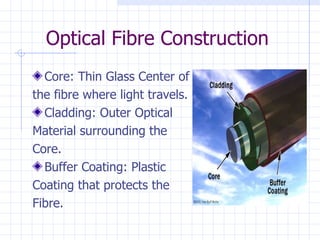
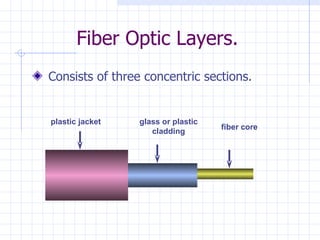
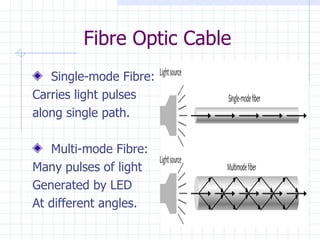
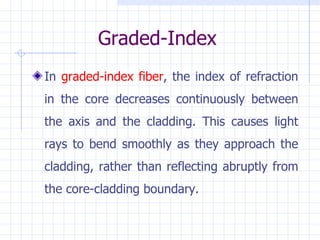
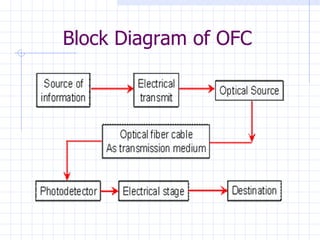
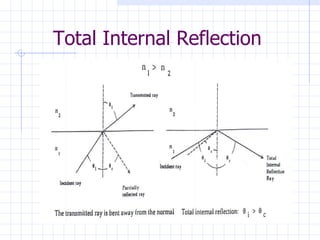
The document summarizes Tarun Kumar Matriaya's summer training internship with North Central Railways in Allahabad from June 30 to July 30, 2009. It provides an overview of optical fiber communication and its uses in Indian Railways. Optical fibers have advantages over other communication methods like being thinner, less expensive, and having high bandwidth. Indian Railways uses optical fiber communication to optimize train scheduling, measure speeds, distribute signals, and monitor traffic lights.