This document discusses the connection between verbal communication and culture. It covers several topics:
1) Human languages have distinctive features like arbitrariness and creativity as well as rule patterns for phonology, morphology, syntax, semantics and pragmatics.
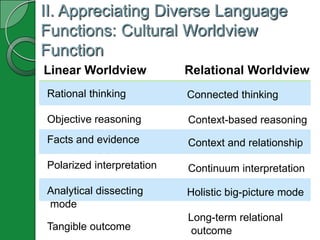
2) Language serves cultural worldview, social reality, cognitive and group membership functions. It also shapes social change. For example, linear vs. relational worldviews influence logical reasoning styles.
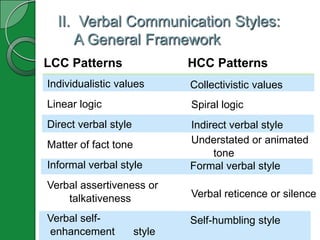
3) Verbal communication styles differ between low-context cultures (LCC) and high-context cultures (HCC). LCC uses direct styles while HCC uses more indirect and situation-dependent styles.
4) Intercultural communication requires empathy, parap