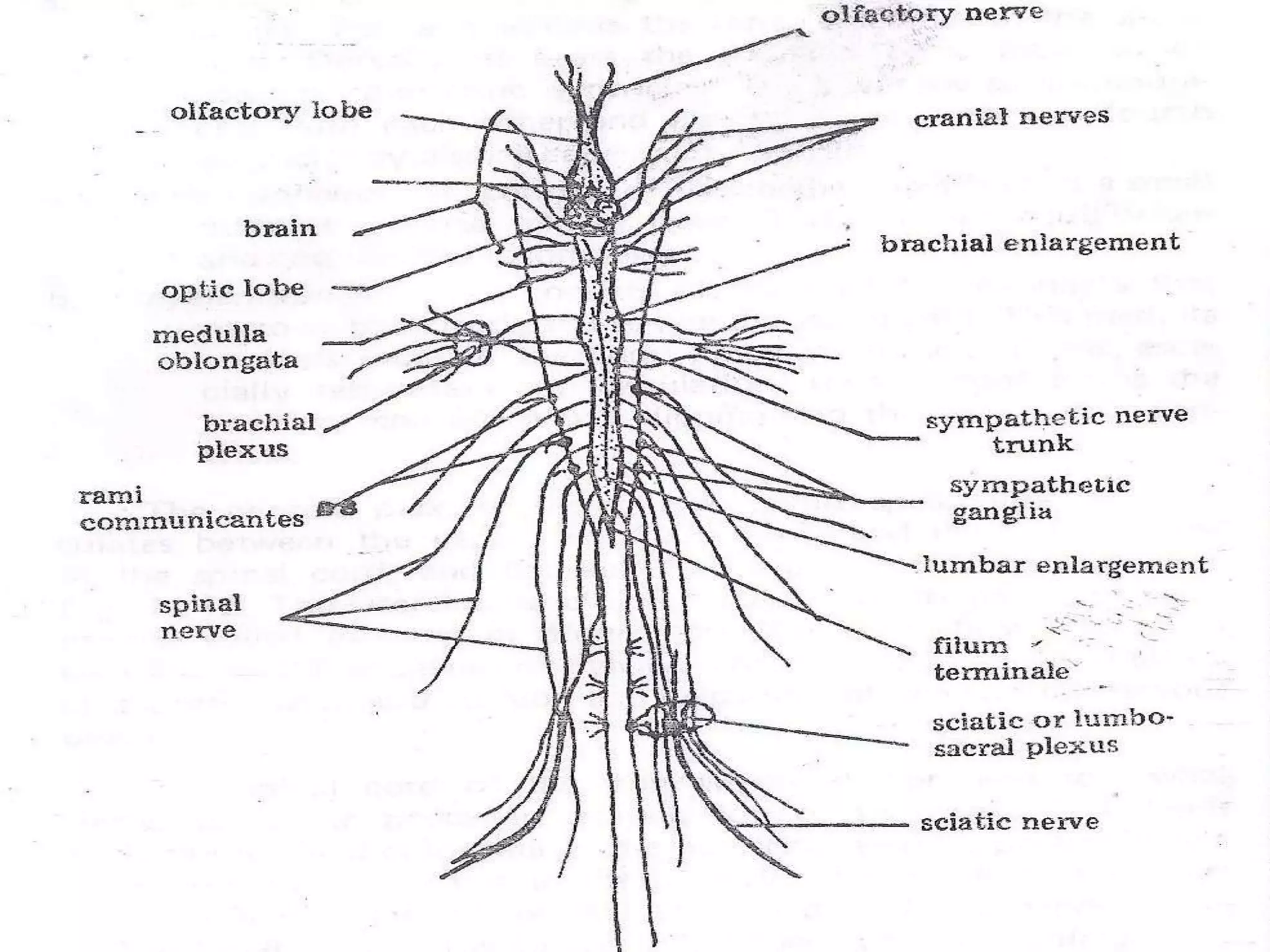
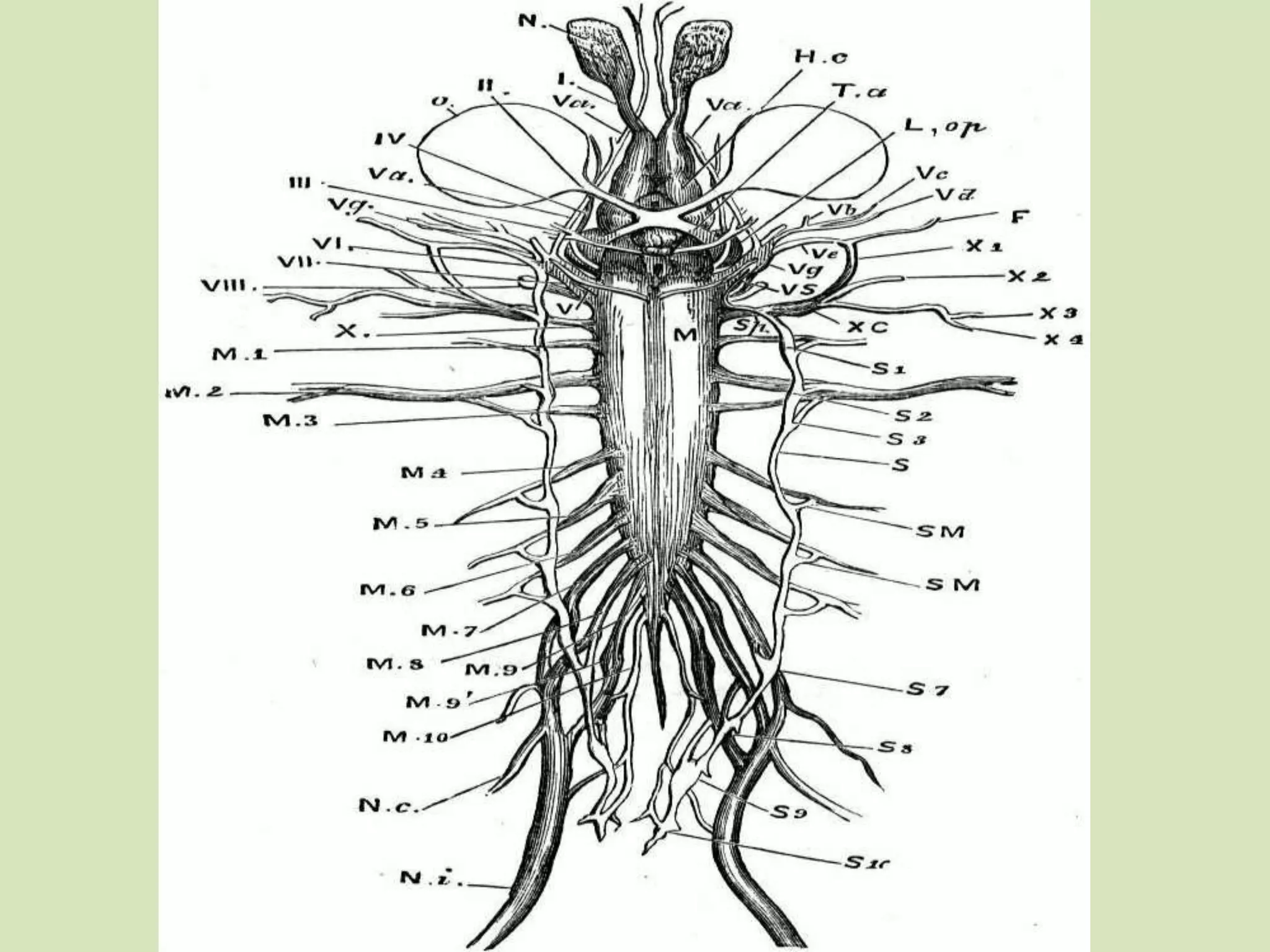
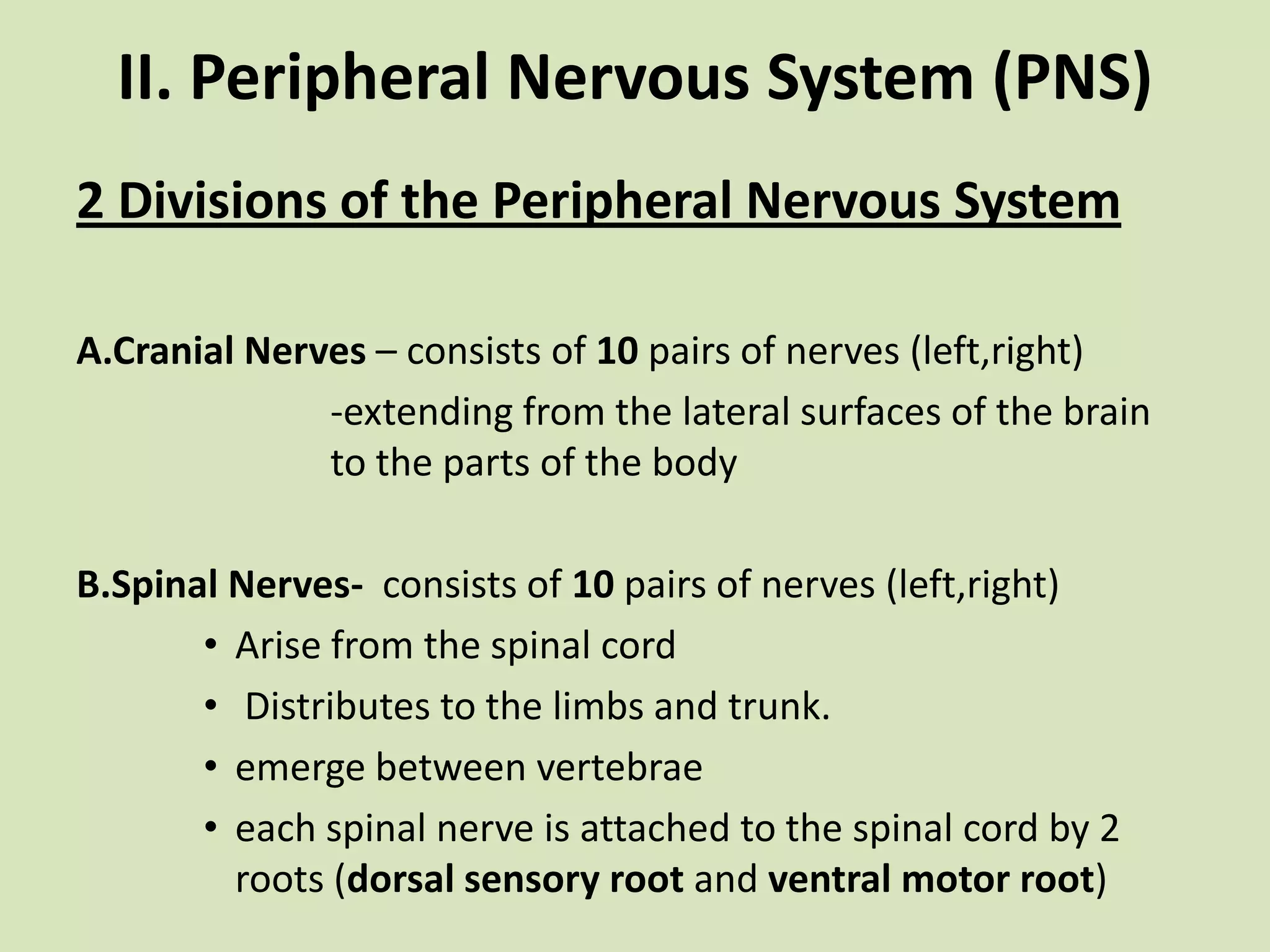
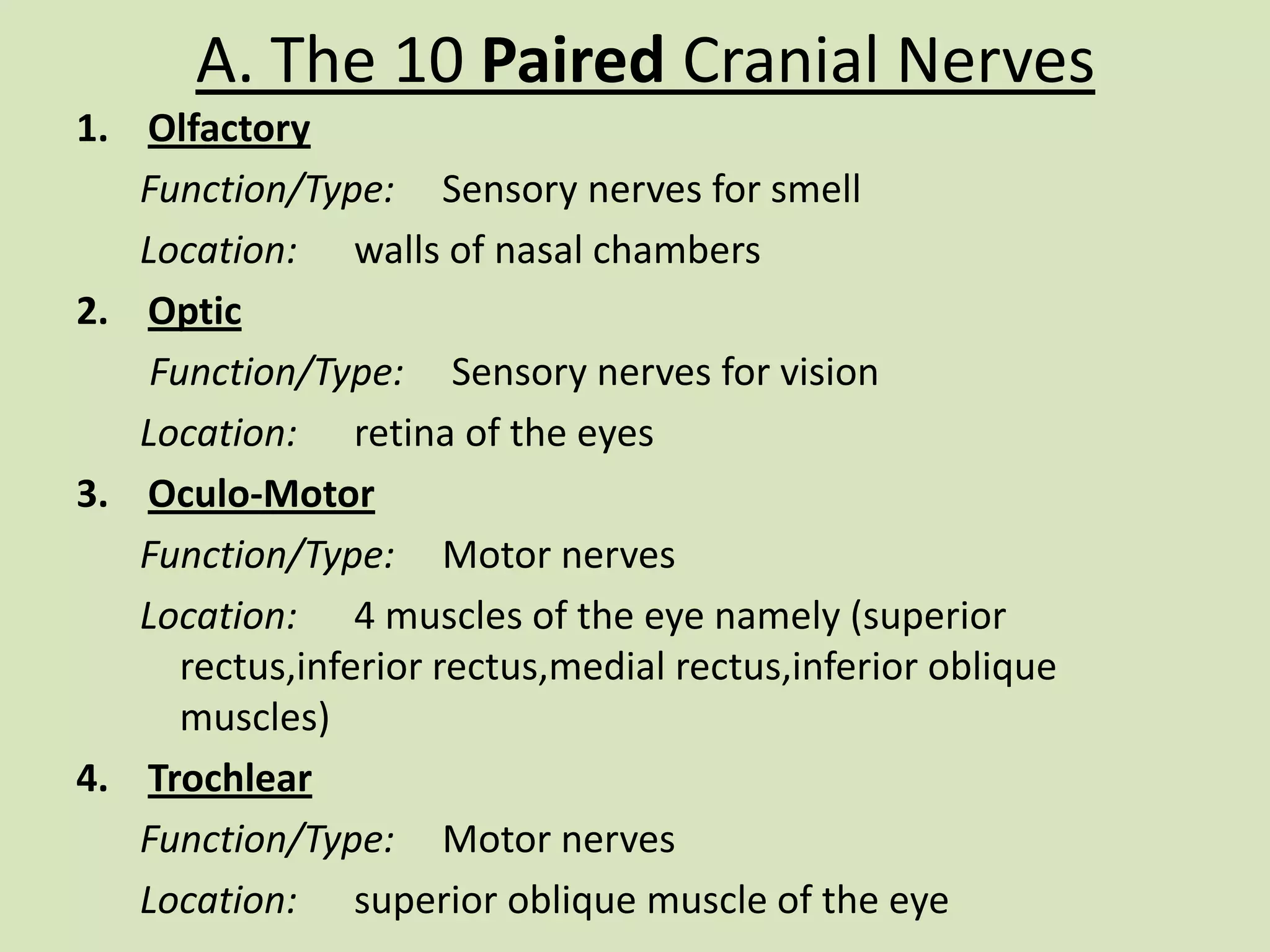
