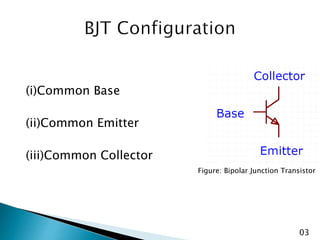
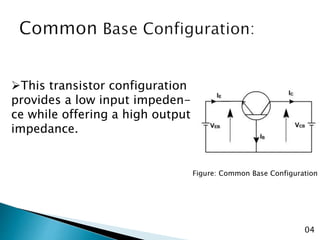
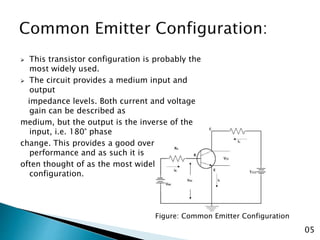
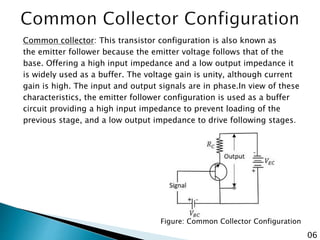
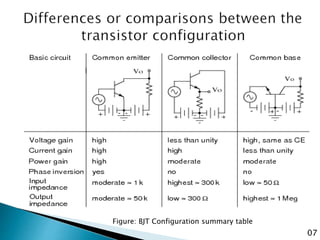
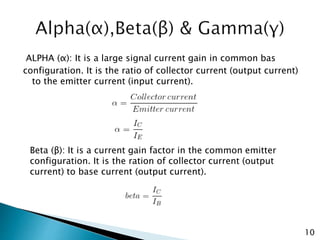
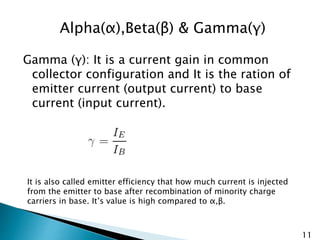
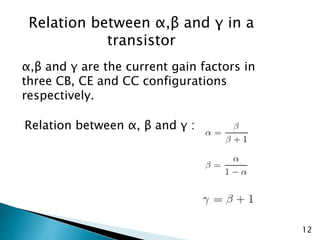
The document discusses various transistor configurations: common base, common emitter, and common collector, emphasizing their advantages and disadvantages. It explains the alpha, beta, and gamma current gain factors for each configuration, highlighting the common emitter as the most widely used. The summary also mentions applications and limitations of these configurations in electronics.