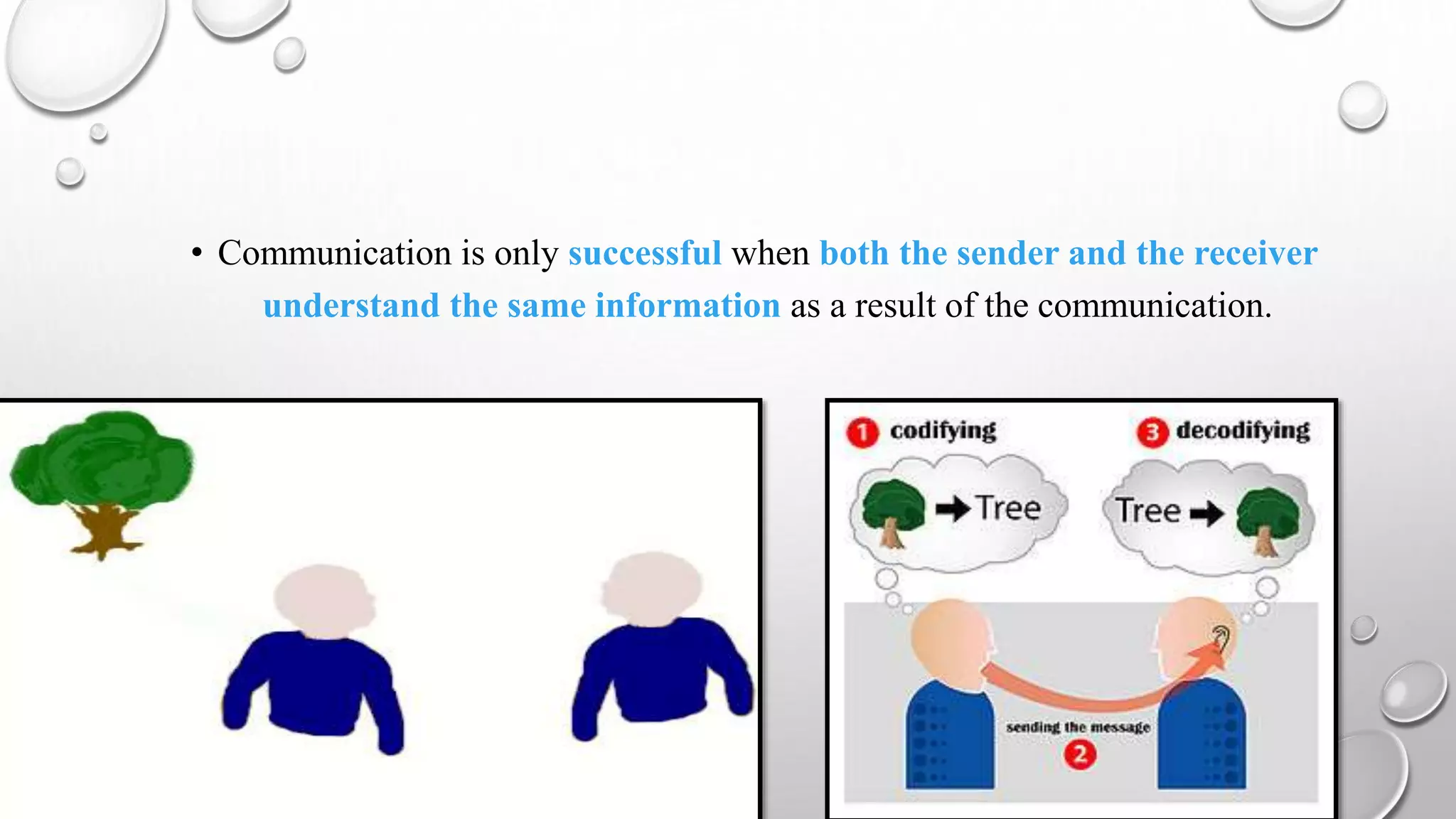
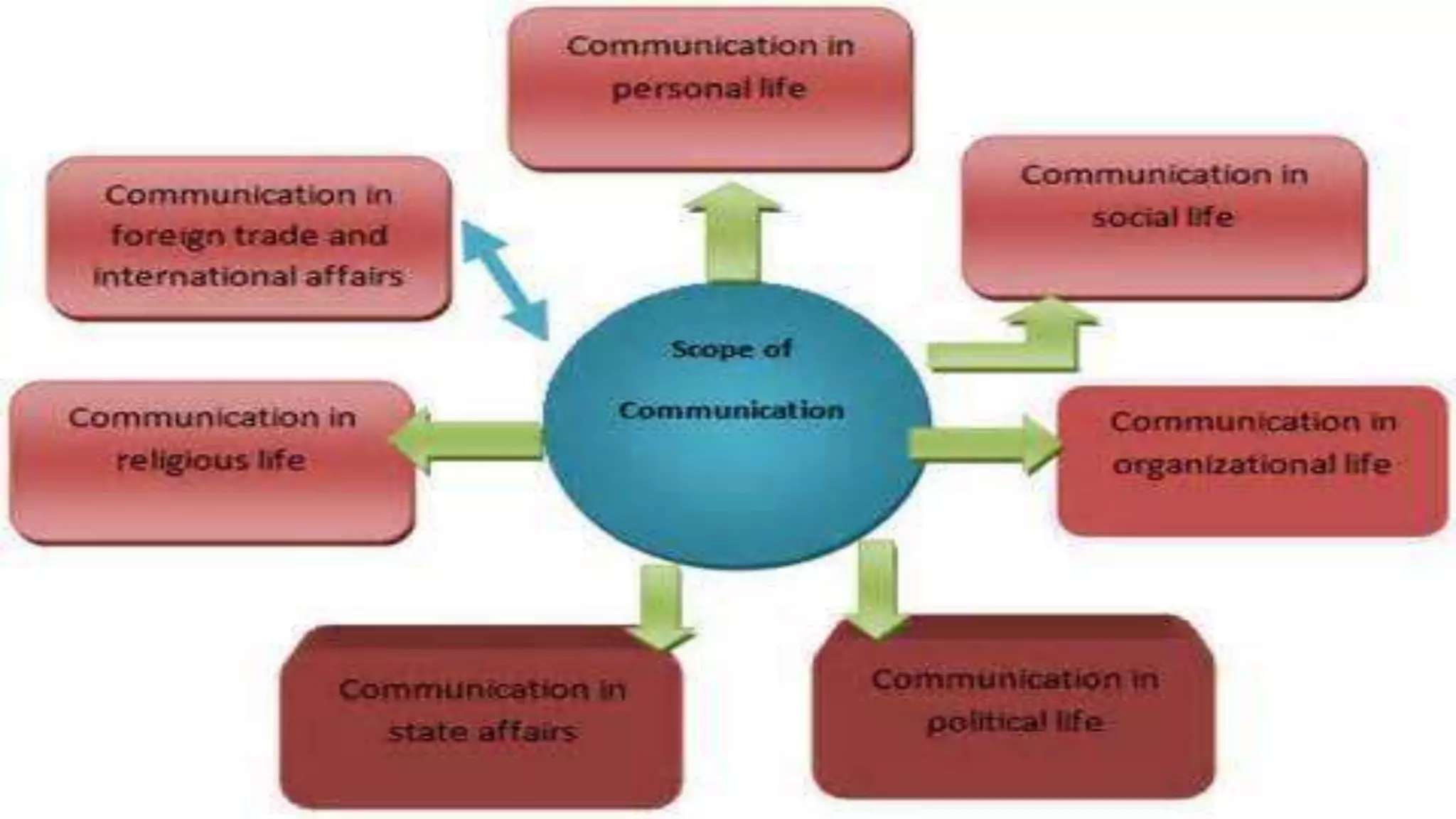