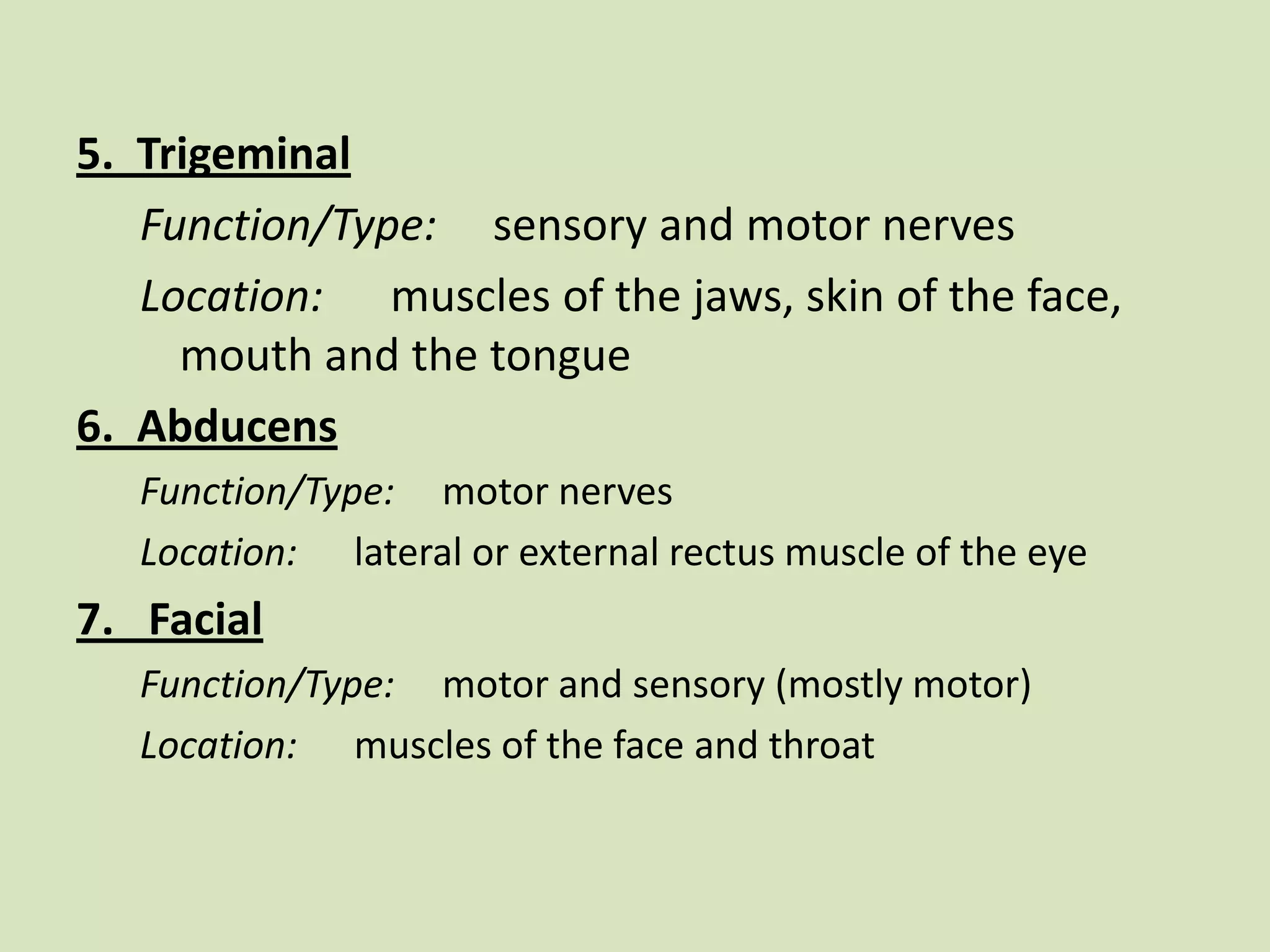
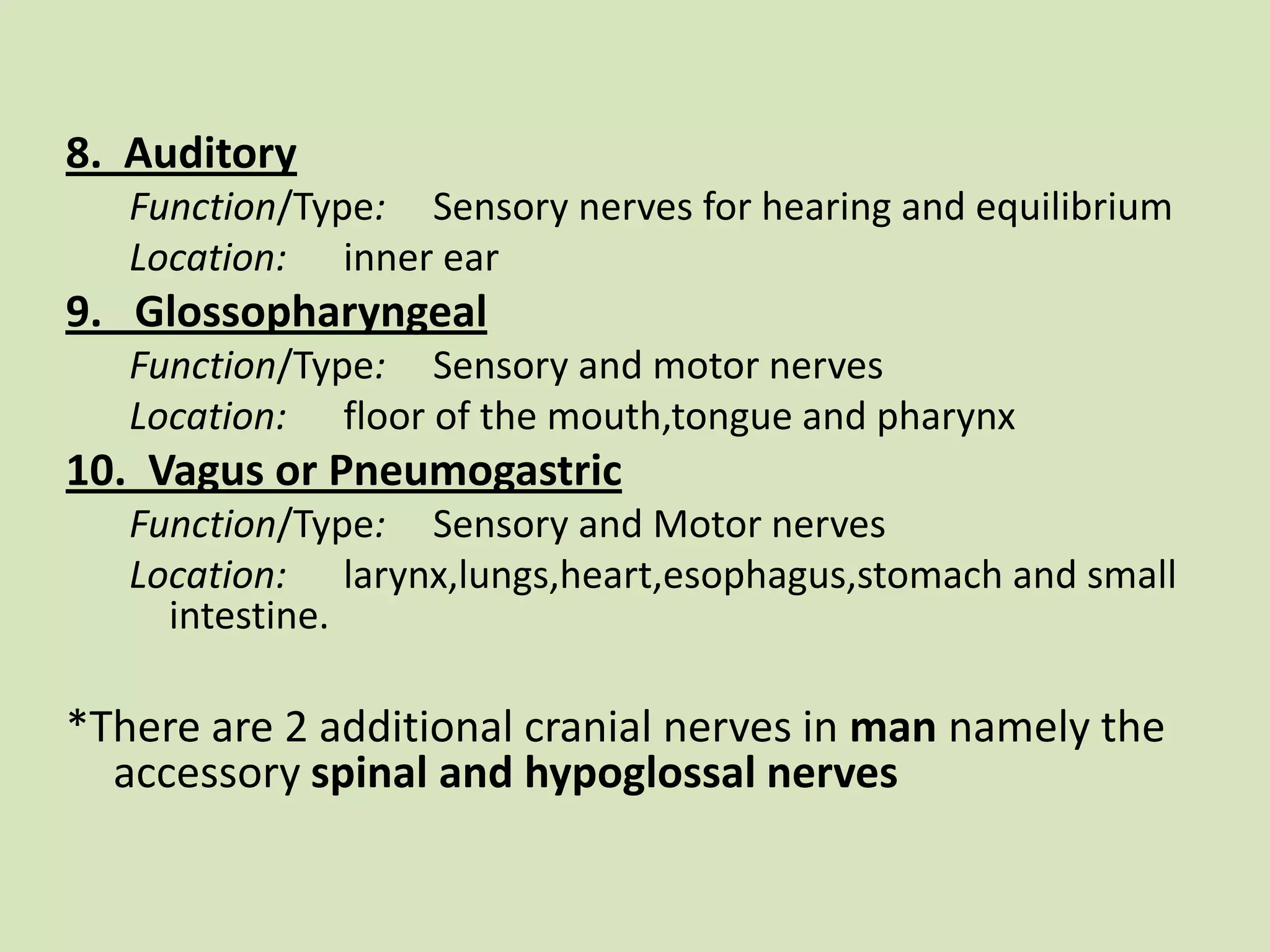
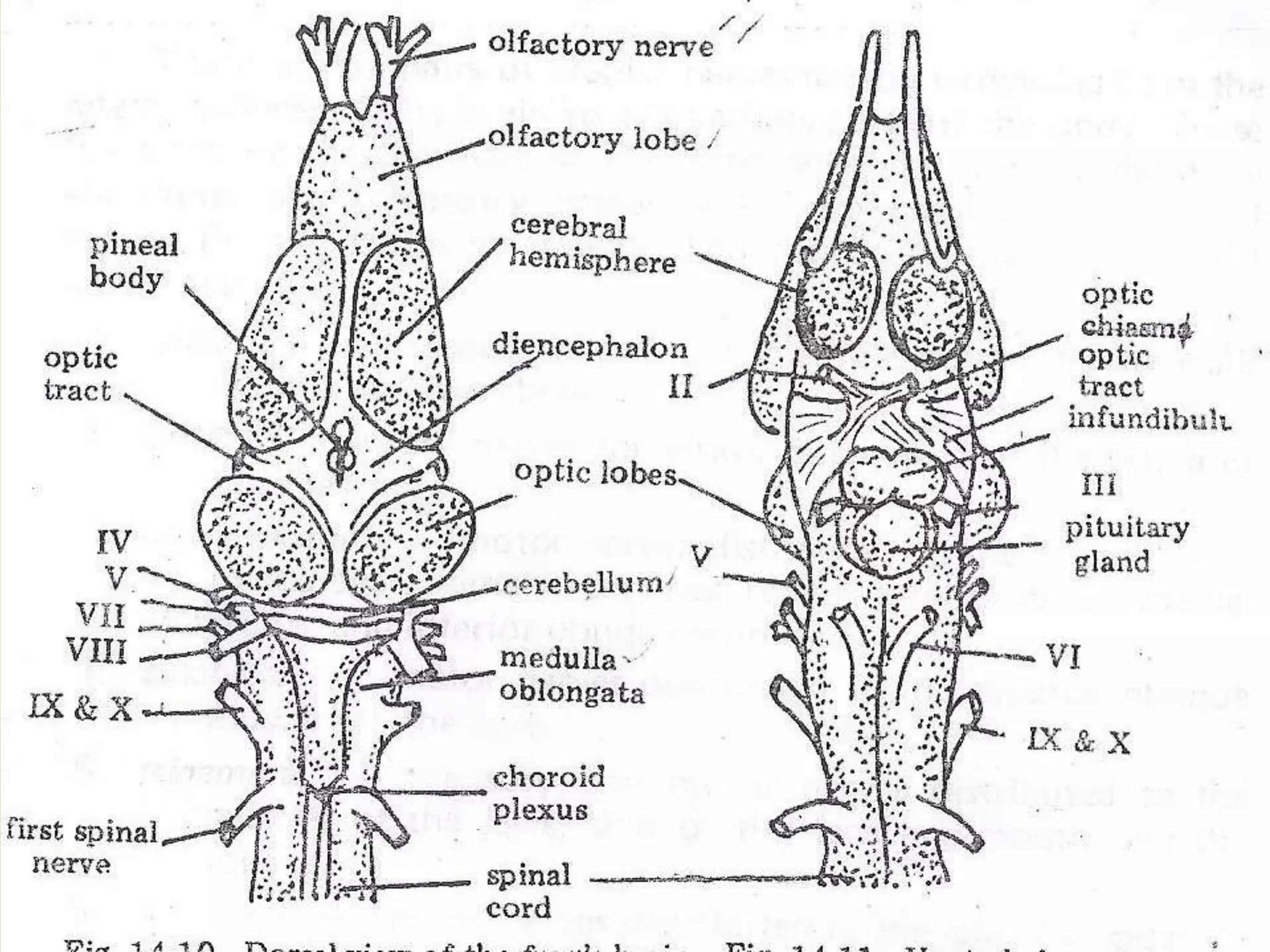
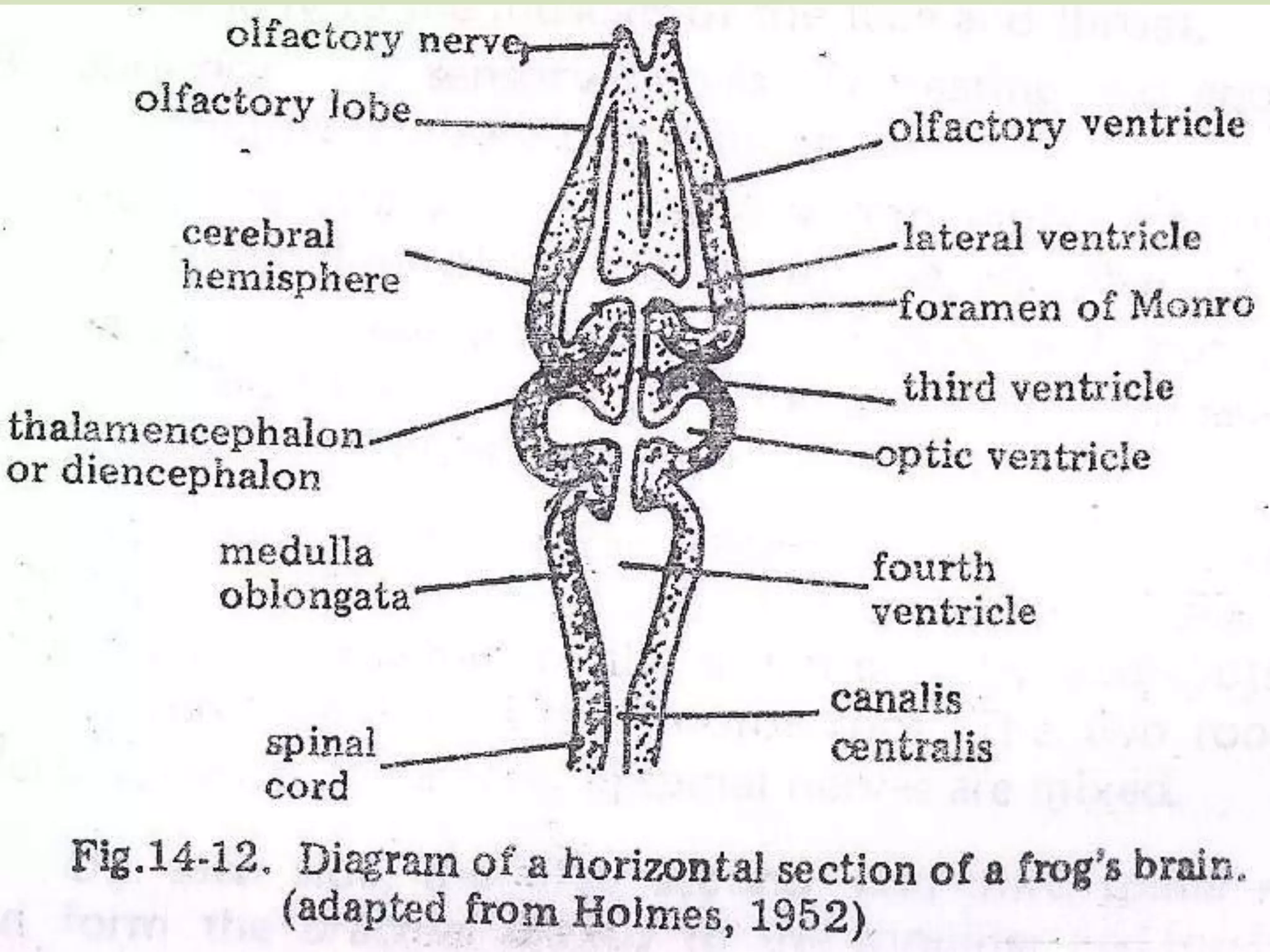
