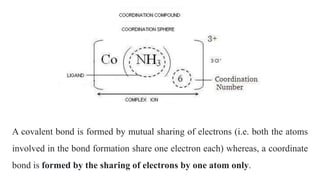
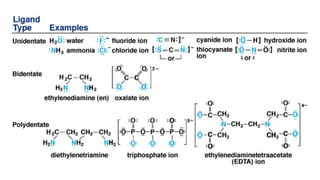
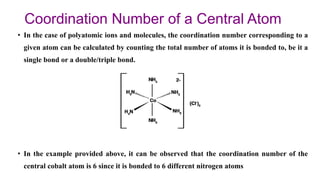
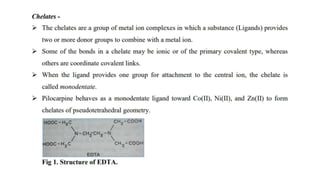
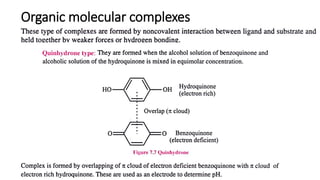
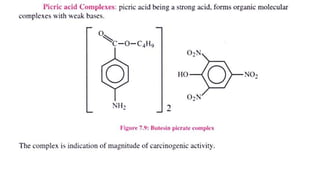
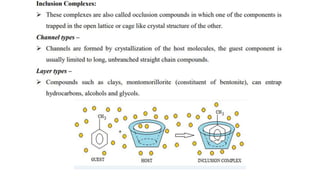
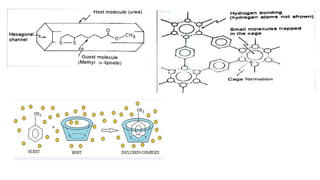
The document discusses complexation, which is the combination of individual groups or molecules to form larger molecules or ions. Complexes are formed through coordination bonds between a central metal atom or ion and surrounding ligands. Ligands can be monodentate, bidentate, or polydentate. Complexation has applications in drug delivery through properties like enhanced solubility and stability. Metal ion complexes and organic molecular complexes are discussed as examples. Protein binding of drugs is another type of complexation that affects drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion by binding drugs and rendering them pharmacologically inactive. Factors influencing protein binding include drug properties, protein properties, and patient factors.