Embed presentation
Downloaded 107 times





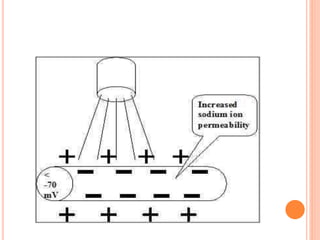



Combination therapy involves applying ultrasound and electrical stimulation simultaneously. It has several advantages, including reducing accommodation effects from interferential therapy, treating deeper lesions more effectively, and localizing ultrasound treatment. The mechanism is that ultrasound reduces the nerve membrane resting potential, bringing it closer to firing threshold, while electrical stimulation induces depolarization with a smaller current due to ultrasound potentiation. Diagnostic use specifies parameters like 0.5W/cm2 ultrasound at 1MHz with 100Hz interferential current. Therapeutic use follows individual modality doses tailored for each lesion.