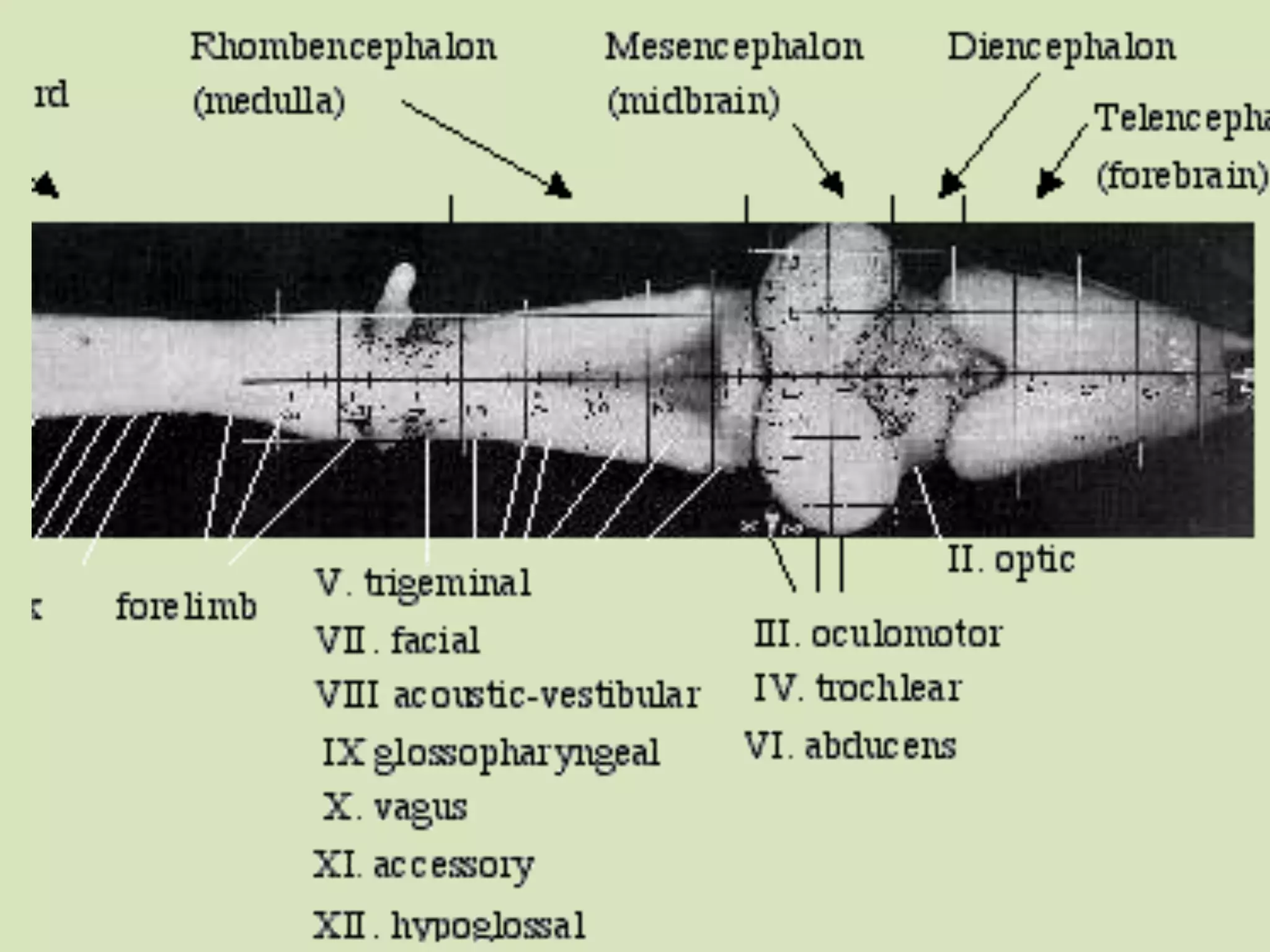
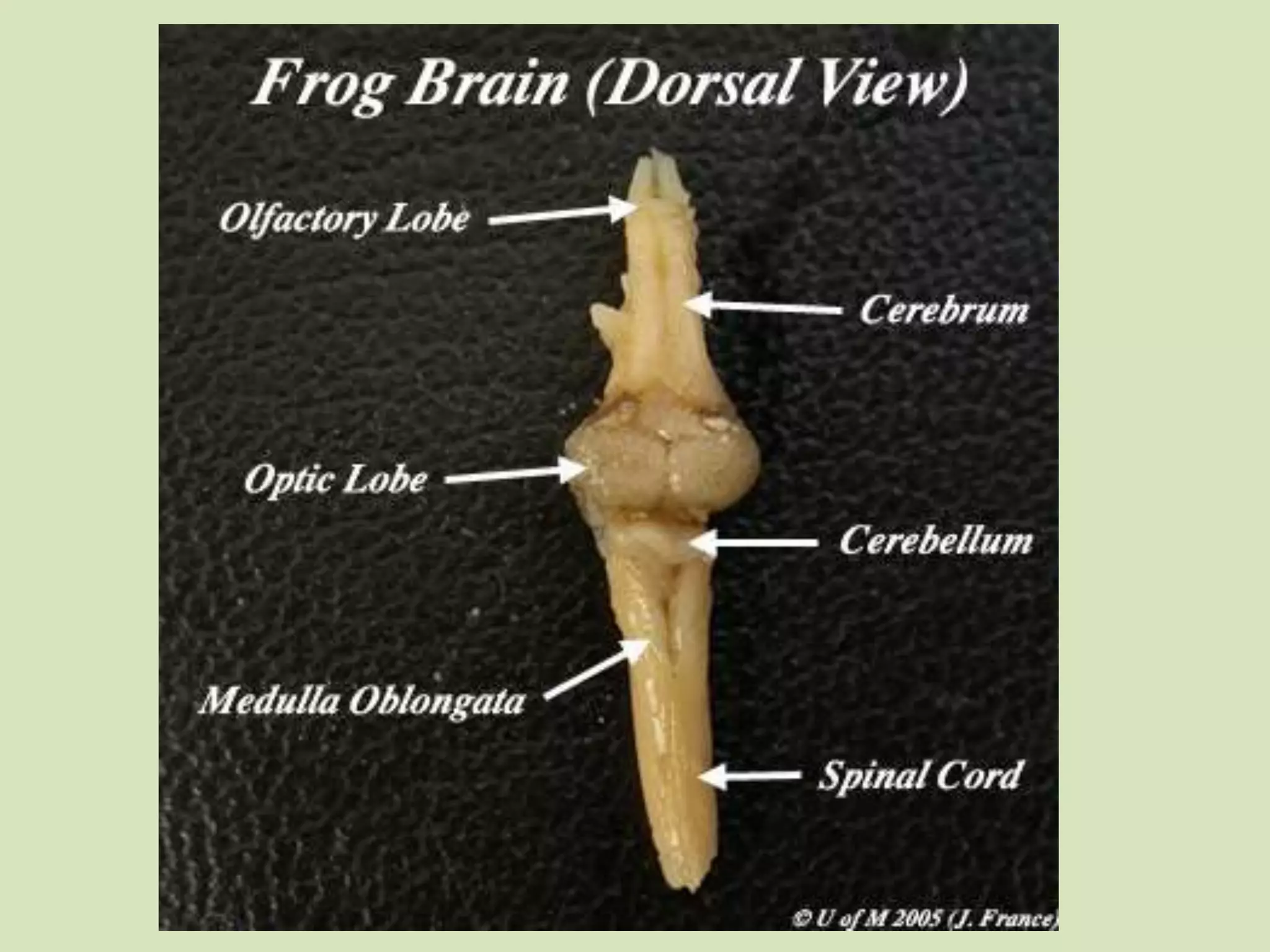
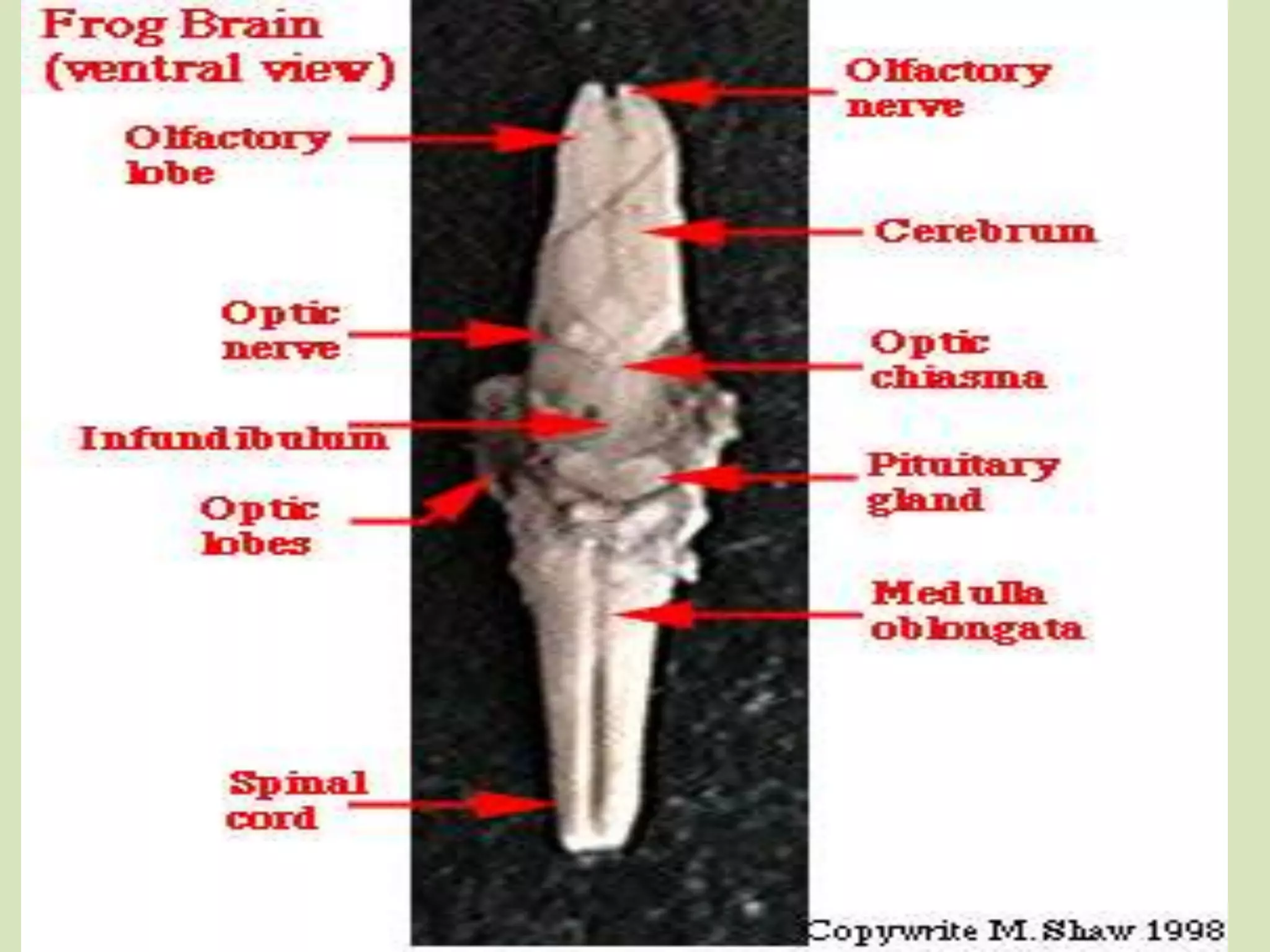
