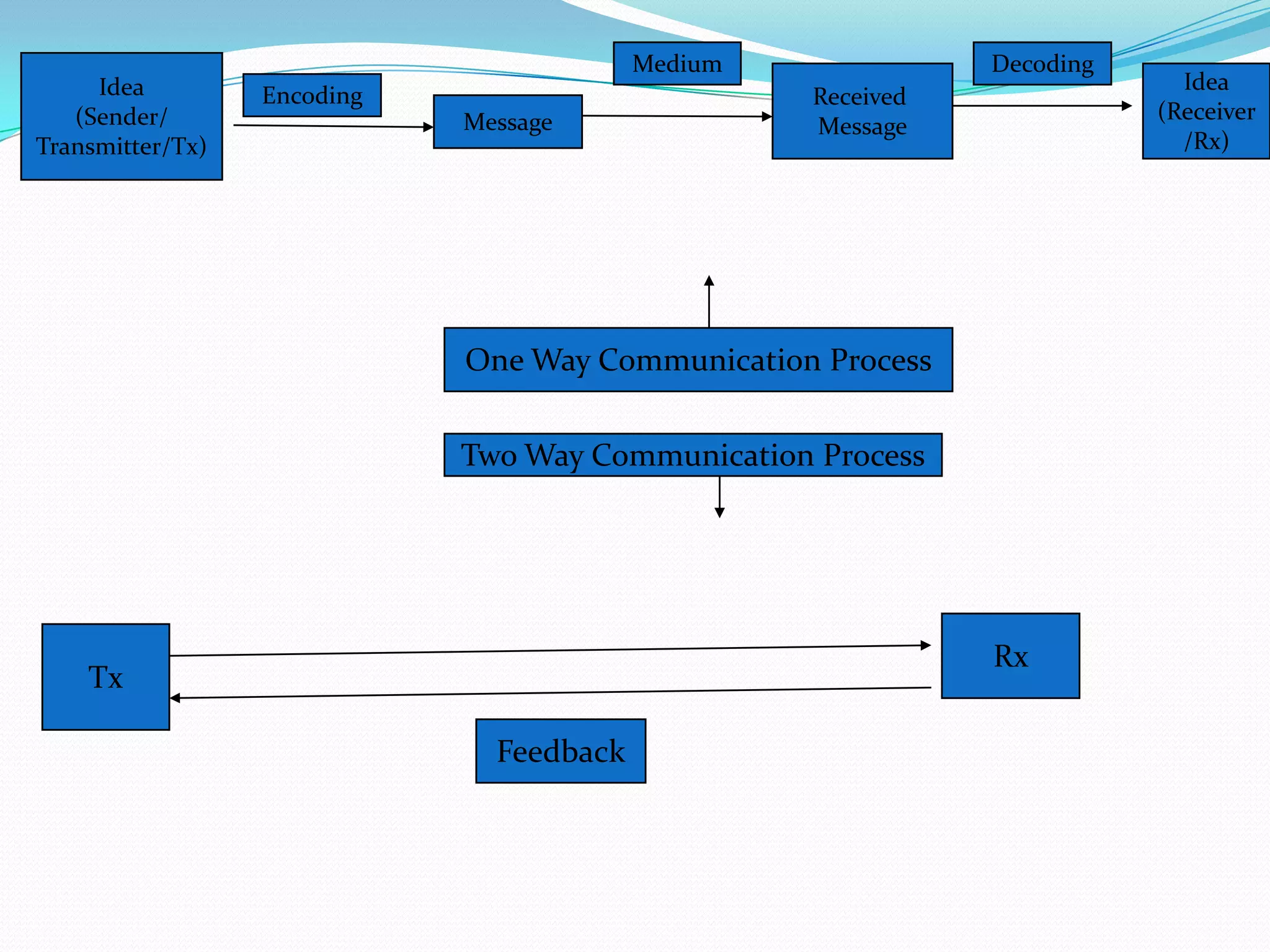
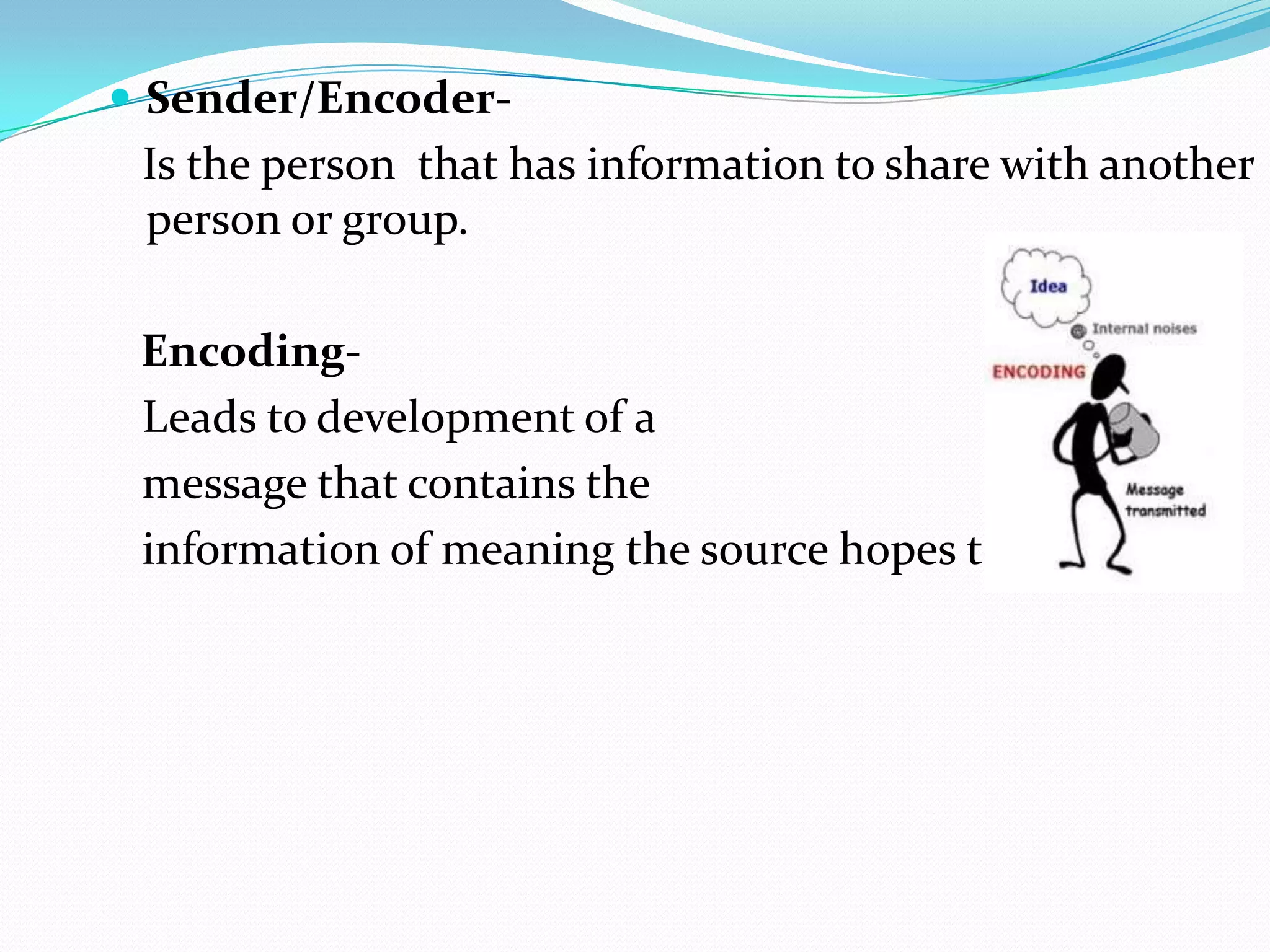
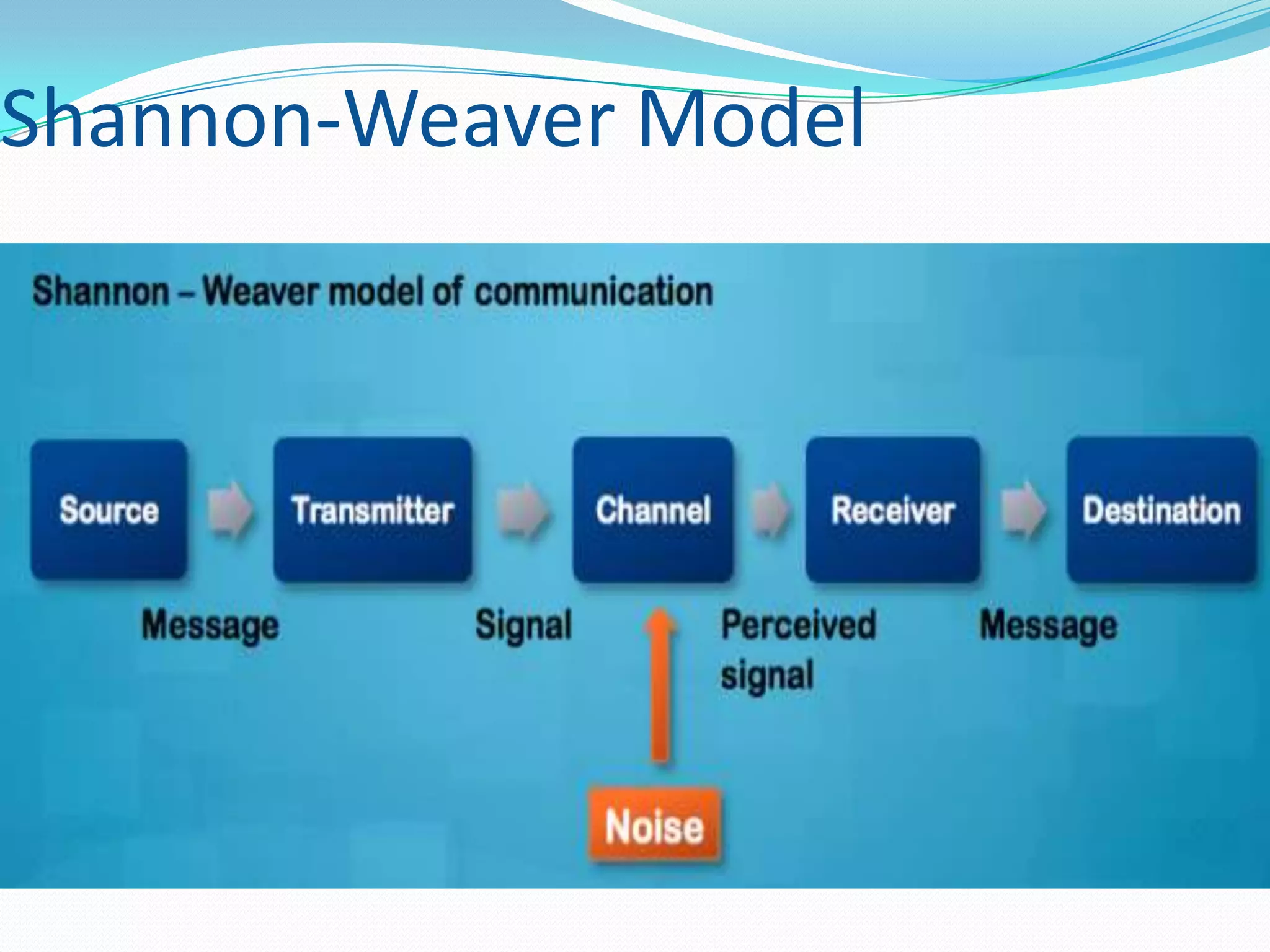
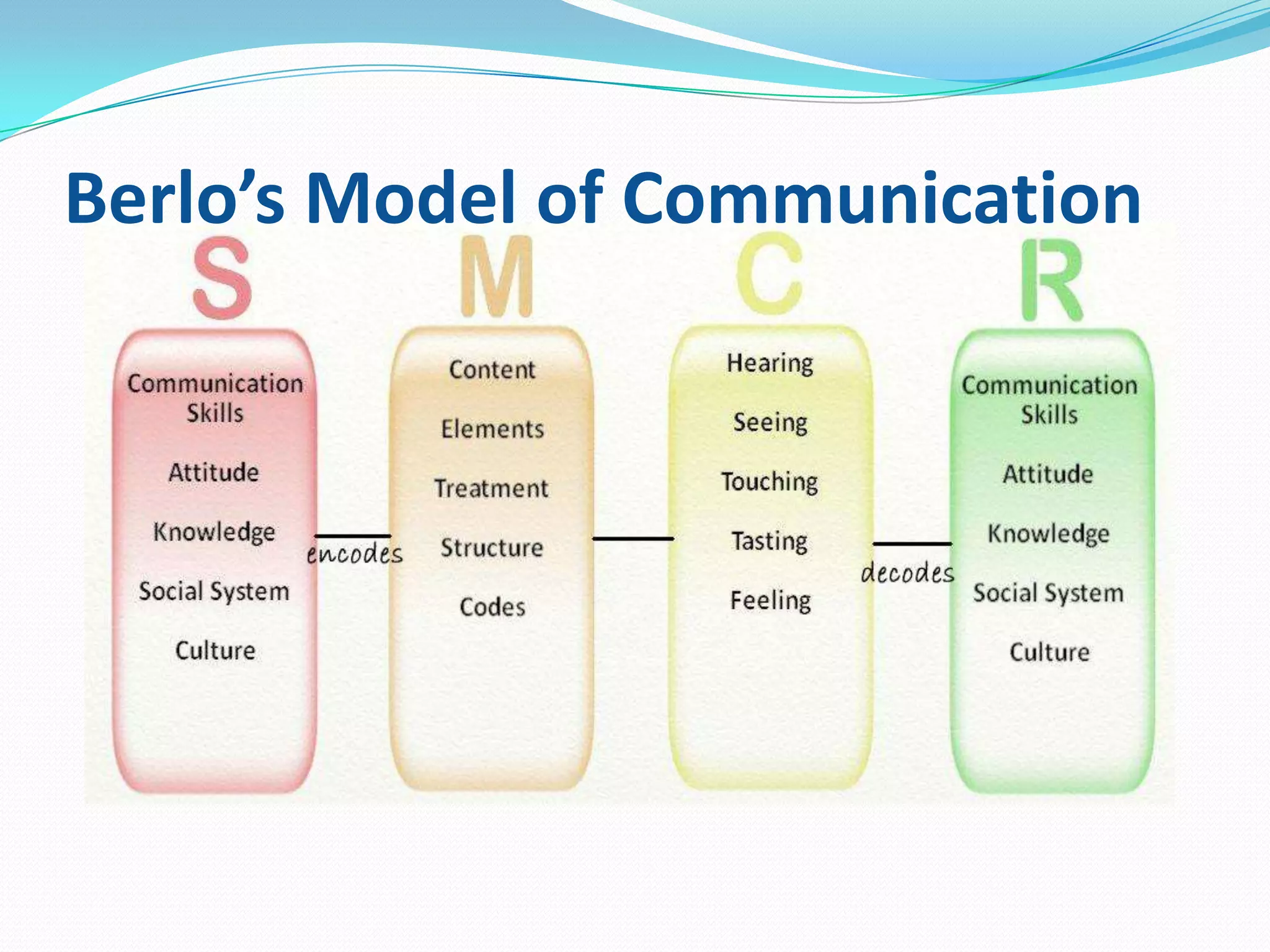
