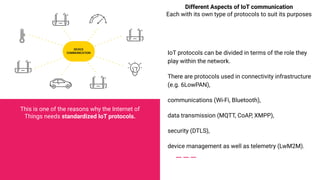
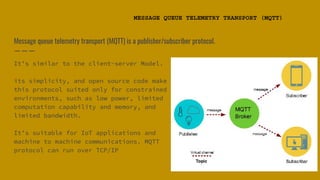
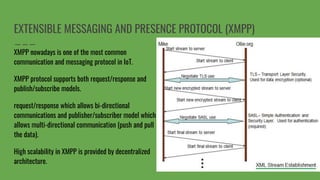
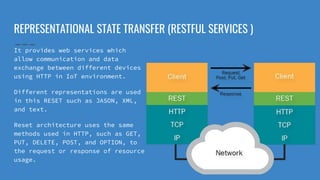
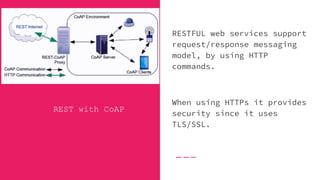
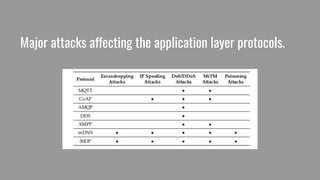
The document introduces Jigar Makhija, an associate software engineer with expertise in IoT application protocols and a background in computer applications and information technology. It emphasizes the importance of IoT protocols for communication between connected devices, detailing various protocols such as CoAP, MQTT, and XMPP, and discussing their roles in ensuring effective communication in constrained environments. The document also highlights security vulnerabilities in application-layer protocols and ongoing research for mitigation measures.