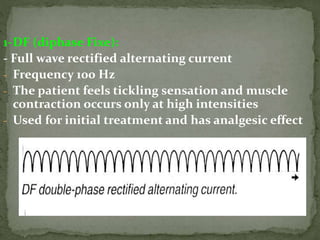
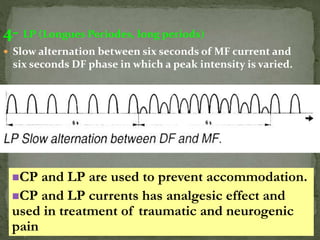
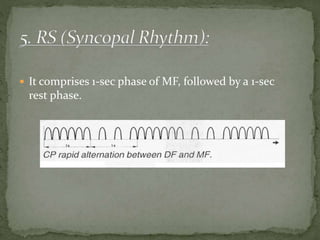
Diadynamic therapy employs low current electro-therapy for analgesic and spasmolytic effects, utilizing mixed currents from galvanic and impulse types. It includes five classic current types (df, mf, cp, lp, rs) with varying frequencies and applications for pain relief, increased circulation, and muscle re-education. Precautions must be taken to limit treatment time to prevent skin damage, with specific contraindications outlined for its use.