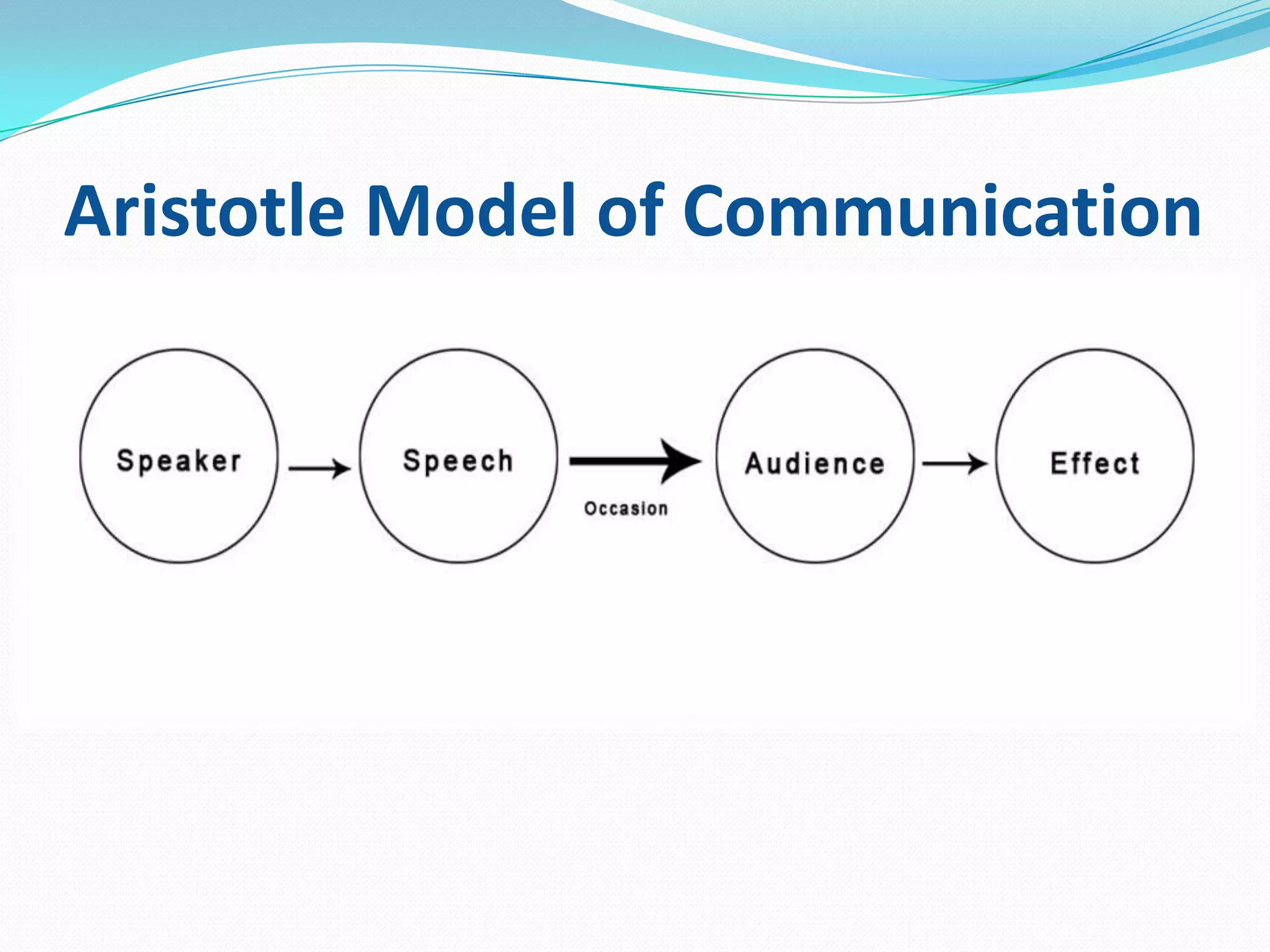
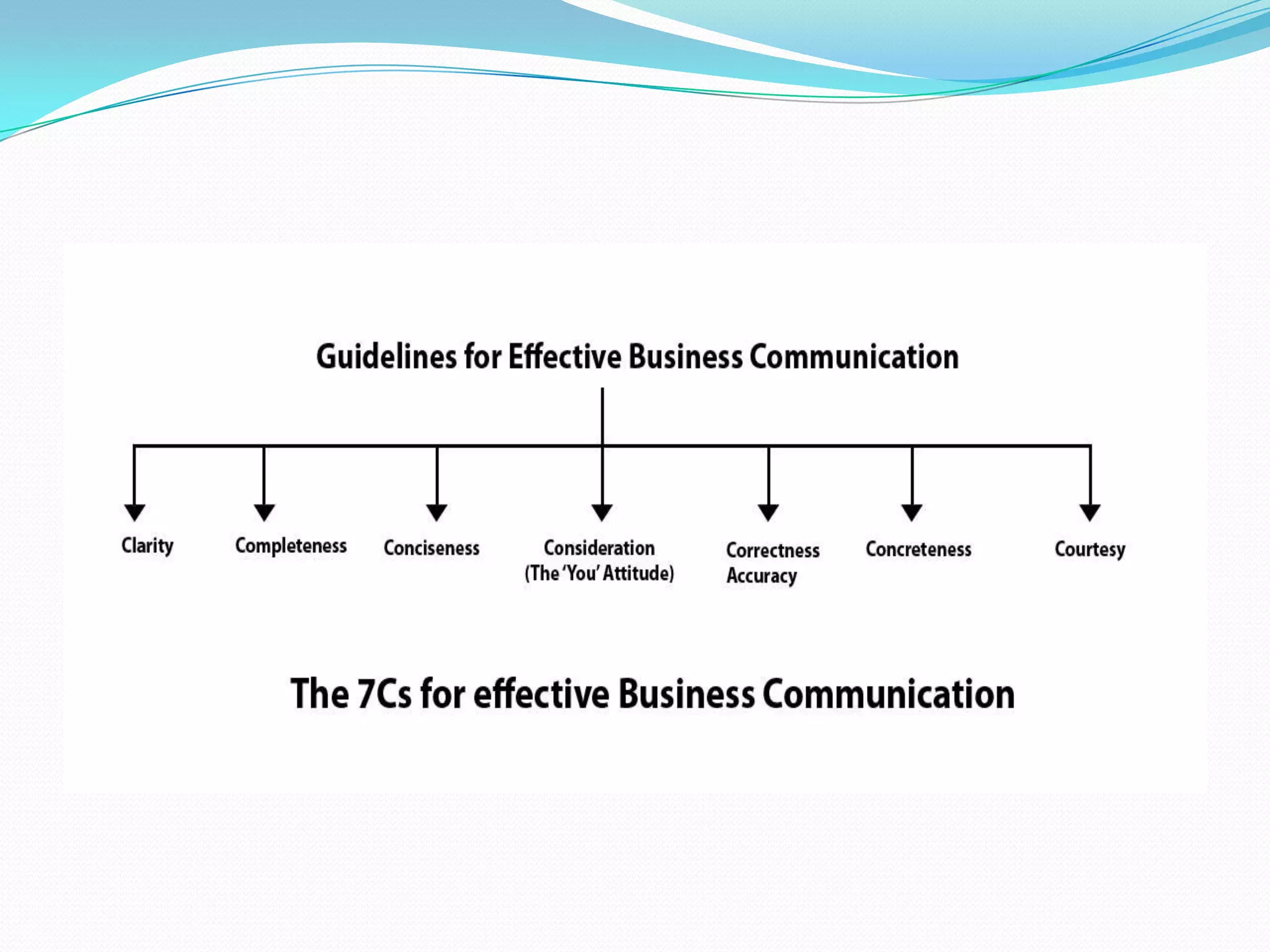
This document provides an overview of business communication. It defines communication and outlines the basic process which includes a sender encoding a message that is sent through a medium and decoded by the receiver. It also describes models of communication including the Shannon-Weaver, Berlo, and Aristotle models. The document highlights the importance of business communication for functions like planning, coordination, and maintaining external relationships. It also emphasizes ensuring communication is complete, considers the audience, is concise, clear, concrete, courteous, and correct. Feedback is noted as important for completing the communication process and measuring effectiveness.