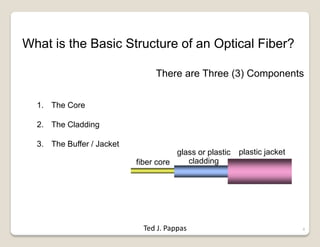
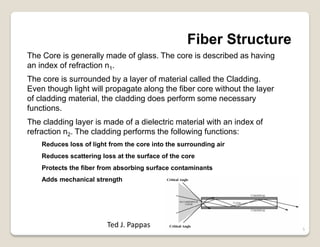
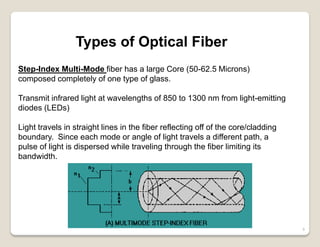
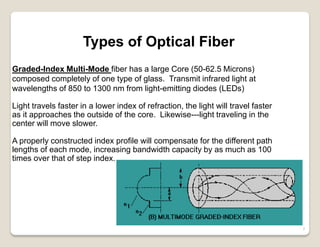
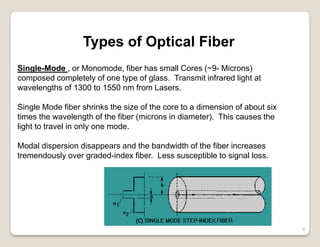
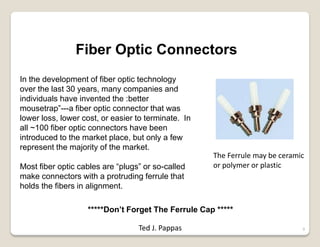
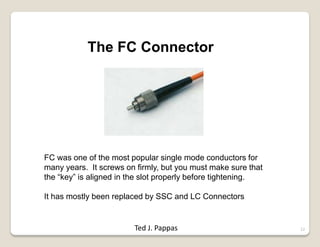
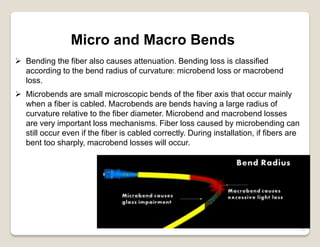
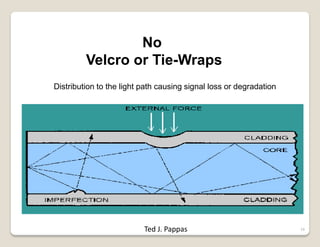
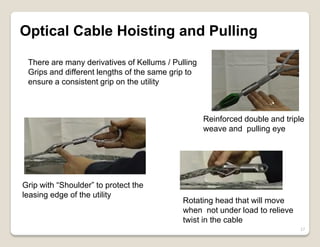
Fiber optic lines are very thin strands of glass that can carry signals in the form of light. Fiber optic cables are being used more by telecommunications companies because they are cheaper to manufacture than copper wires, thinner yet can carry more data, experience less signal degradation over distance, and allow signals to be transmitted without interference between fibers. The basic components of a fiber optic line are the core that carries the light, a cladding layer around the core, and a protective plastic jacket. There are different types of fiber optic lines that carry signals in different ways depending on the size of the core and structure of the glass. Fiber optic connections also come in different types but must hold the fiber ends precisely aligned to minimize signal loss.