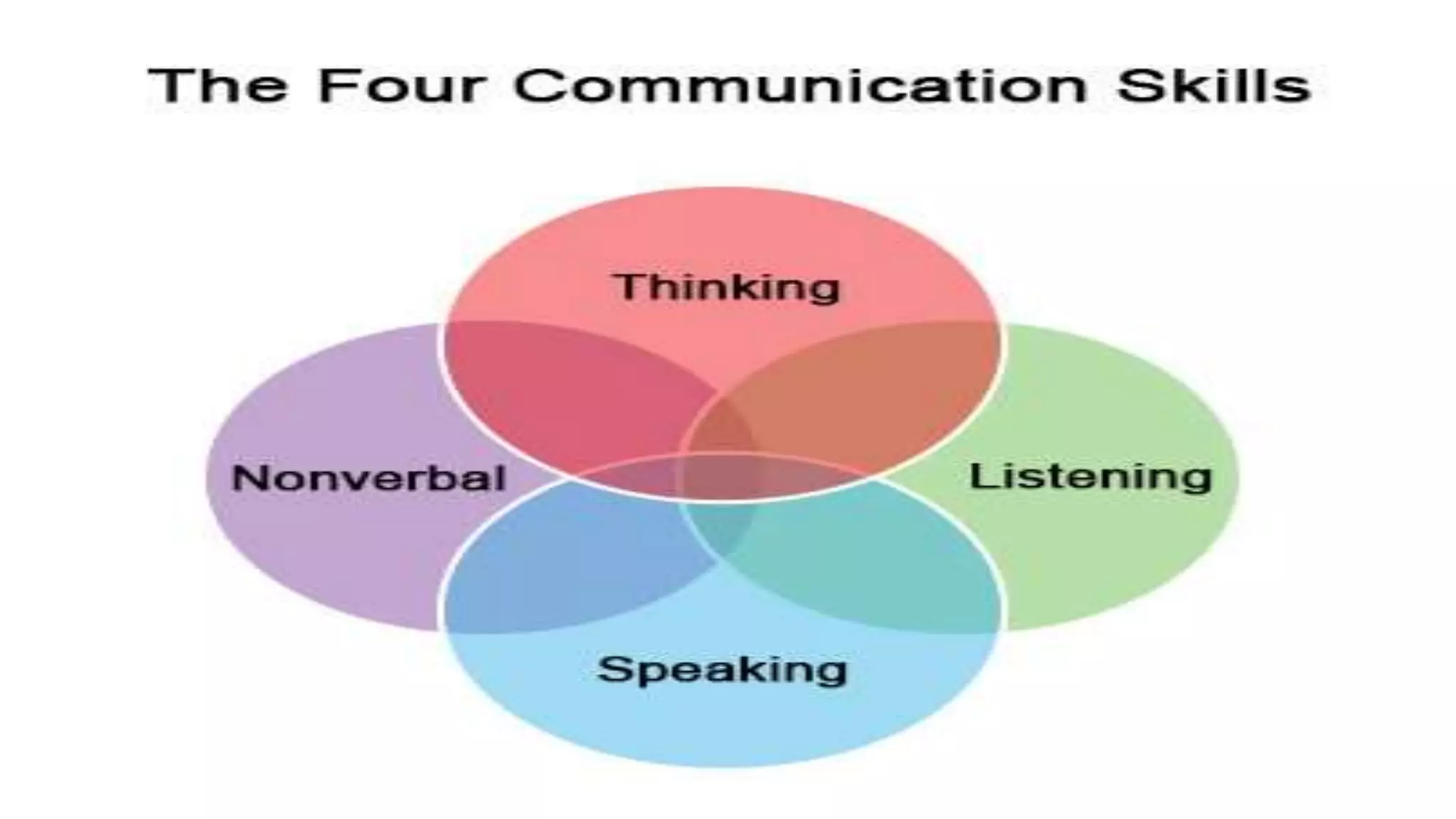
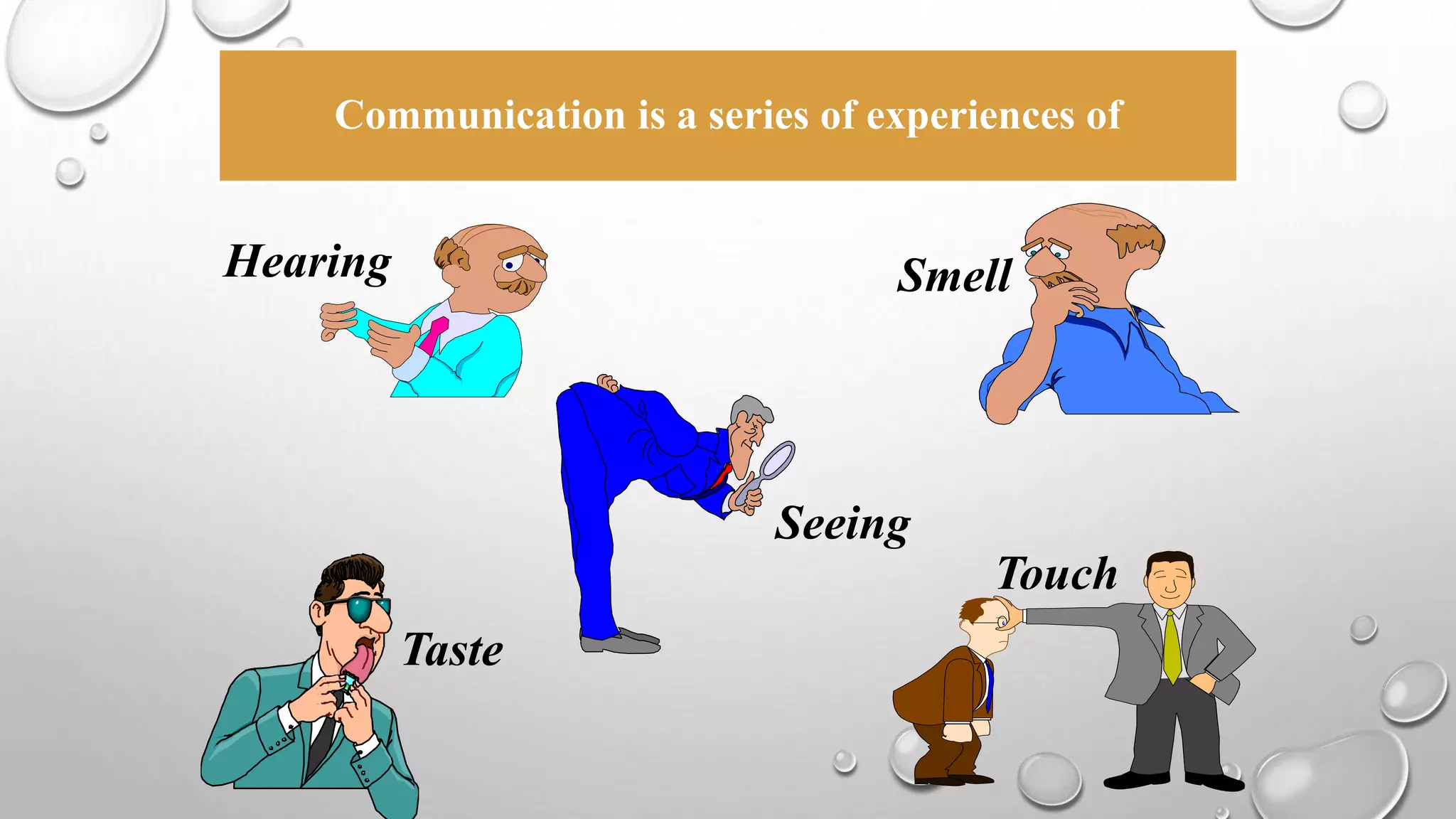
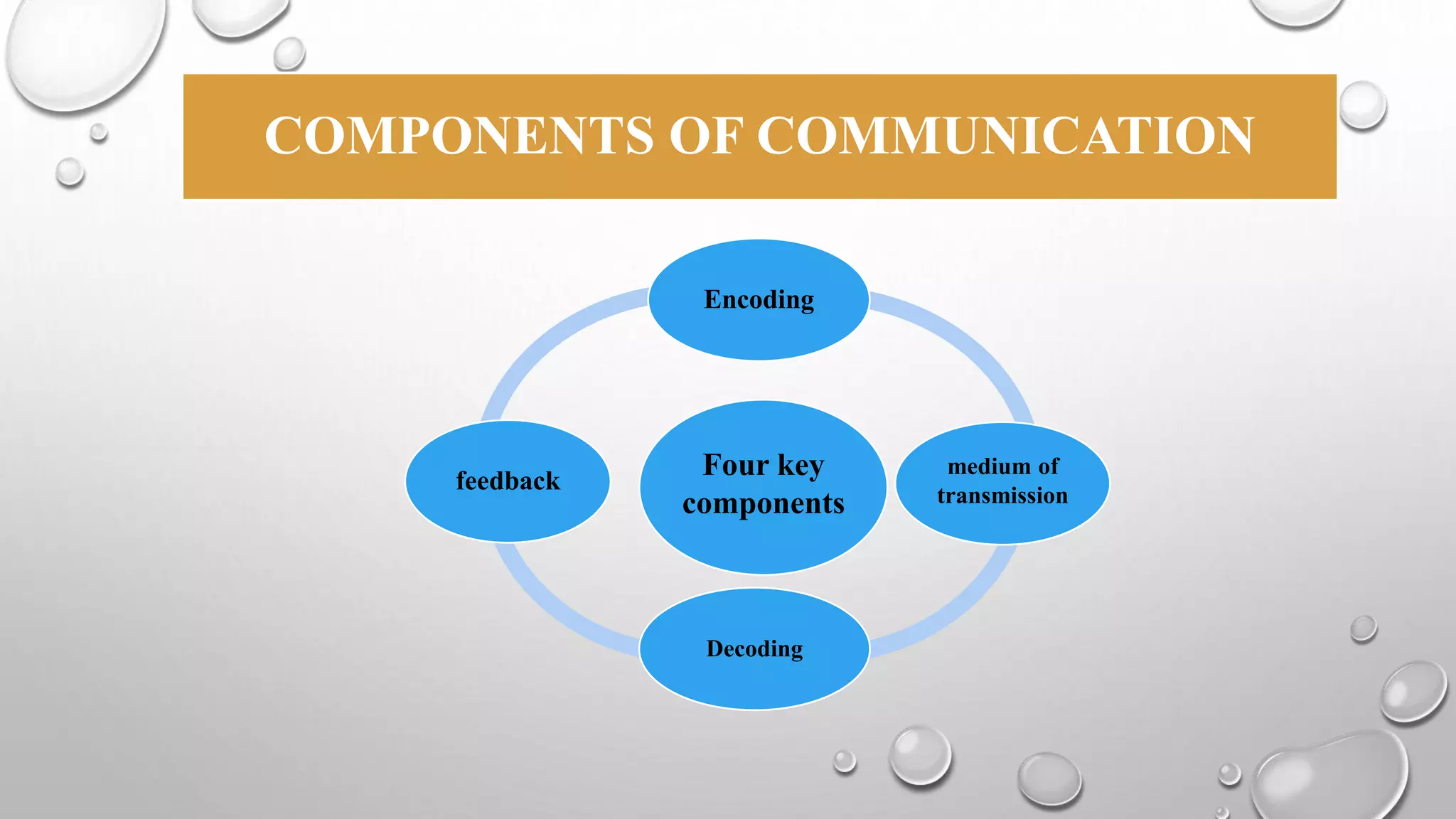
