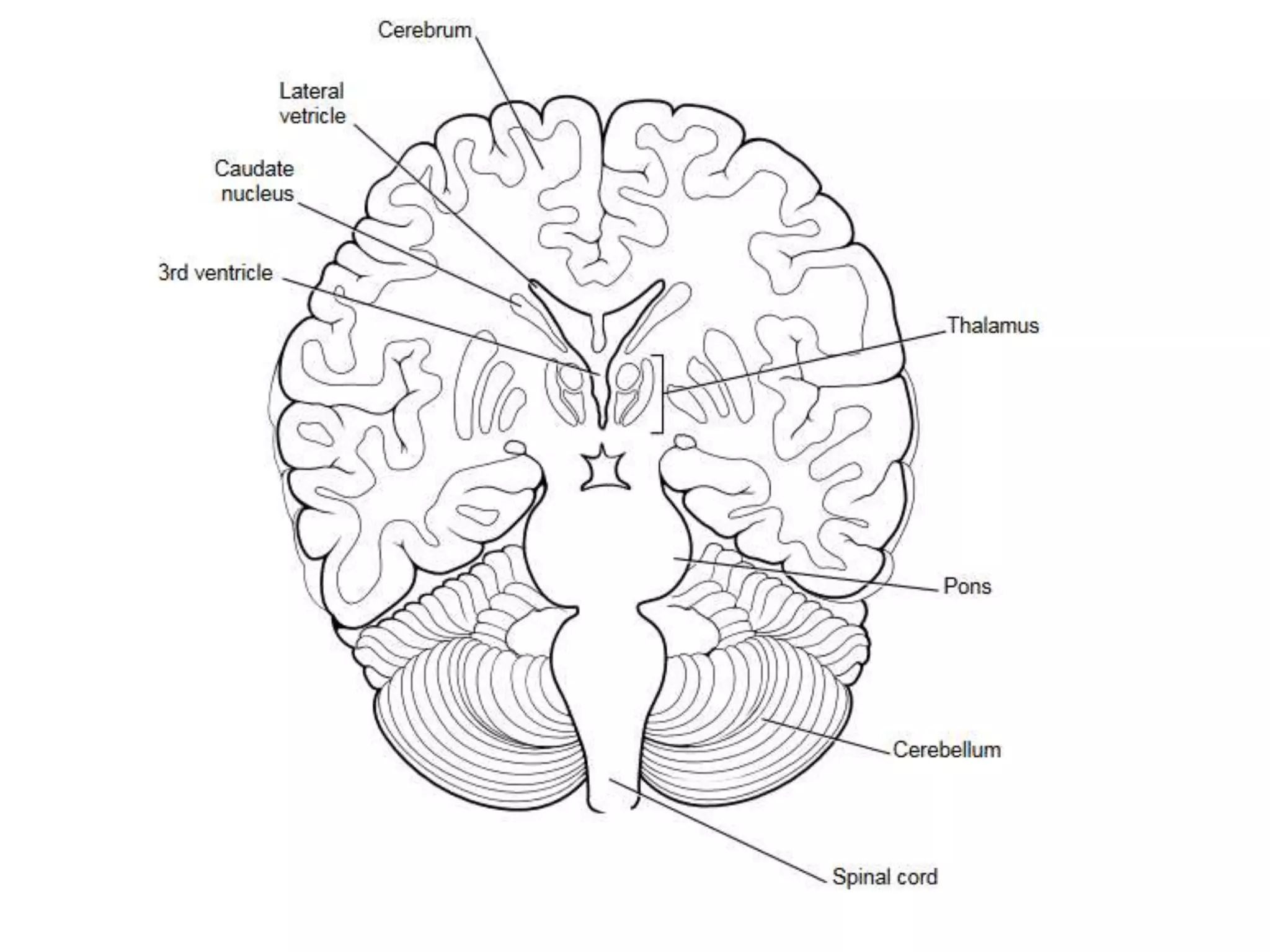
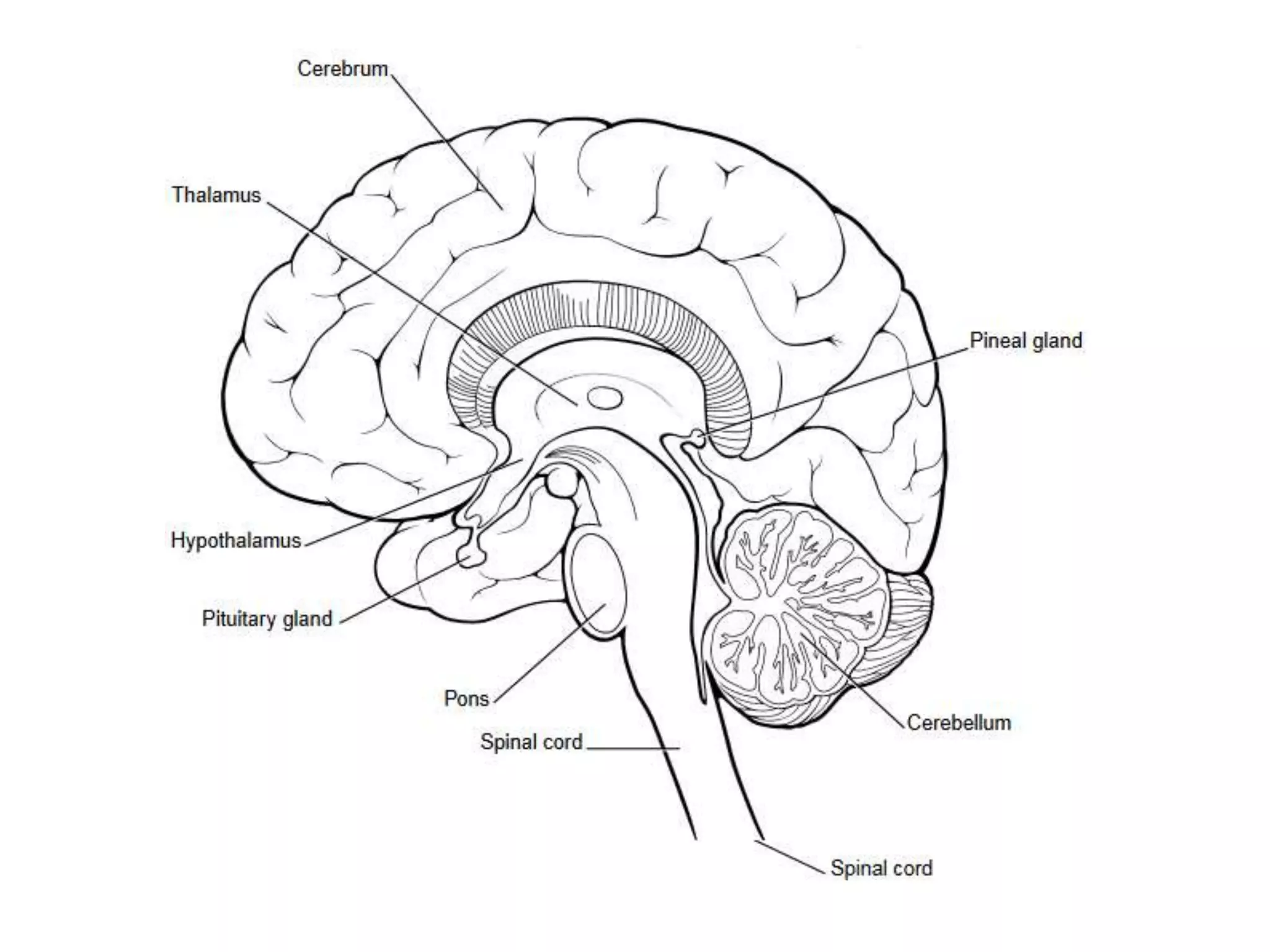
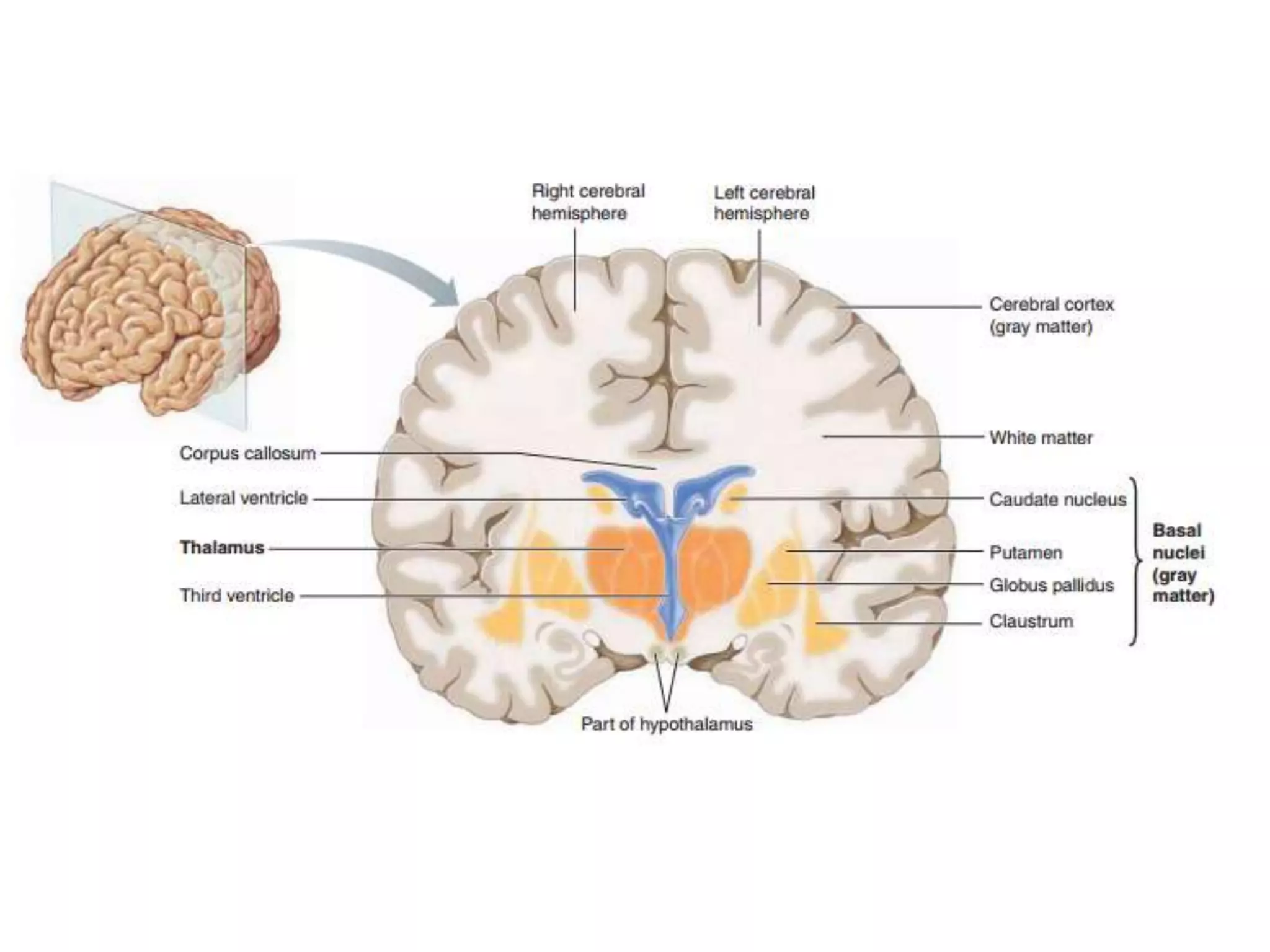