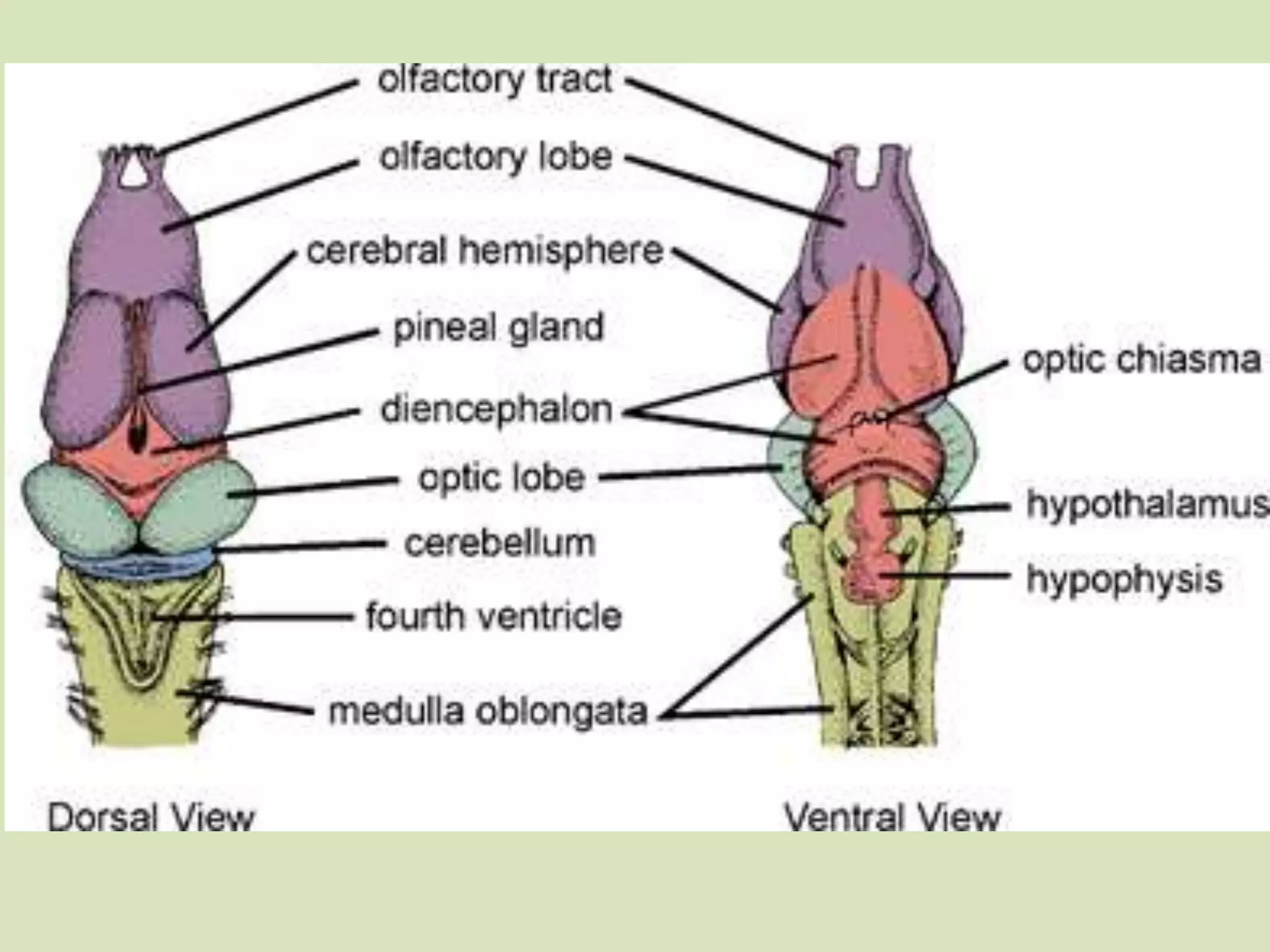
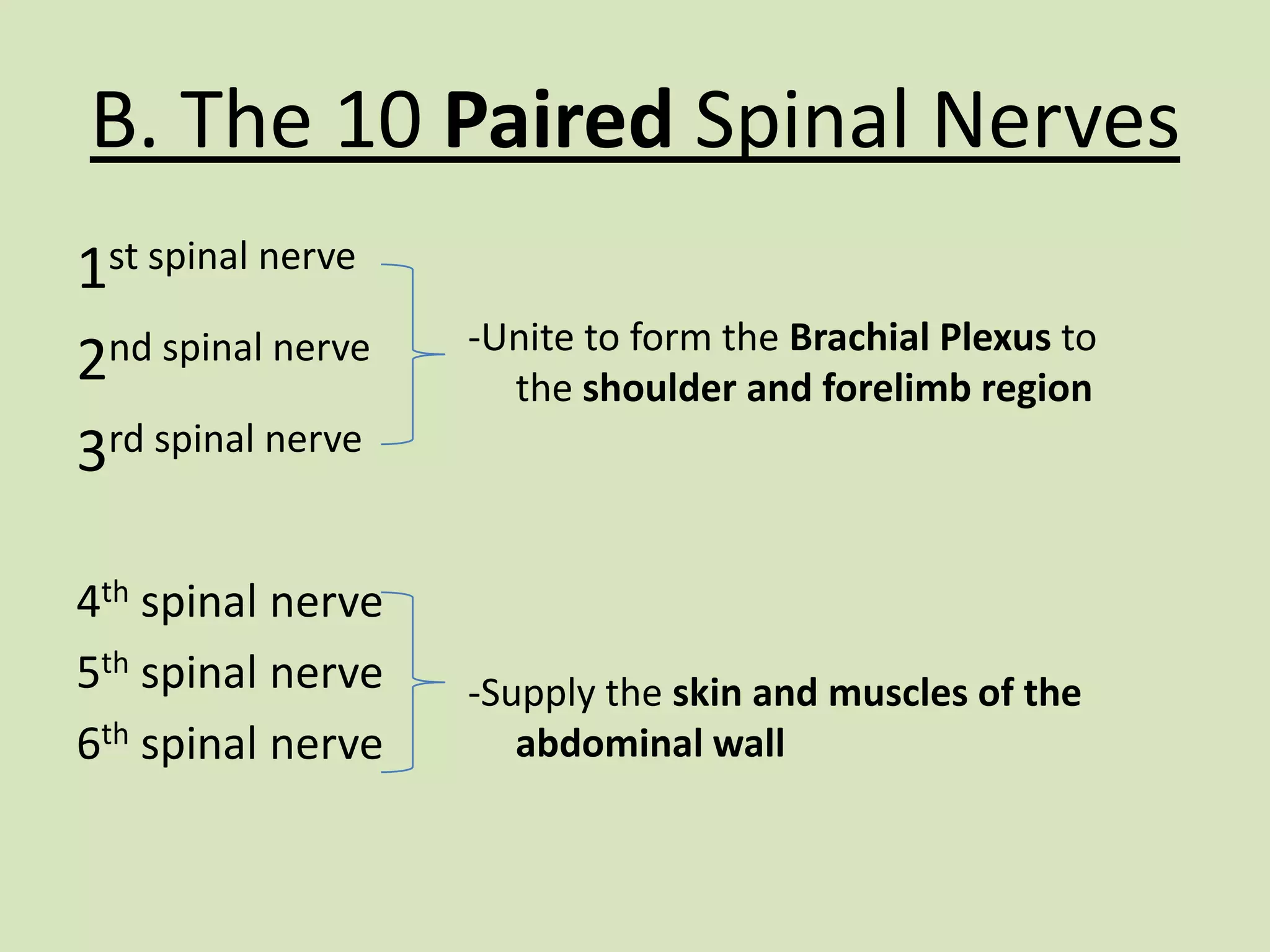
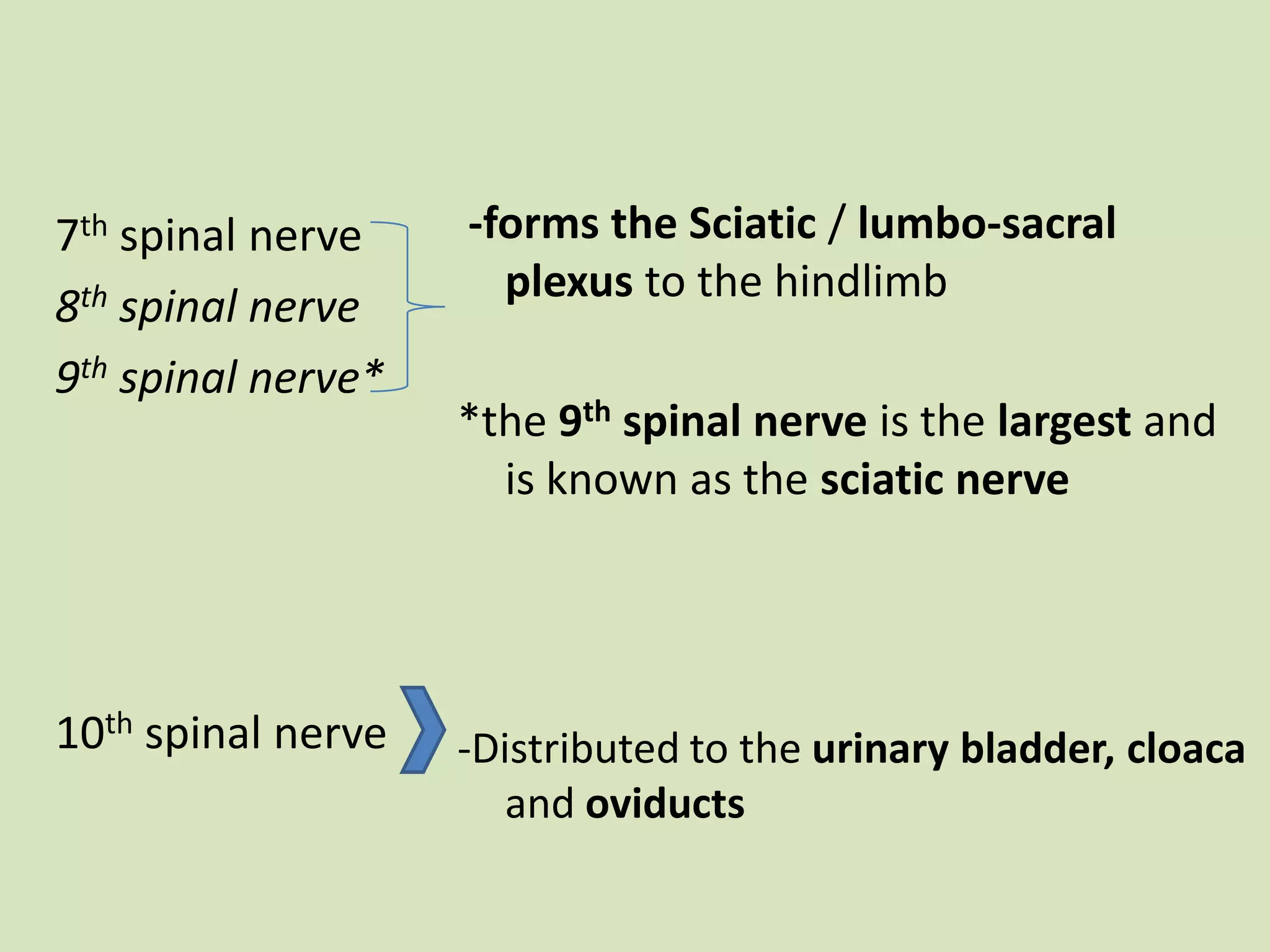
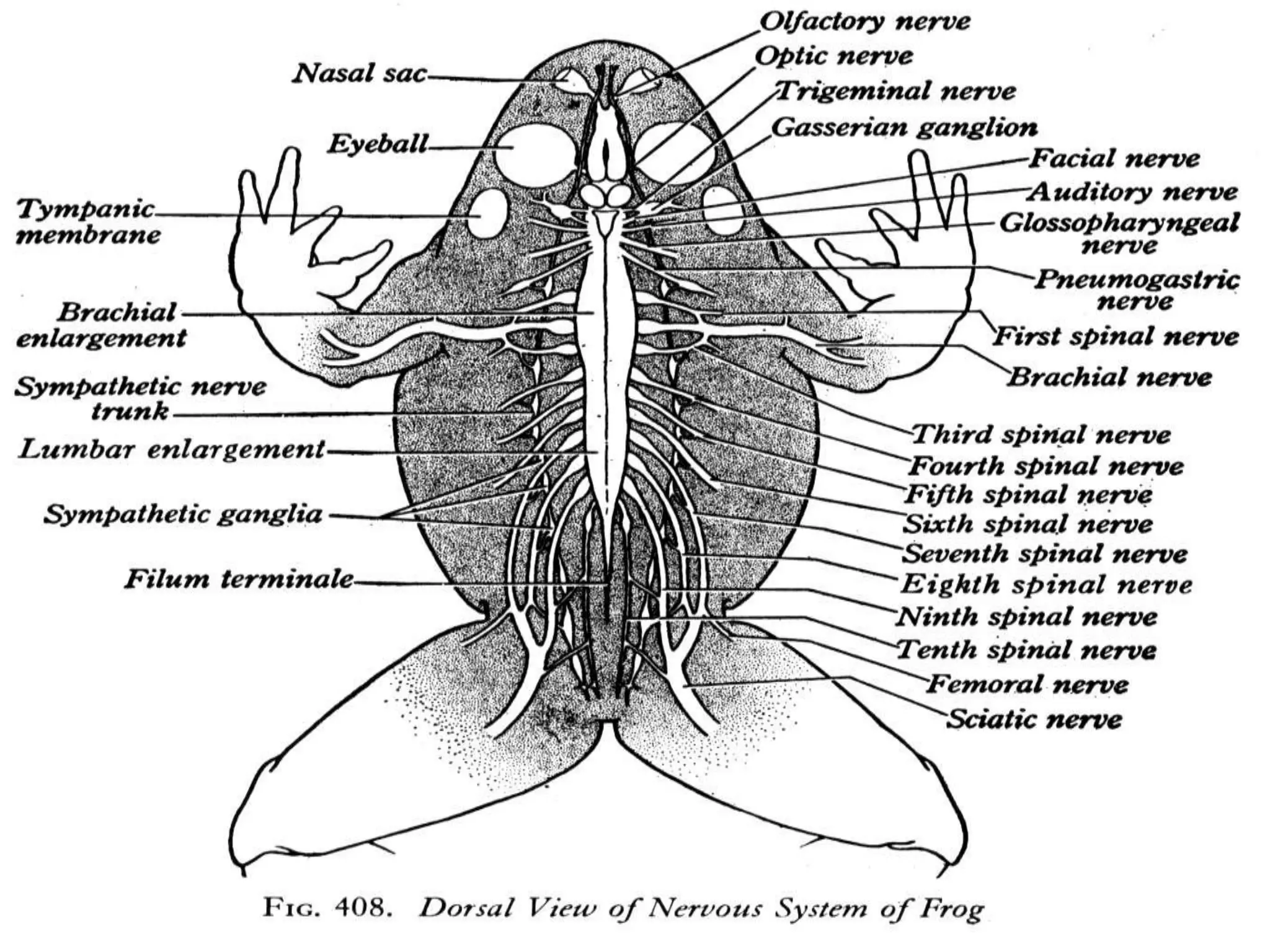
