Embed presentation
Downloaded 814 times








![Bachman (1990)REMEMBERLocutionaryact: Performance of an utterance“It’s cold in here.”Illocutionary act: Intended meaning[The windows is open. So I should close it.]Perlocutionary act: Consequences of the utterance (whether intended or not)[Someone closes the window.]Dialect](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/communicativecompetence-101203025413-phpapp01/85/Communicative-competence-16-320.jpg)

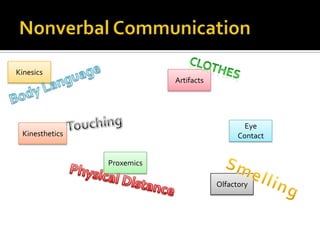

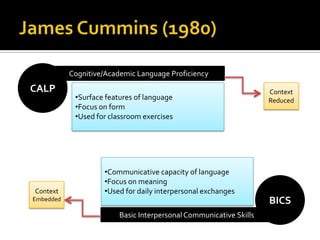
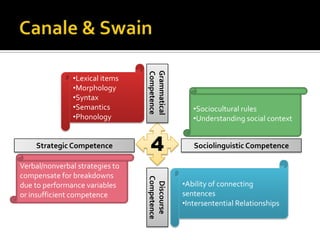
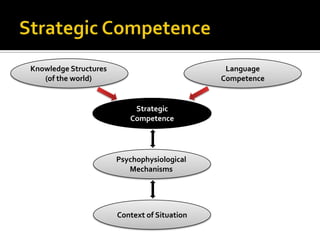
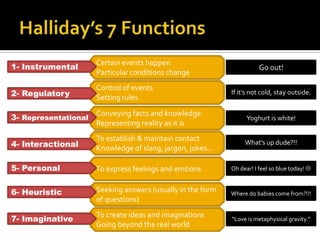
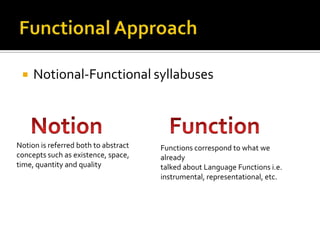
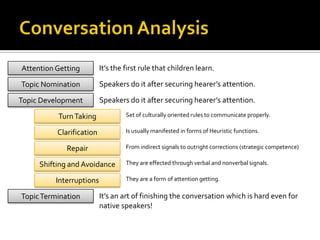
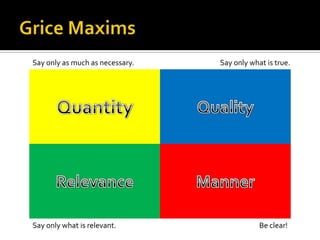
Communicative competence refers to an individual's pragmatic ability to use language effectively and appropriately based on context. It involves multiple dimensions including grammatical competence, sociolinguistic competence, discourse competence, and strategic competence. Theorists like Hymes, Savignon, and Cummins contributed to the understanding of communicative competence, distinguishing between basic interpersonal skills and cognitive academic language proficiency. Pragmatics is the study of how context contributes to meaning. It involves sociopragmatics, pragmalinguistics, and examines language use across situations, cultures, and through nonverbal channels.















![Bachman (1990)REMEMBERLocutionaryact: Performance of an utterance“It’s cold in here.”Illocutionary act: Intended meaning[The windows is open. So I should close it.]Perlocutionary act: Consequences of the utterance (whether intended or not)[Someone closes the window.]Dialect](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/communicativecompetence-101203025413-phpapp01/85/Communicative-competence-16-320.jpg)