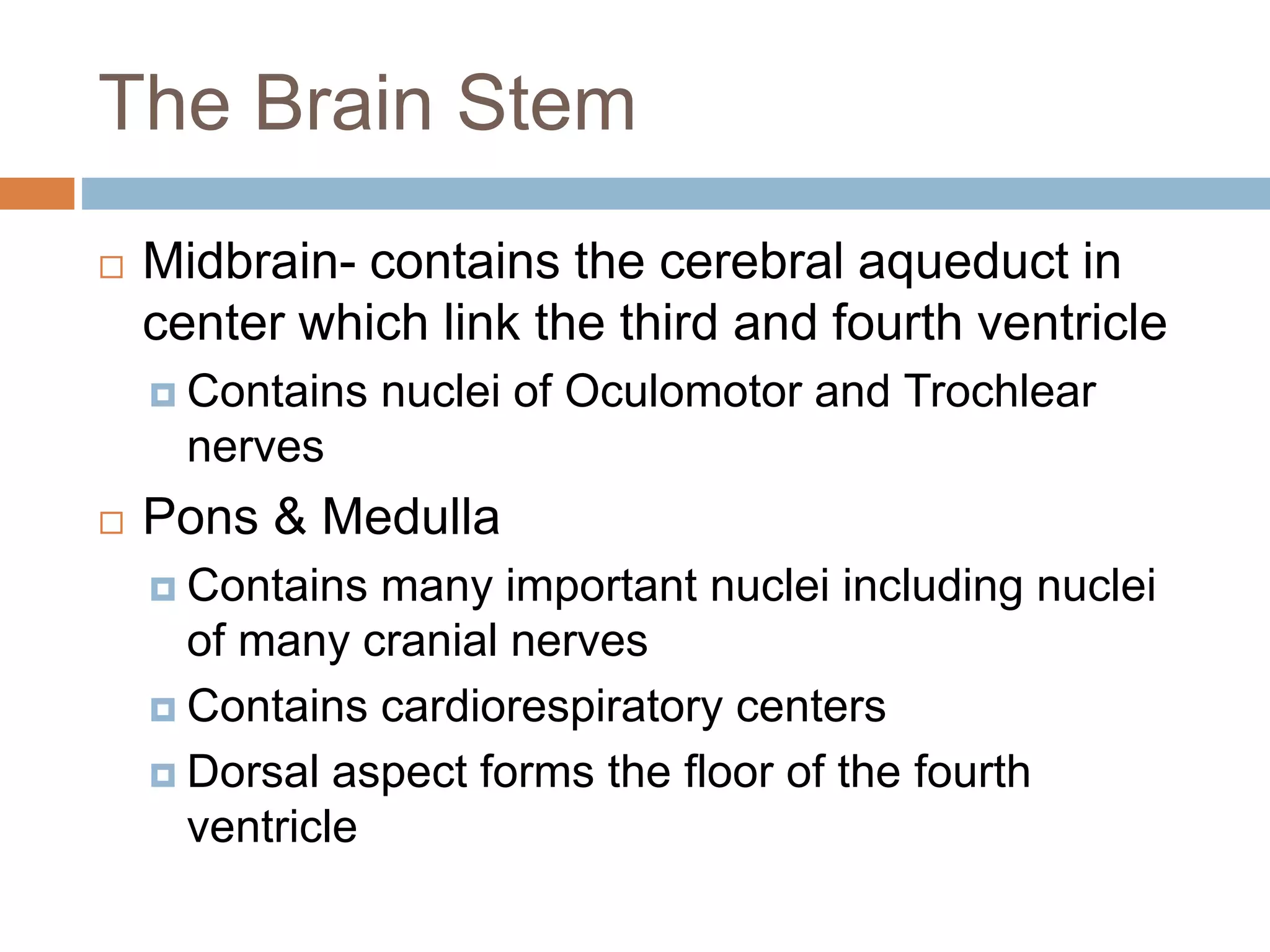
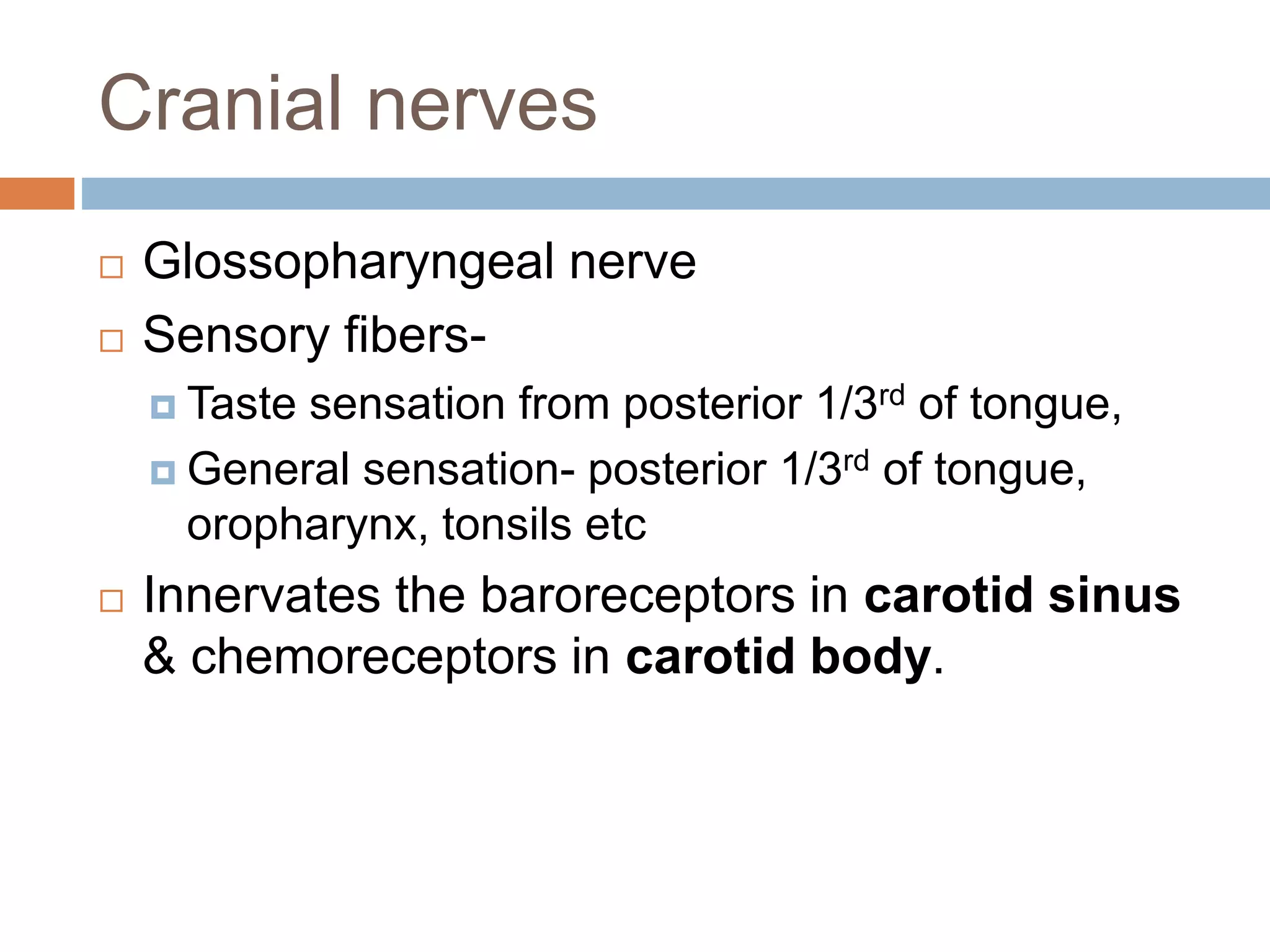
