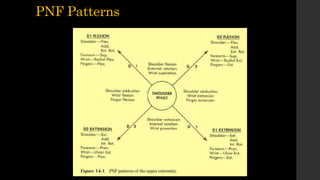
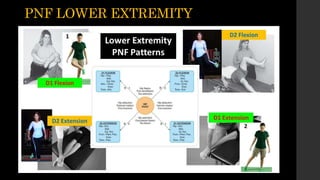
PNF is a treatment approach based on the principle that all patients have untapped potential. It integrates principles of motor control and motor learning. The basic procedures of PNF include applying resistance, using irradiation and reinforcement, providing manual contact and verbal cues, and incorporating body positioning, vision, traction, approximation, stretching, timing, and movement patterns. The goal is to facilitate muscle contractions and motor control through optimal resistance applied in different ways like resisting specific motions or muscle groups.










![Verbal Stimulation (Commands)
• Guide the start of movement or the muscle contractions.
• Affect the strength of the resulting muscle contractions.
• Give the patient corrections
• The verbal command tells the patient what to do and when to do it
• Preparatory instructions need to be clear and concise, without
unnecessary words
For example, the command for the lower extremity pattern of flexion-
adduction-external rotation with knee flexion might be [preparation]
“ready, and”; [action] “now pull your leg up and in”; [correction] “keep
pulling your toes up” (to correct lack of dorsiflexion)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/proprioceptiveneuromuscularfacilitationpnf-200324013612/85/Proprioceptive-neuromuscular-facilitation-pnf-12-320.jpg)