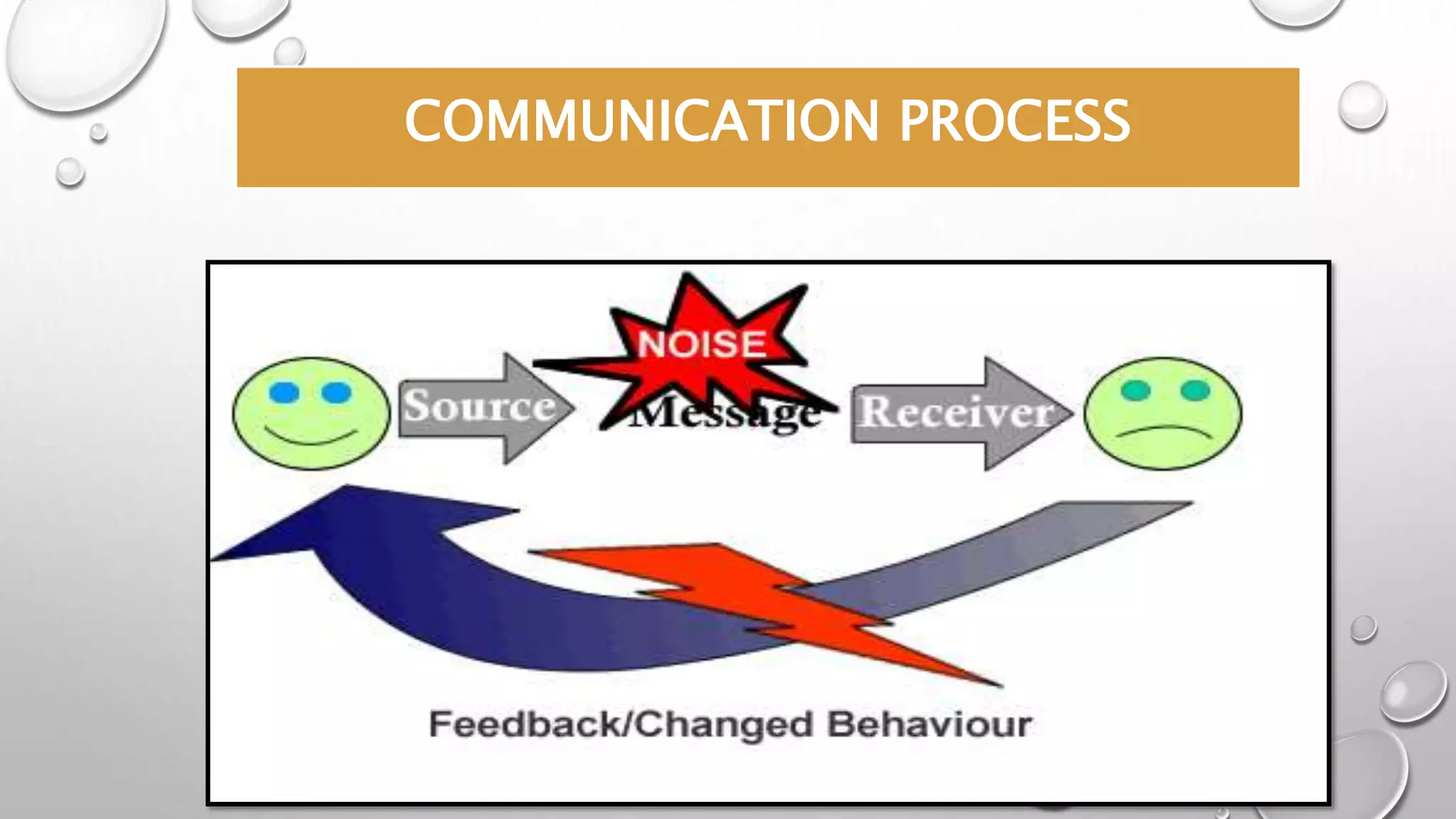
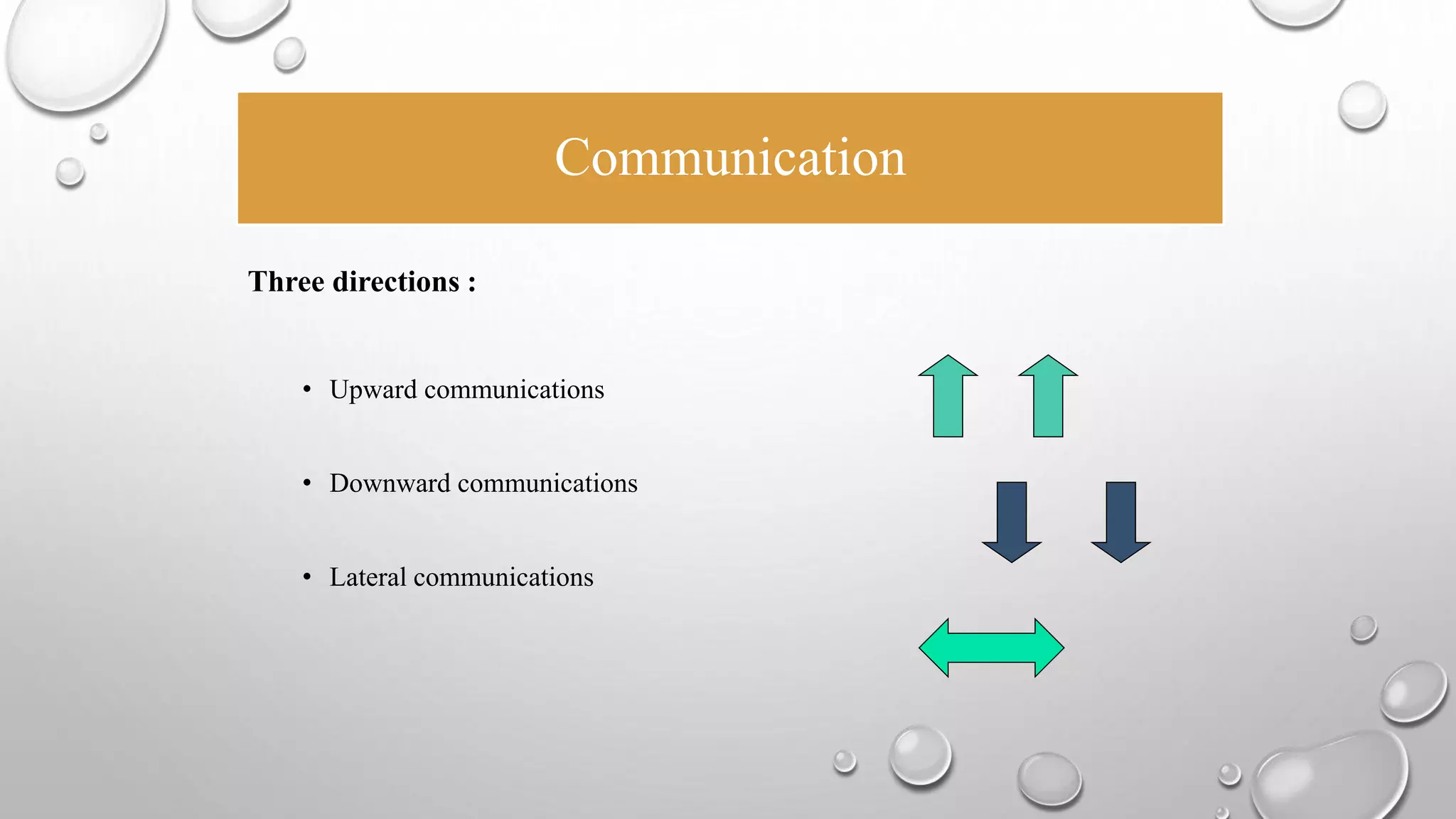