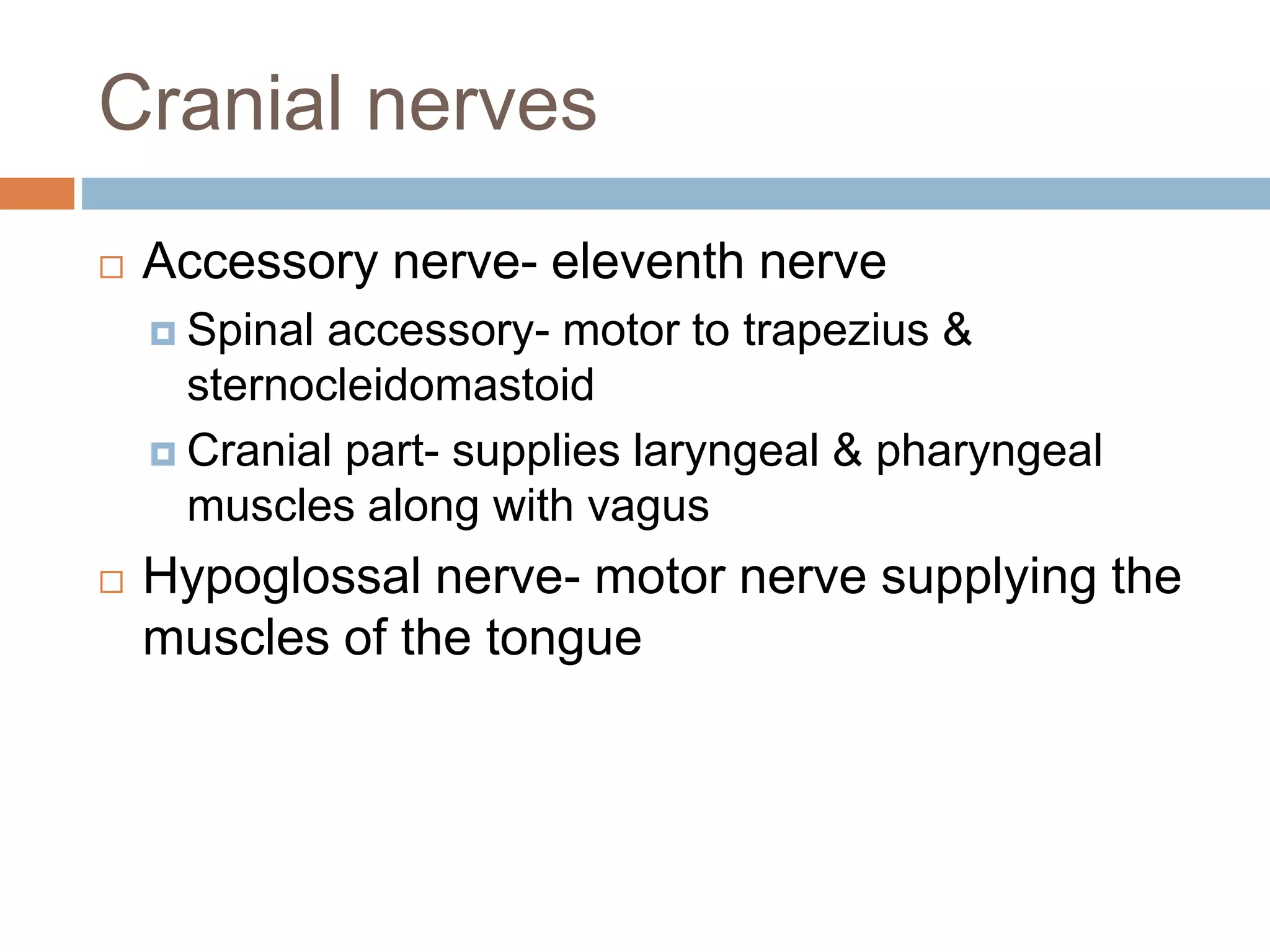
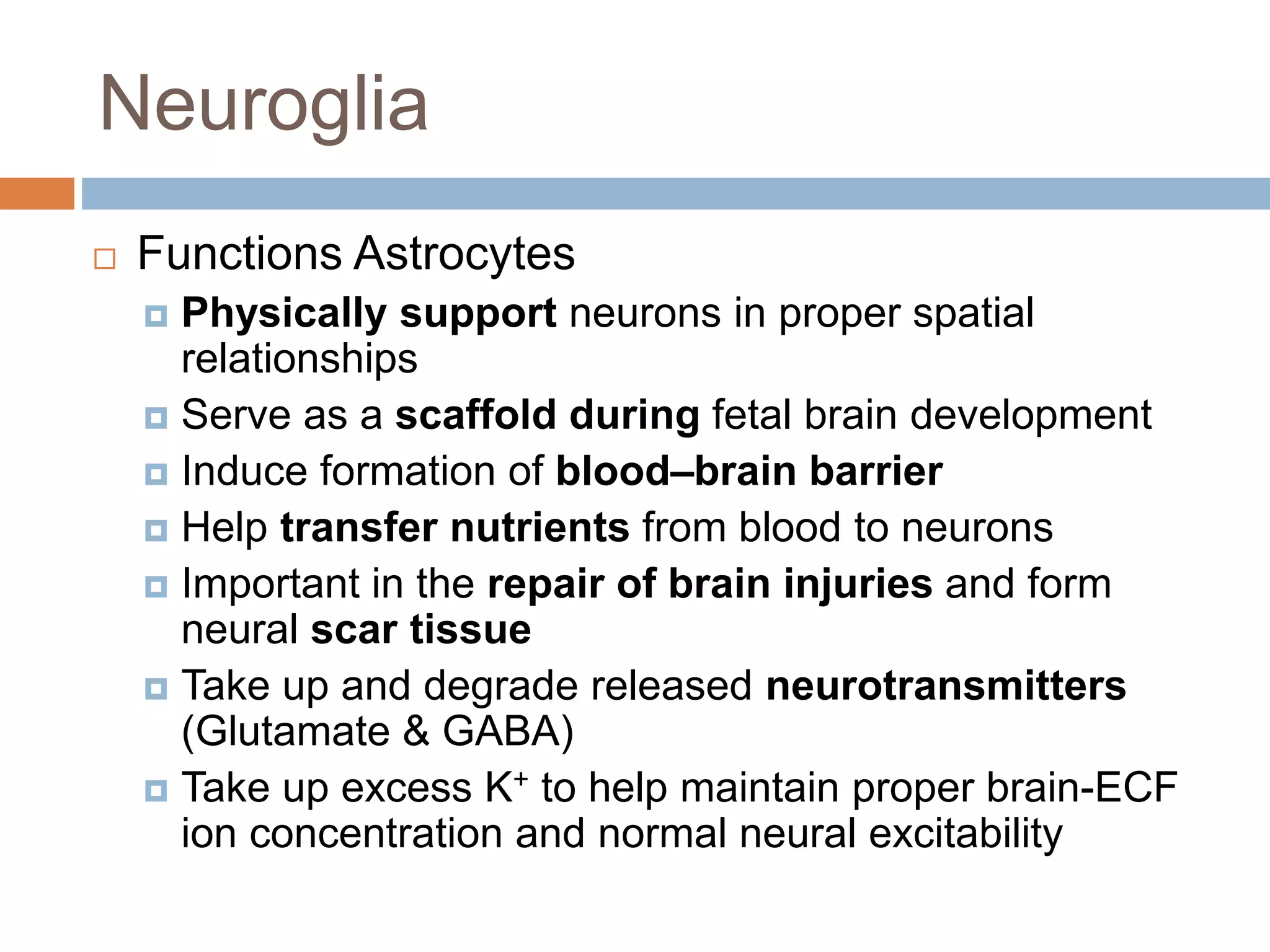
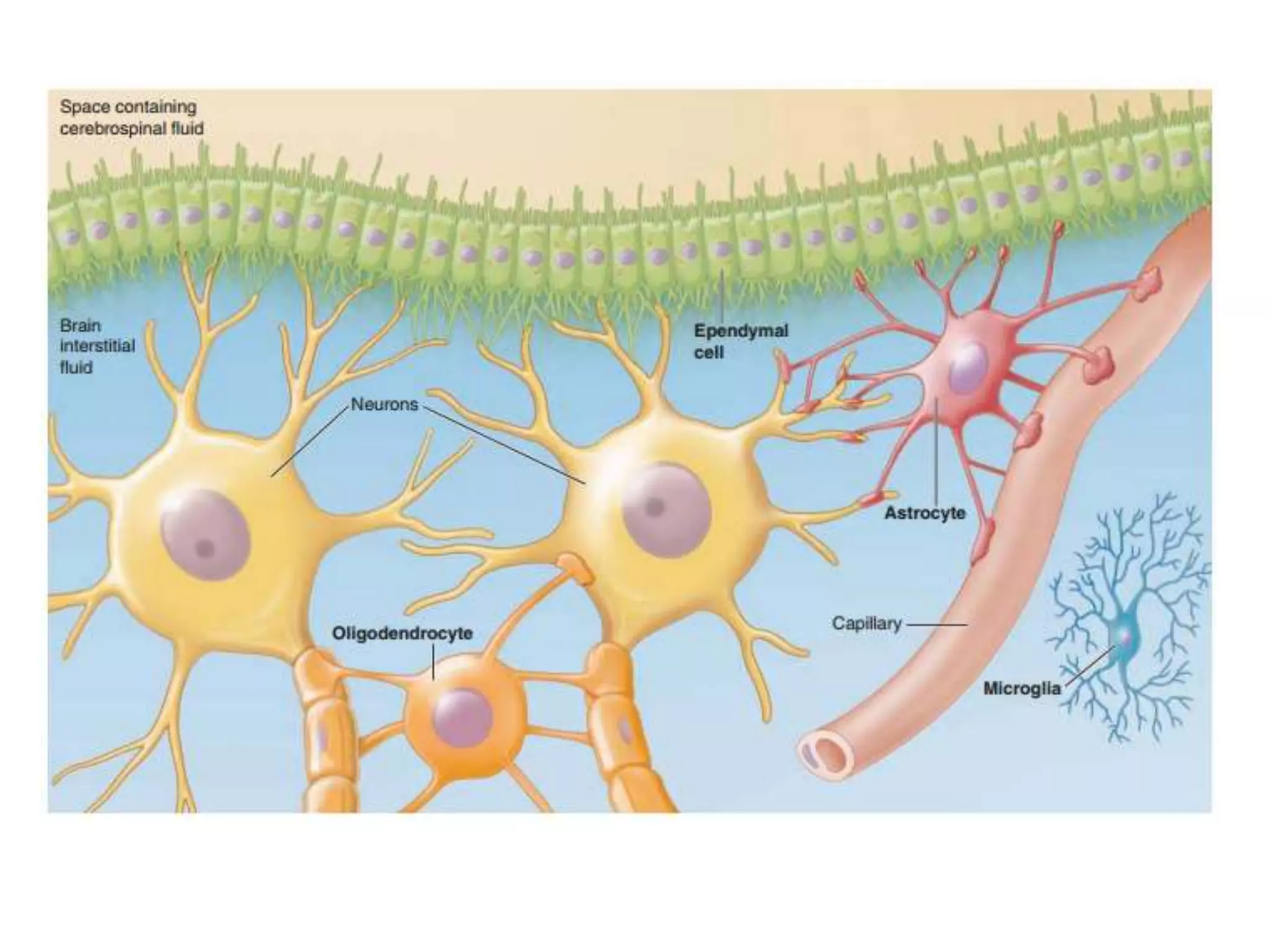
