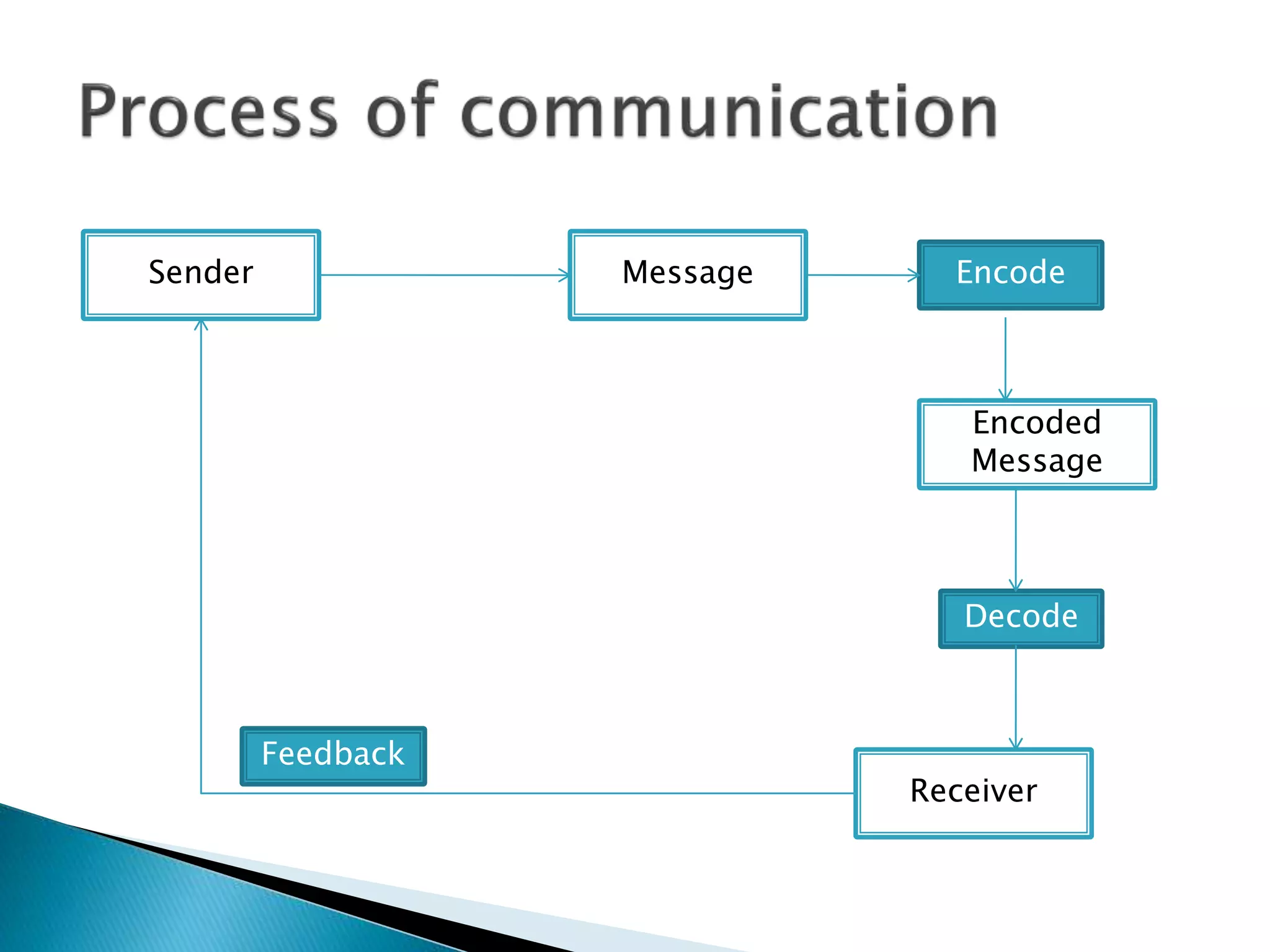
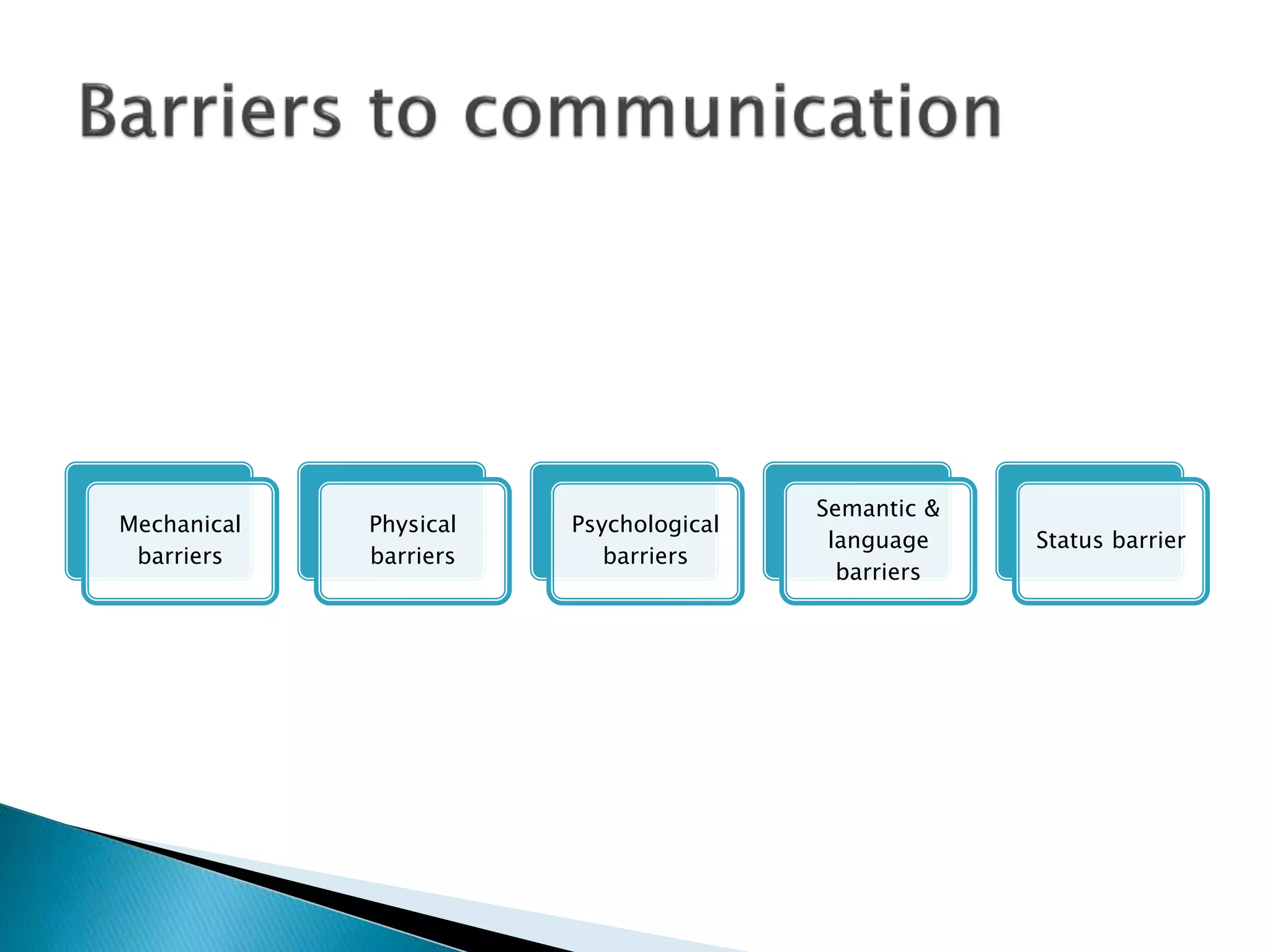
This document discusses communication and the communication process. It defines communication as the sharing of information, ideas, opinions, emotions, facts, or attitudes. The communication process involves a sender encoding a message, transmitting it to a receiver who decodes it. Communication is an ongoing, social activity that aims for mutual understanding through feedback and response. Barriers to effective communication can be mechanical, physical, psychological, semantic, related to language or status. The document also discusses ways to improve communication such as listening, obtaining feedback, simplifying messages, repetition, using an appropriate environment, and overcoming cultural differences. Benefits of good communication include faster problem solving, better decision making, improved stakeholder response, increased productivity, and stronger business relationships.