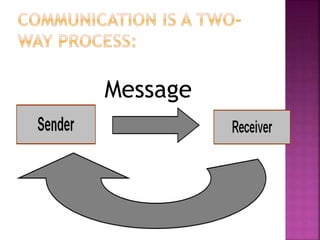
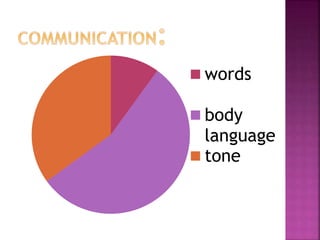
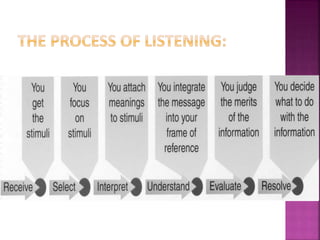
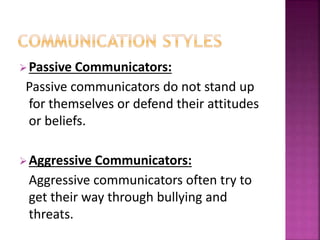
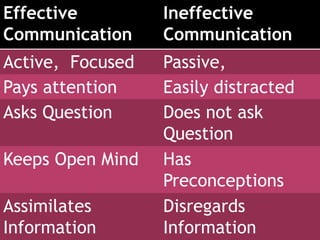
This document discusses communication skills, including defining communication, verbal and nonverbal communication, listening skills, communication styles, barriers to communication, and improving communication abilities. Effective communication involves clearly conveying a message through various channels while understanding the audience and context. Barriers like language or cultural differences can interfere with successful communication but can be overcome through awareness and relationship building.