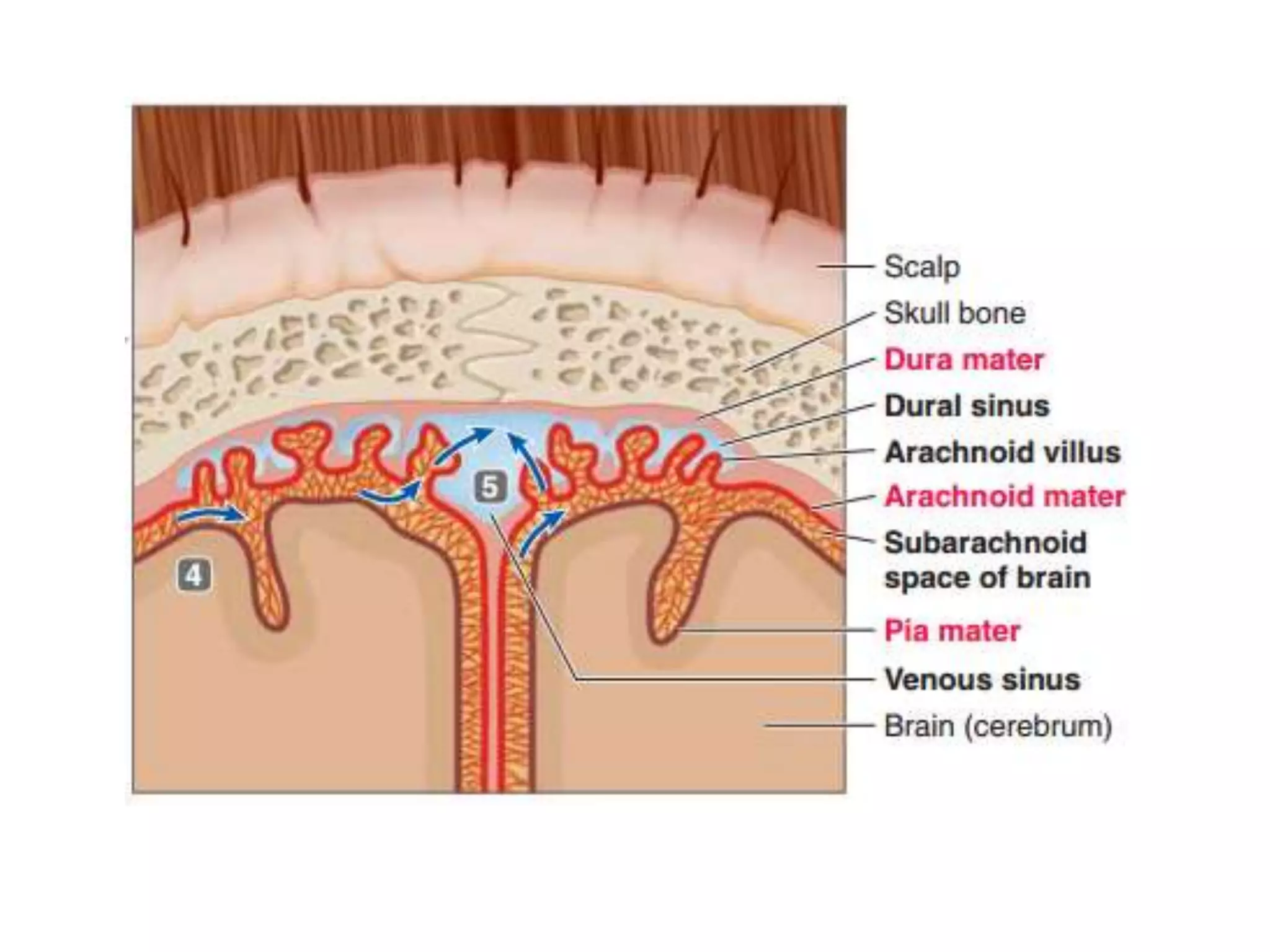
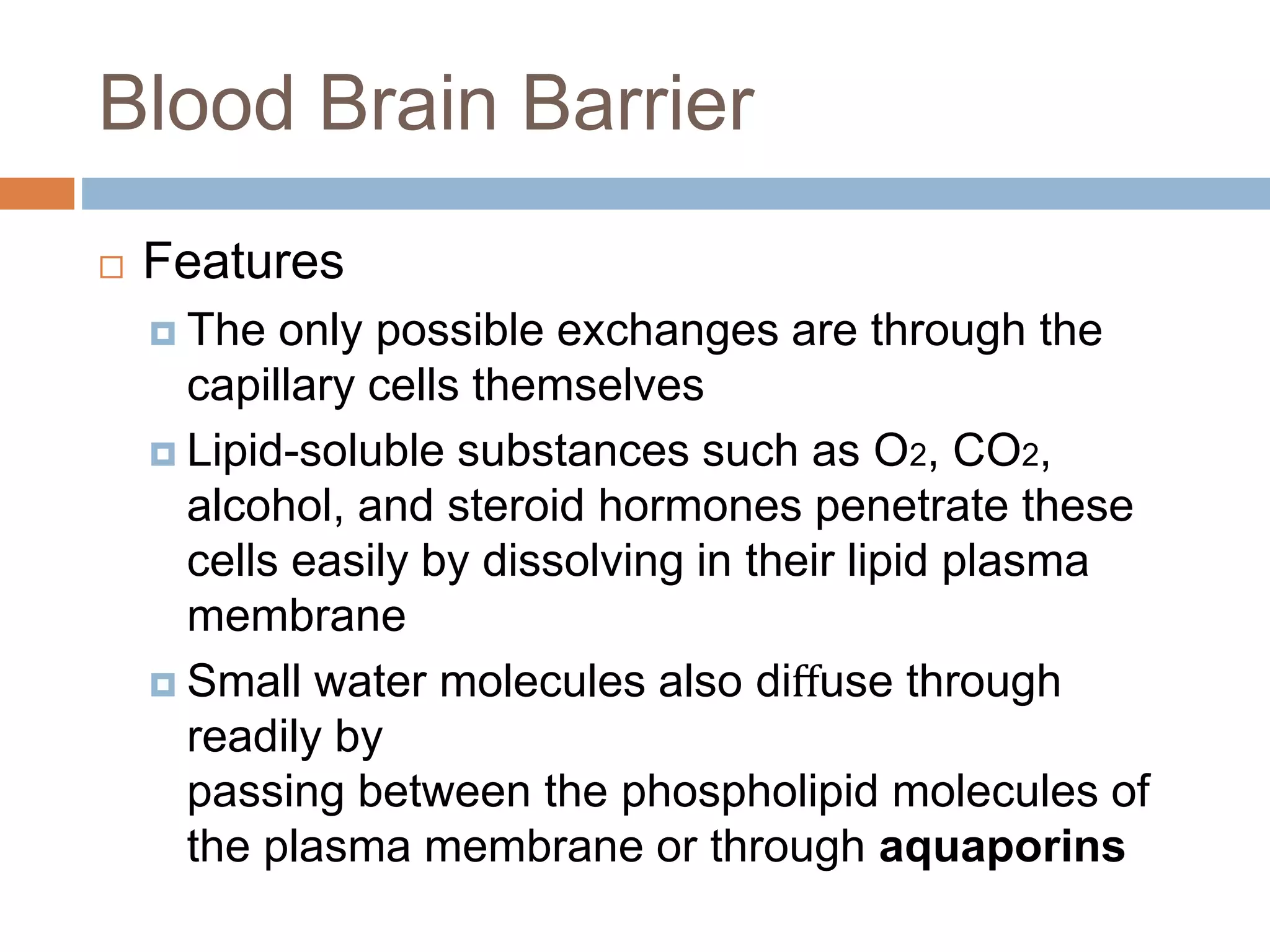
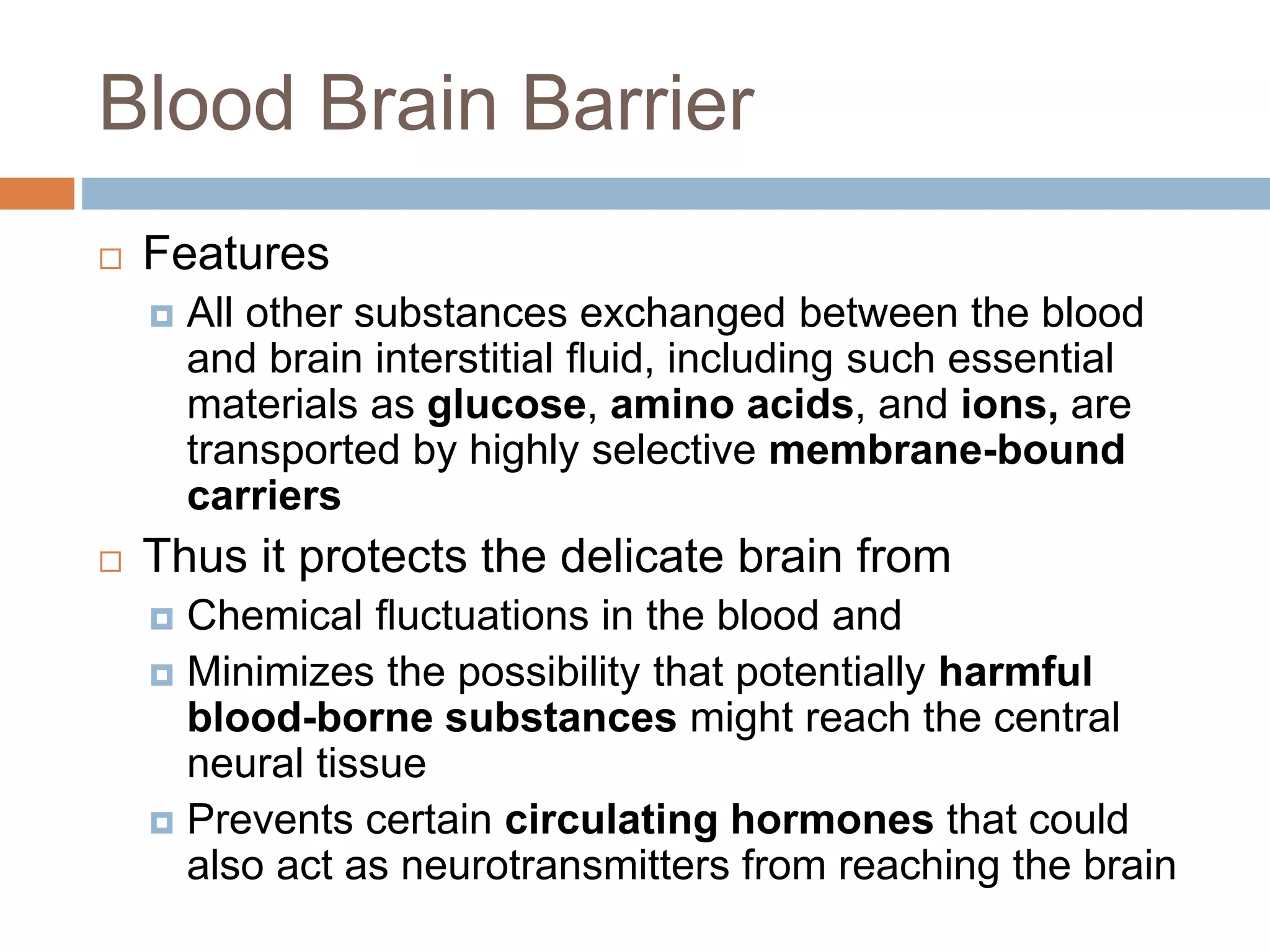