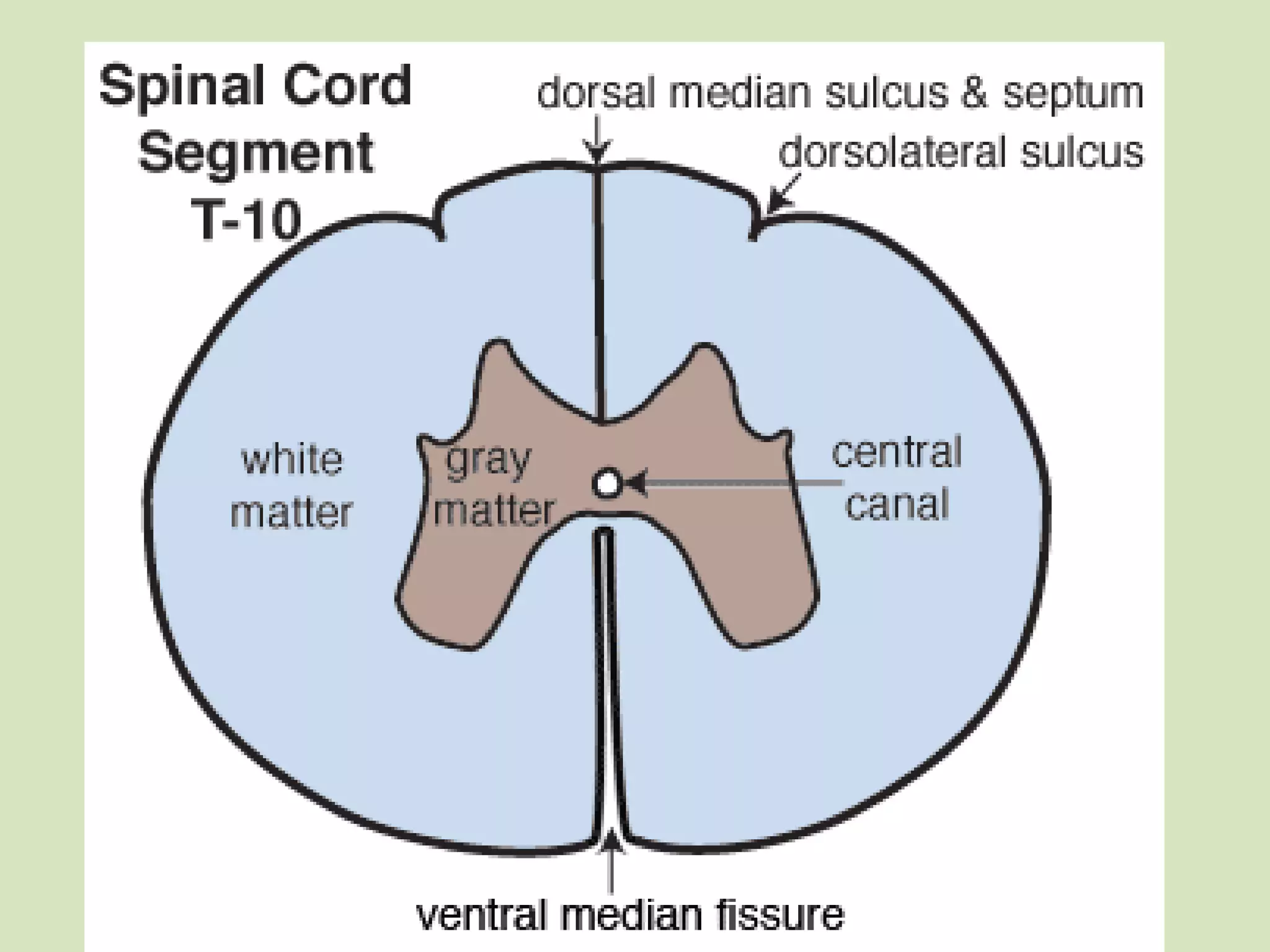
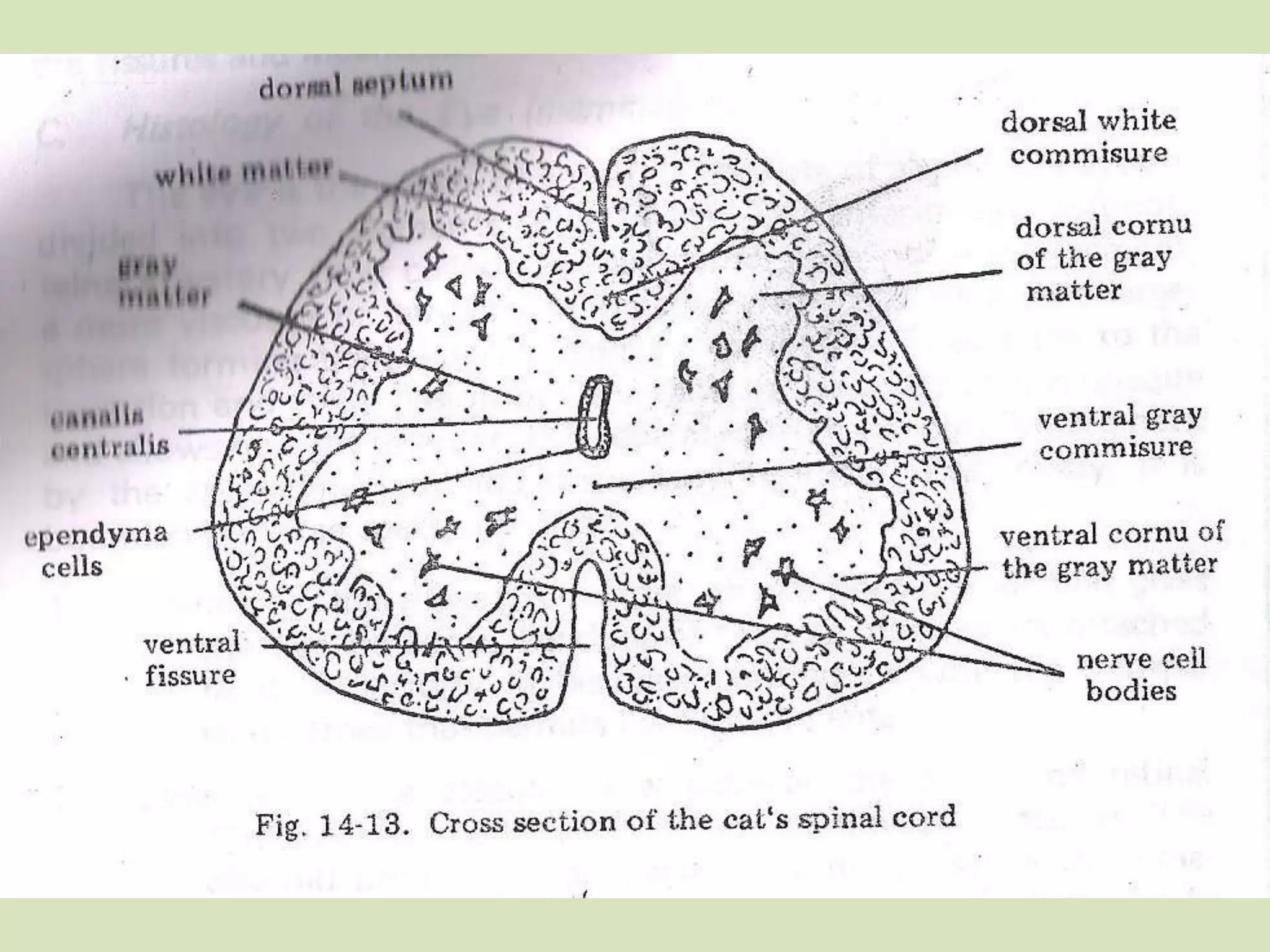
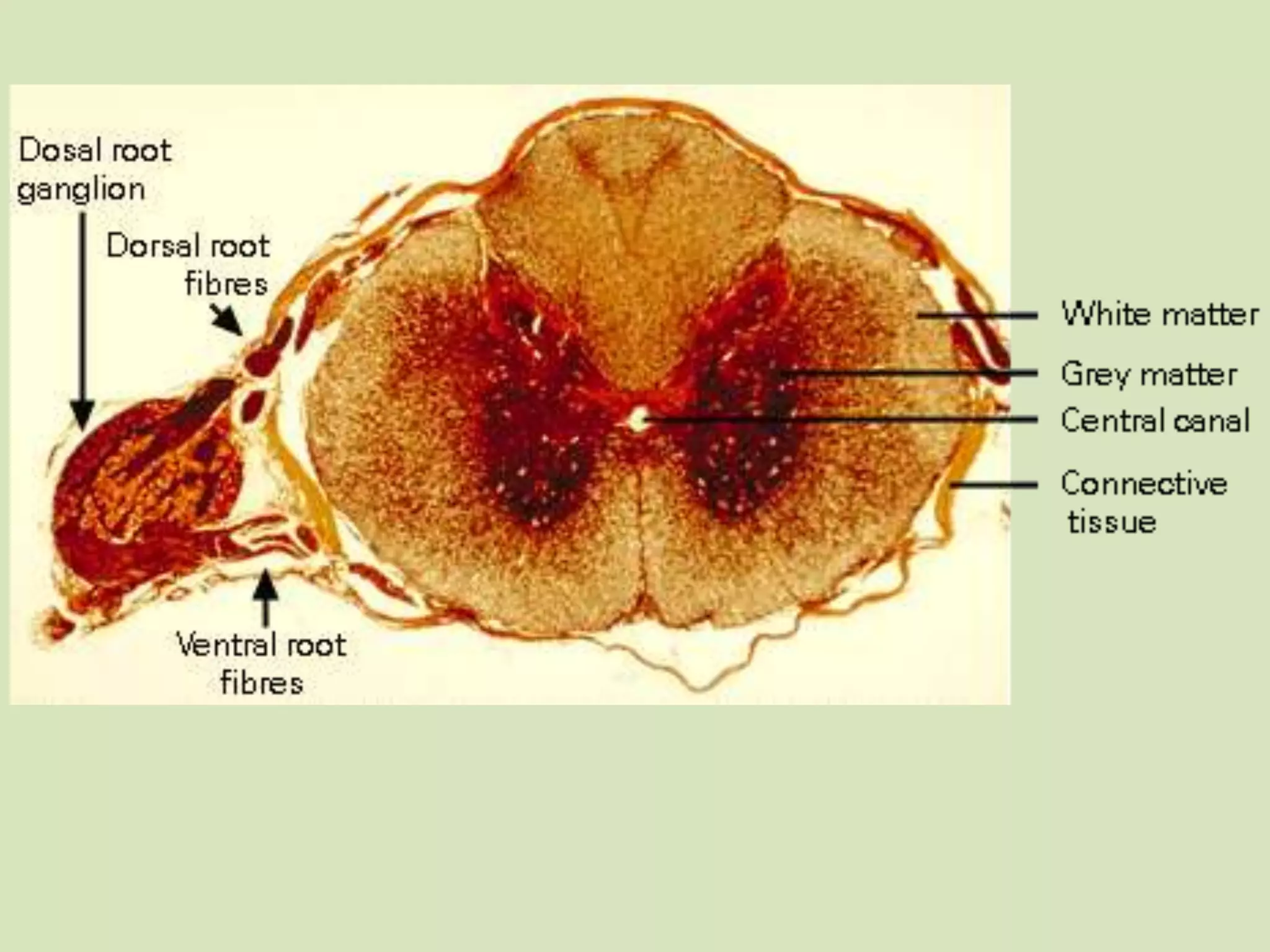
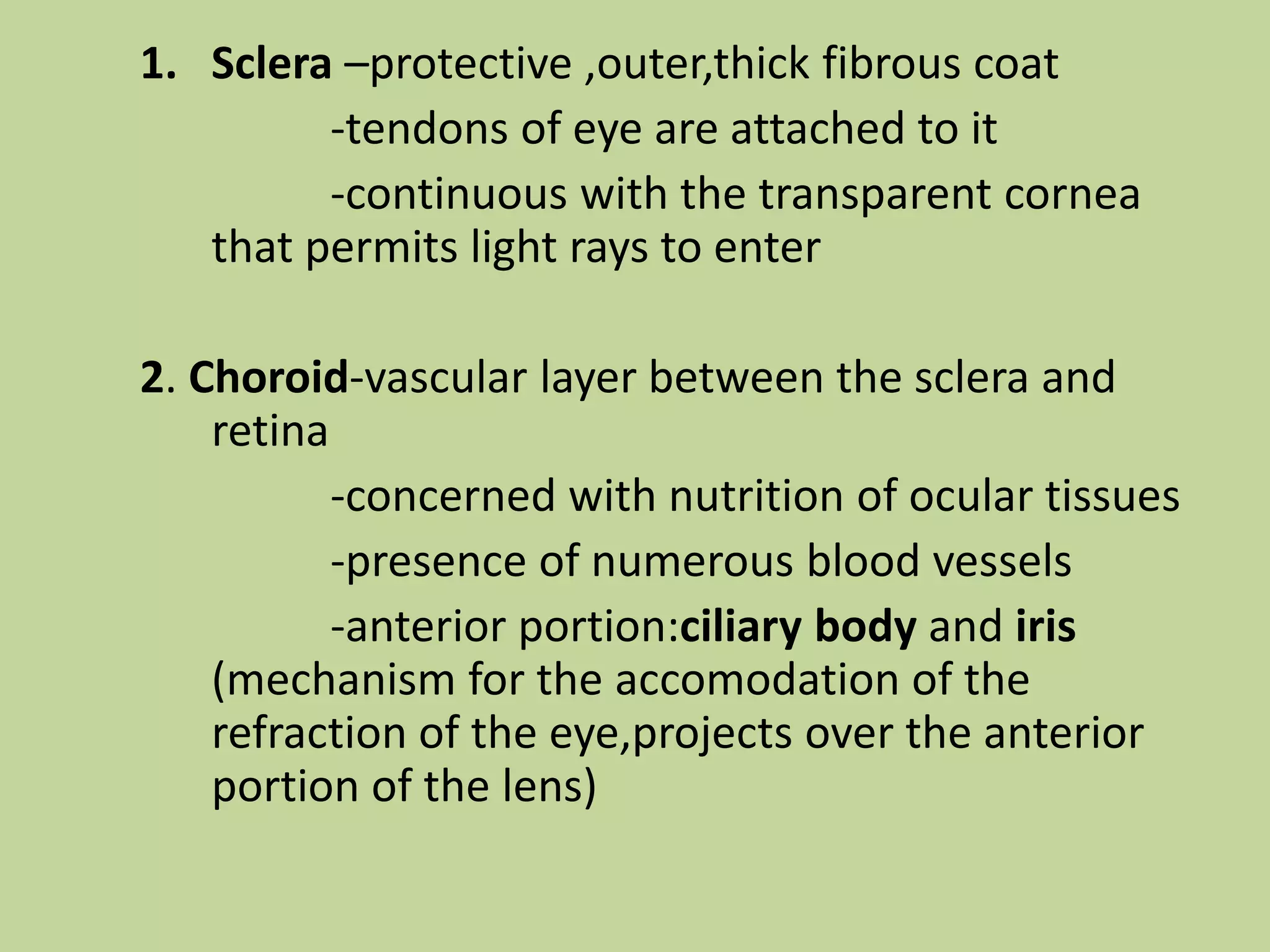
