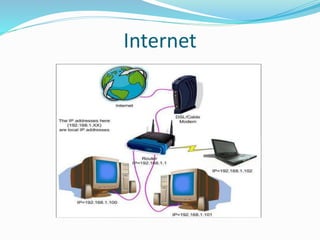
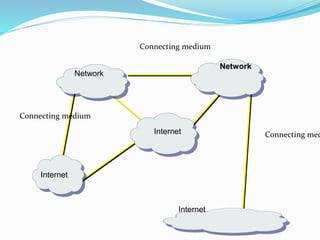
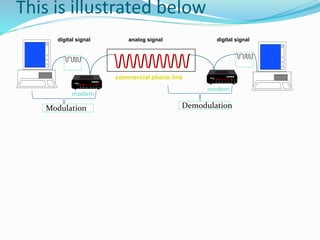
The document discusses the history and development of the internet. It began in the 1960s as ARPANET, a small network connecting computers funded by the US Department of Defense. In the 1970s, Vint Cerf and Bob Kahn created TCP/IP, the fundamental communication protocols that allowed different networks to interconnect and form the internet. Their work laid the foundation for how data is transmitted over the global network of interconnected networks that we now know as the internet.