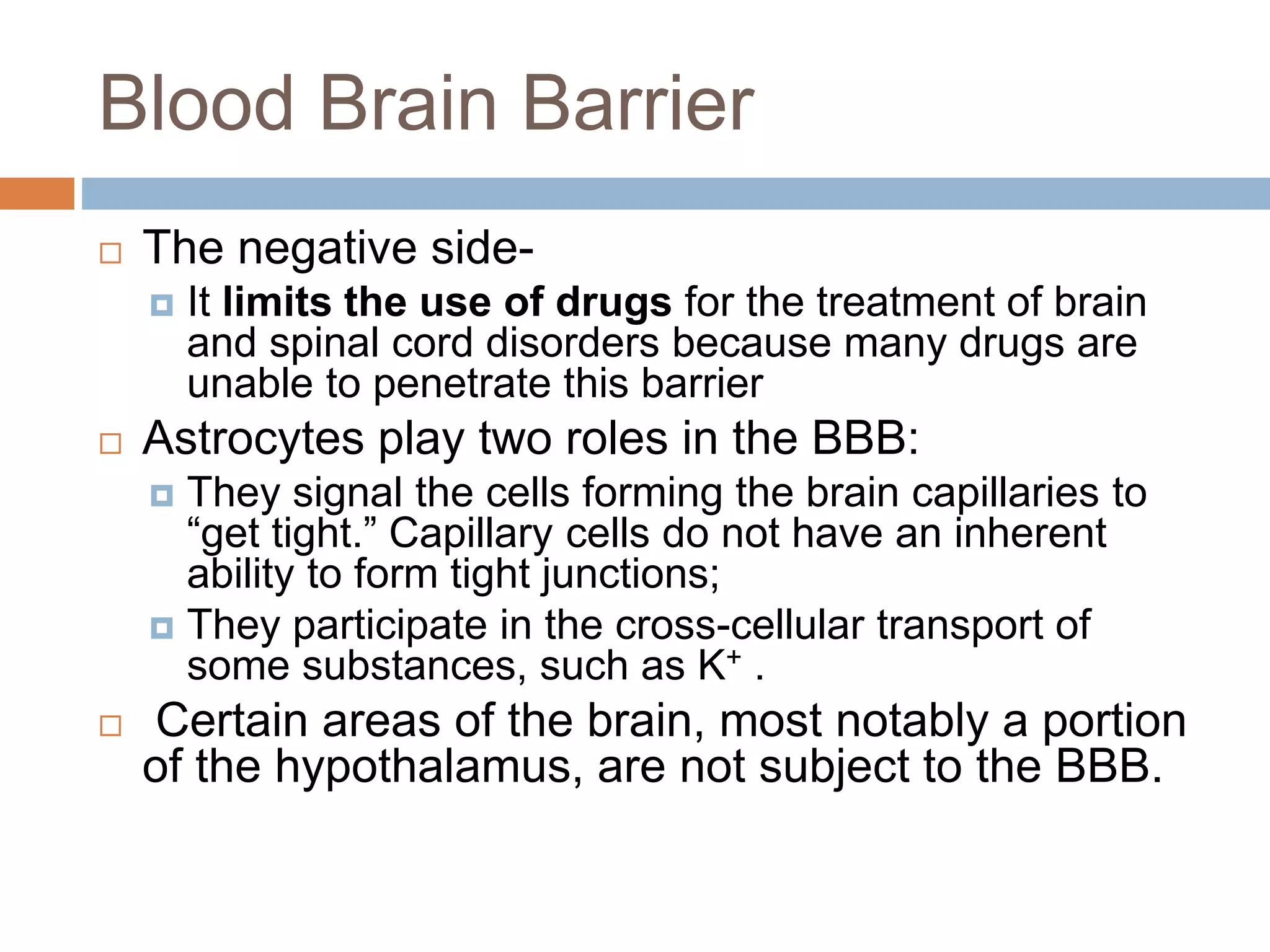
The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system (CNS; brain and spinal cord) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS is organized into the forebrain, brainstem, and cerebellum. It contains neurons and glial cells. The PNS connects the CNS to the body and is divided into somatic and autonomic divisions. It transmits signals between the CNS and peripheral organs.