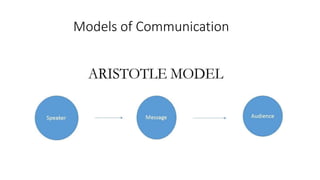
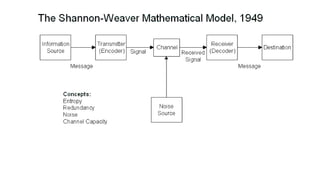
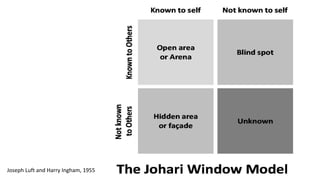
This document provides an overview of the basics of communication. It defines communication as the process of sharing information, ideas, thoughts, and feelings from a source to a receiver through various mediums to develop a common understanding. The document discusses models of communication, types of verbal and nonverbal communication, levels of communication from intrapersonal to mass communication. It also outlines various barriers to effective communication such as environmental, semantic, cultural, psychological, perception, organizational, gender differences, and choosing the wrong communication medium. The document serves to introduce fundamental concepts about the nature and process of communication.