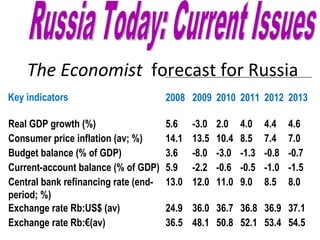
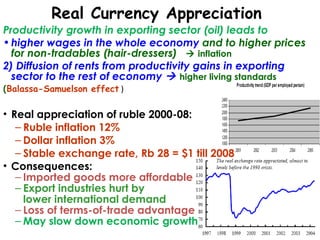
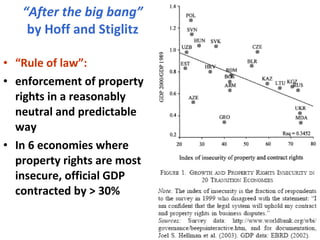
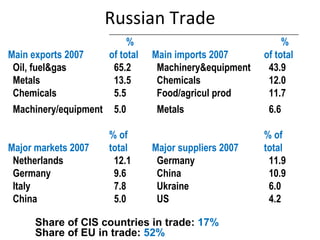
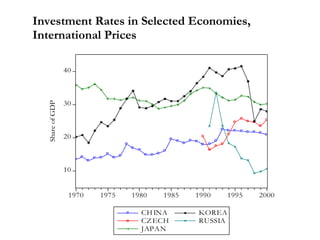
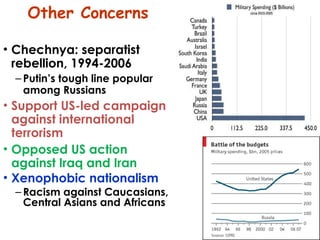
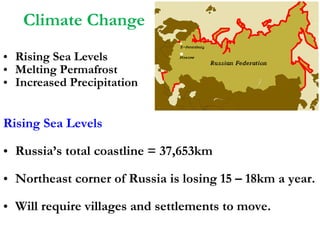
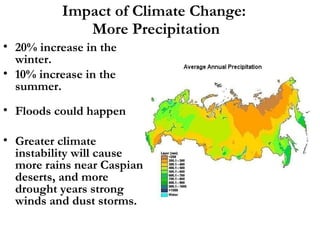
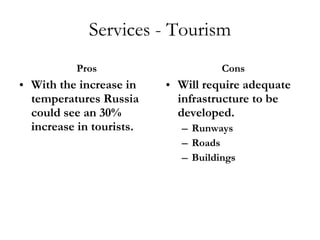
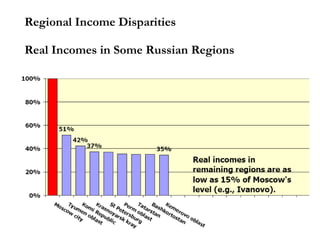
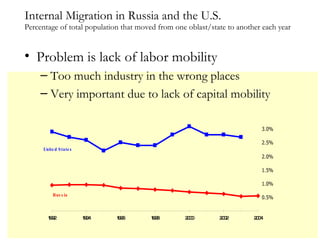
The document summarizes economic forecasts and key issues for Russia from 2008-2013. Real GDP growth is expected to be moderate, with consumer price inflation decreasing annually. The budget and current account deficits are projected to shrink over time. Challenges include reducing political uncertainty to attract more foreign direct investment and developing market-oriented legal and political institutions.