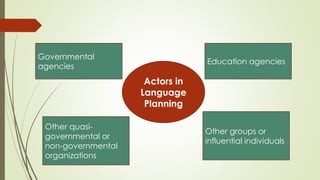
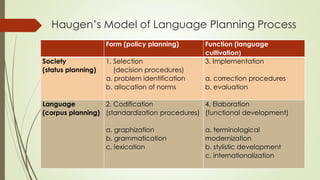
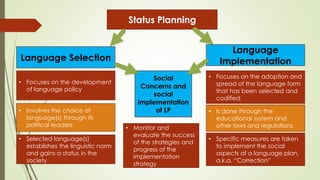
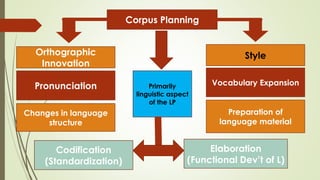
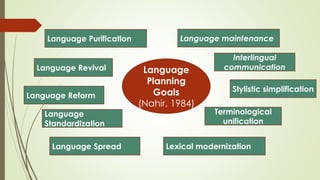
Language planning involves systematic efforts to modify language use in a community, while language policy refers to the body of ideas, laws and regulations around planned linguistic changes. There are two levels of language planning - macro (involving governments and complex changes) and micro (focusing on specific issues). Key actors in language planning include government agencies, education agencies, quasi-governmental organizations, and other influential groups. Activities generally involve status planning (modifying a language's use) and corpus planning (modifying the language itself), with the overall goal of language selection, codification, elaboration and implementation. Codification specifically refers to standardizing a language's orthography, grammar and lexicon.