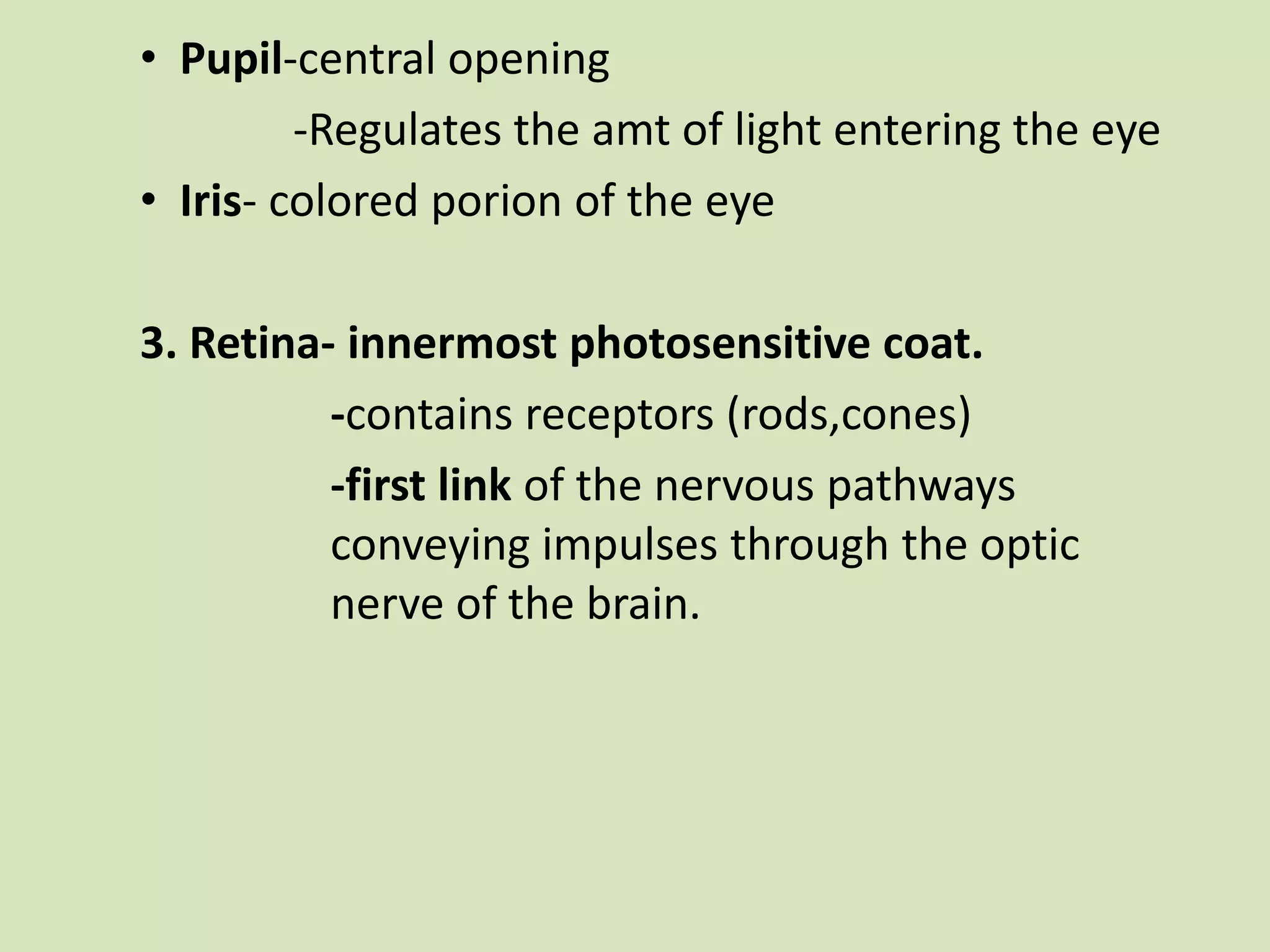
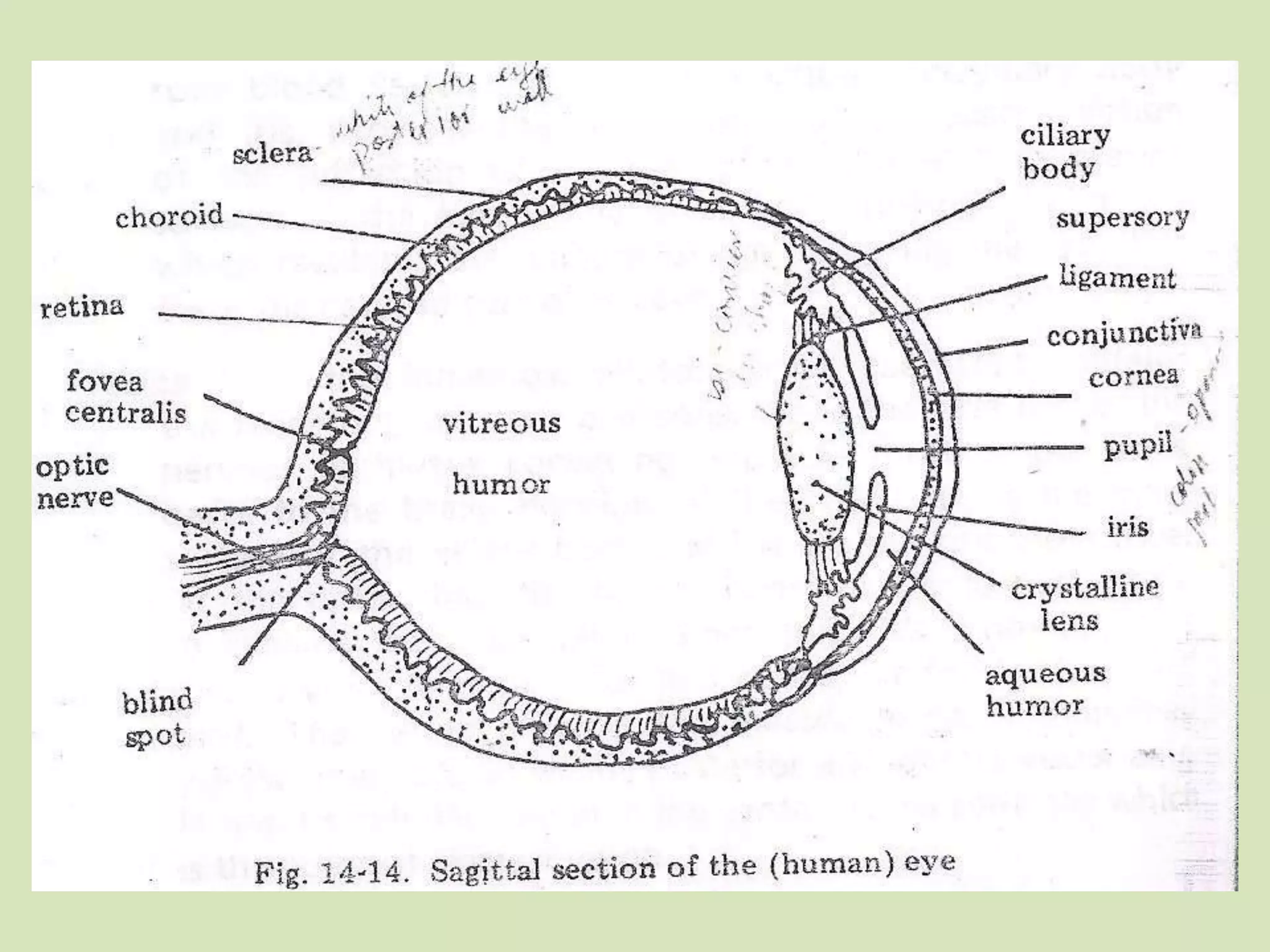
The document provides a detailed overview of the frog's nervous system, which is divided into the central, peripheral, and sympathetic systems. It highlights the structure and function of different parts, including the brain, spinal cord, and various cranial and spinal nerves. Additionally, it discusses the role of the nervous system in coordinating bodily functions and responding to stimuli.