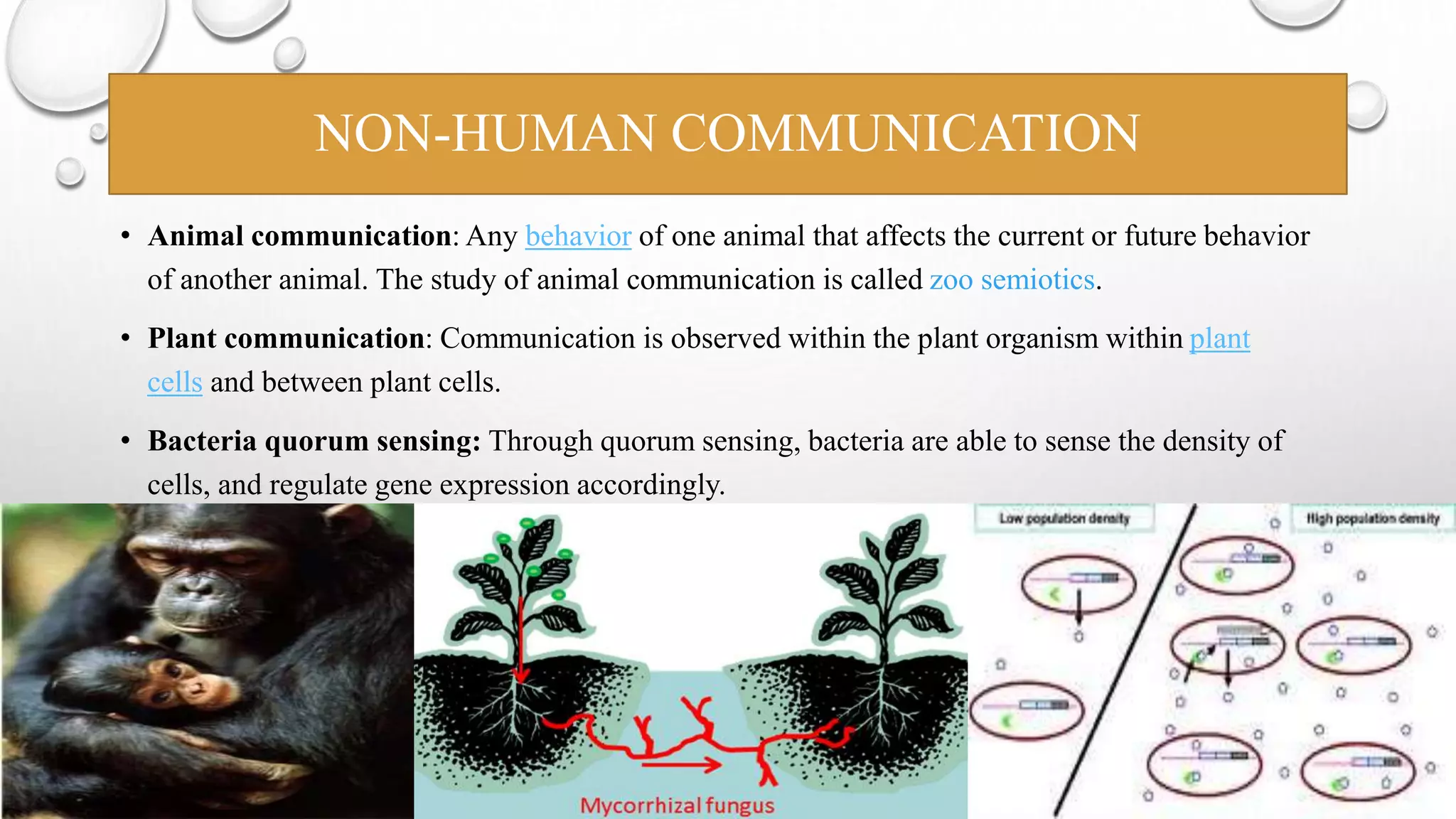
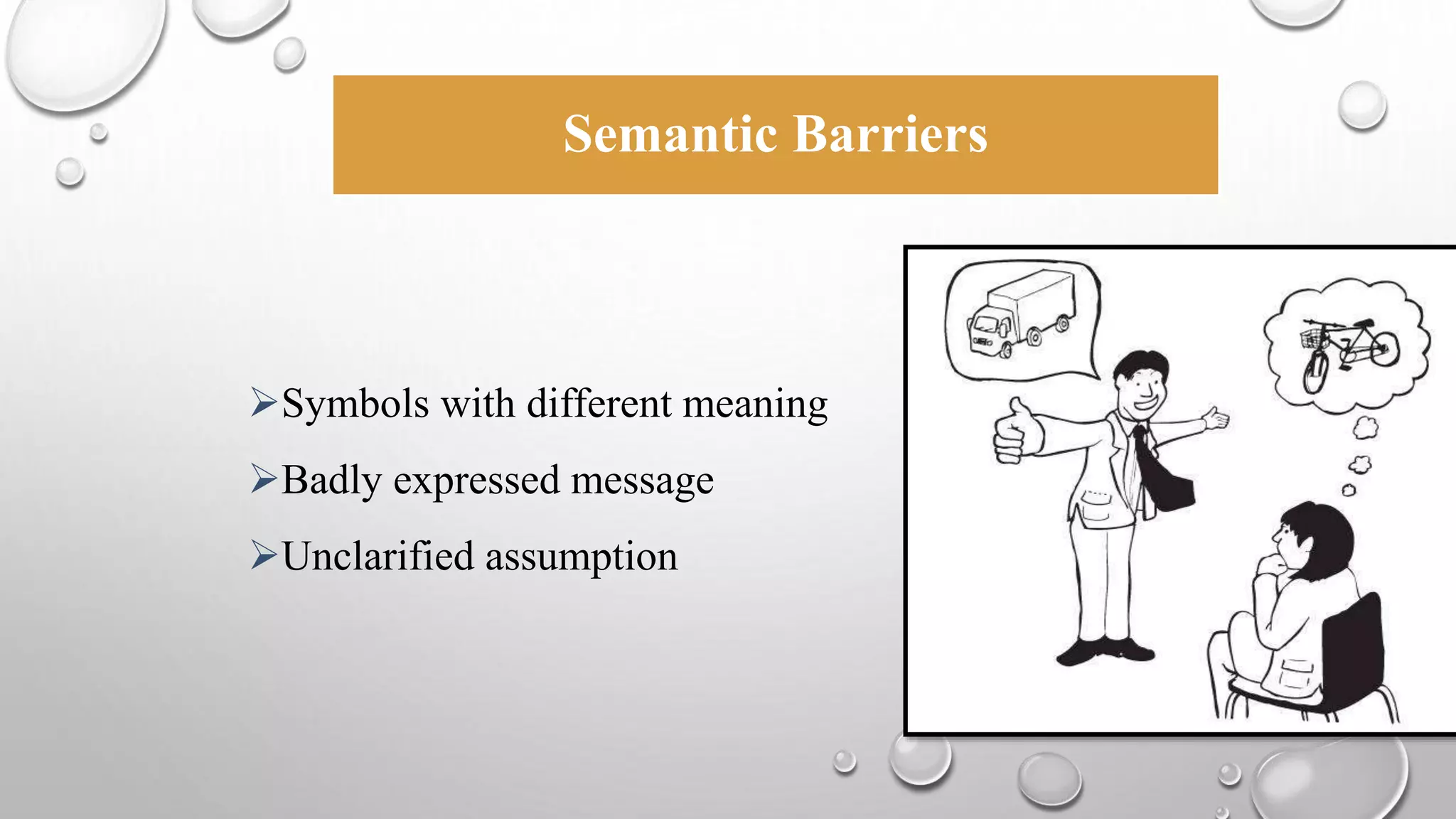
This document discusses communication skills and the communication process. It defines communication as the transmission of a message from a sender to a receiver in an understandable manner. It notes that communication is successful when both parties understand the same information. It also discusses verbal and non-verbal communication, barriers to communication, principles of effective communication, and tips for good communication skills.