Embed presentation
Downloaded 26 times
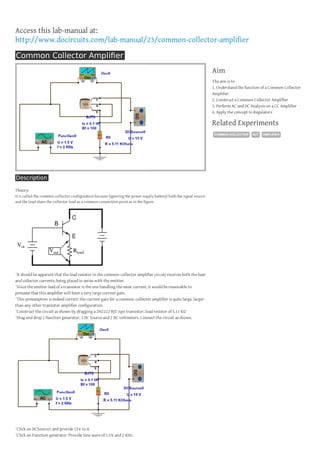


The document provides instructions for constructing and analyzing a common collector (CC) amplifier circuit using a BJT transistor. The CC amplifier has a large current gain. Learners will build the circuit in a simulation with a 2N2222 transistor, 5.1K load resistor, function generator for a 1.5V, 2KHz sine wave input, and voltmeters to measure the input and output. Running time and frequency domain simulations will allow the learner to observe the output following the input signal with the same amplitude but a downward shifted DC level due to the BJT's VBE drop.

