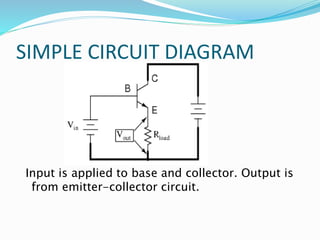
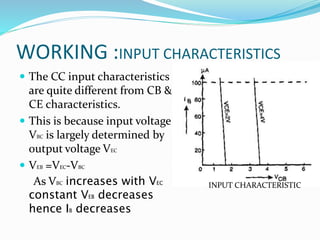
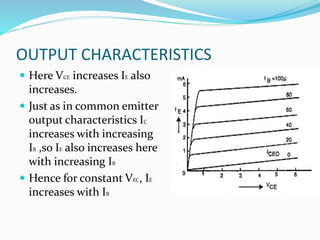
This document discusses the common collector (CC) transistor configuration. In a CC configuration, the base is the input, the emitter is the output, and the collector is common to both. It has a voltage gain slightly less than unity. The CC configuration has different input and output characteristics compared to common base and common emitter. It is useful for impedance matching between circuits and as a "buffer" to keep the output voltage constant over a range when driving a load.