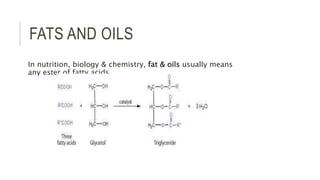
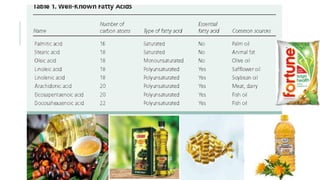
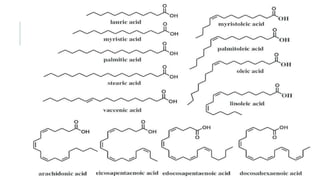
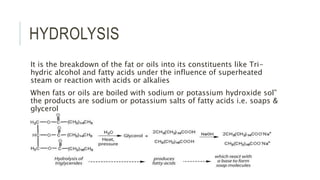
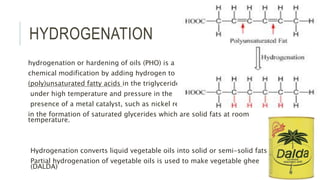
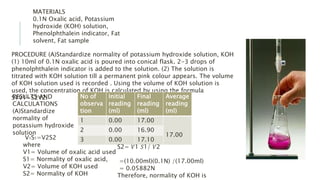
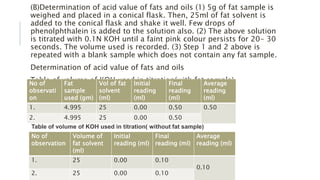
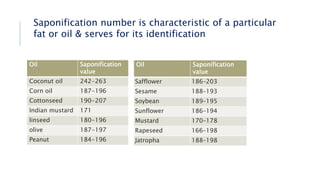
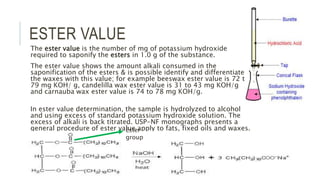
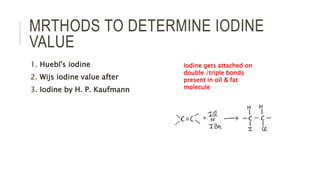
Fats and oils are esters of glycerol with long-chain fatty acids. They are mainly stored as energy reserves in plant seeds and animal tissues. Key properties include hydrolysis, hydrogenation, and saponification. Hydrolysis breaks fats down into glycerol and fatty acids. Hydrogenation adds hydrogen to unsaturated oils to make them more saturated and solid. Saponification uses alkalis to convert fats into soap and glycerol. Rancidity occurs when oils oxidize and develop foul smells. Various analytical methods determine properties like iodine value and saponification value to identify and check purity of oils.