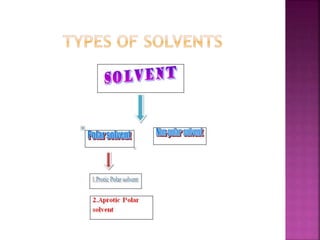
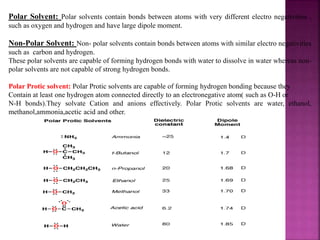
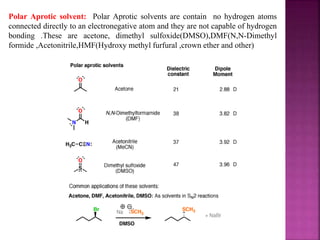
A solvent is a substance that dissolves another substance, forming a solution. The polarity of a solvent can be determined by its dielectric constant, with values less than 15 generally being non-polar and greater than 15 being polar. Polar solvents can be further divided into protic and aprotic types. Protic solvents can form hydrogen bonds, while aprotic solvents cannot form hydrogen bonds but are still polar. Semi-polar compounds can act as intermediate solvents to bring about miscibility between polar and non-polar solvents. Miscibility refers to the mutual solubility of components in liquid-liquid systems, with polar/semi-polar and non-polar solvents being completely miscible.