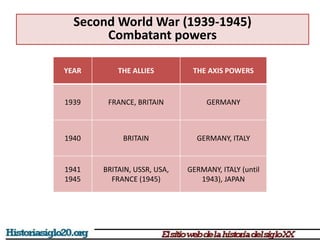
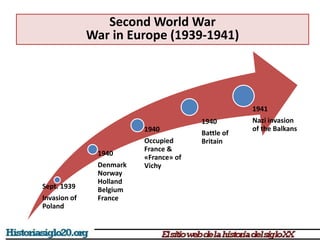
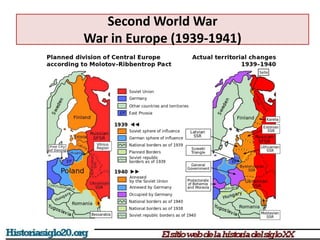
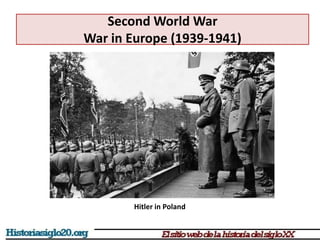
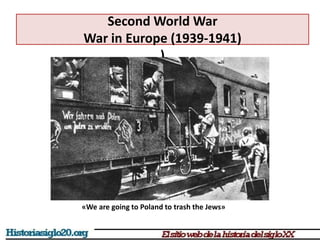
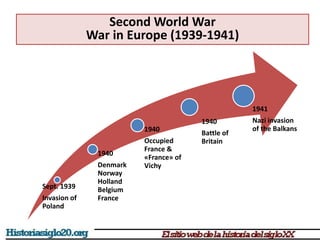
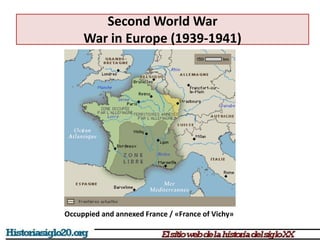
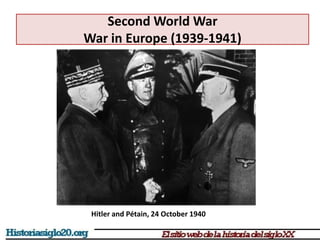
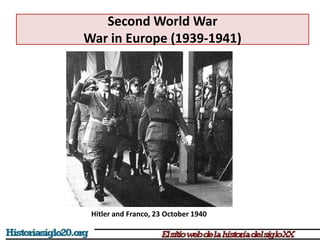
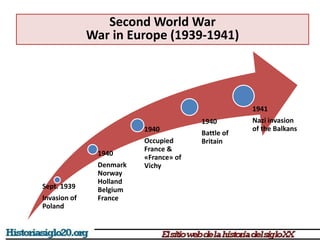
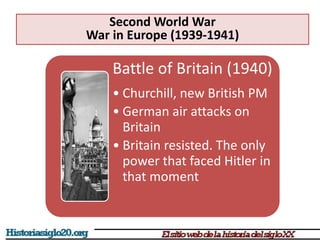
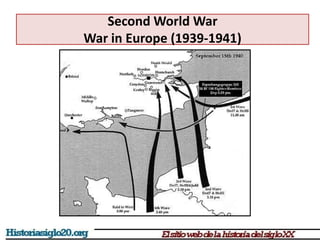
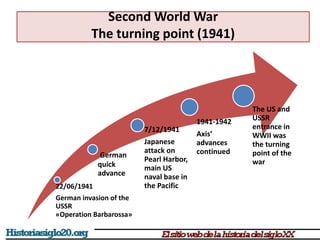
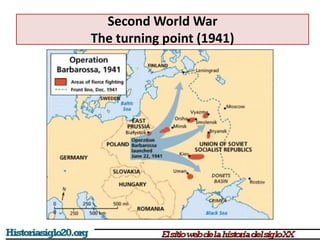
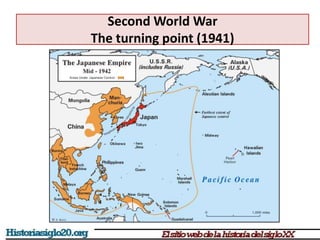
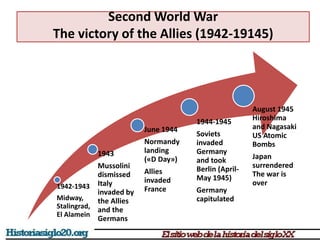
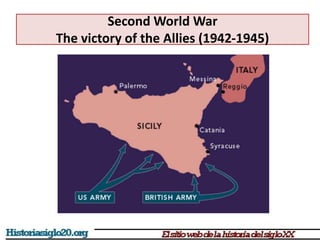
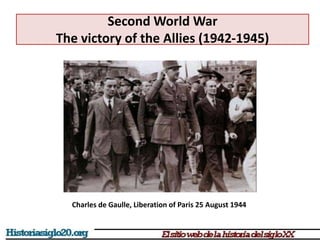
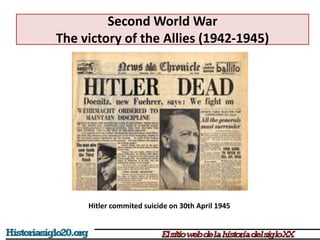
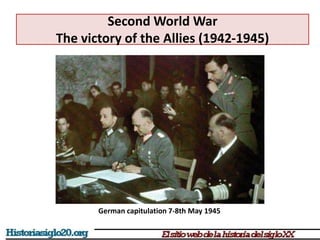
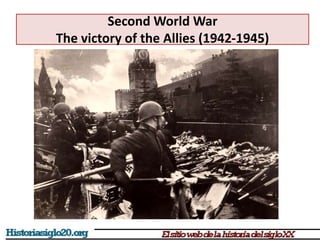
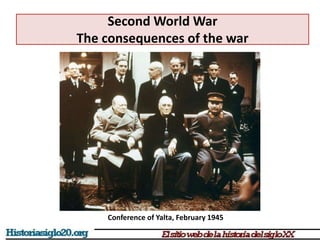
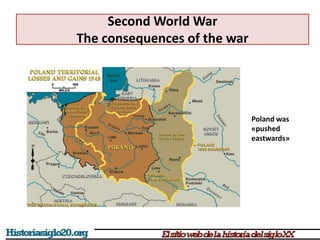
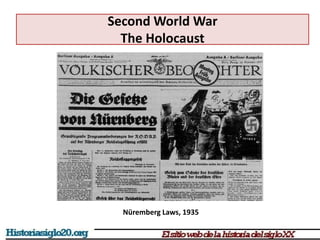
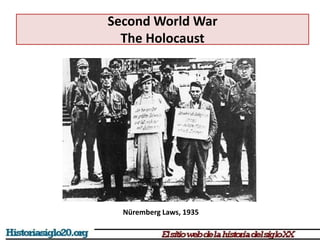
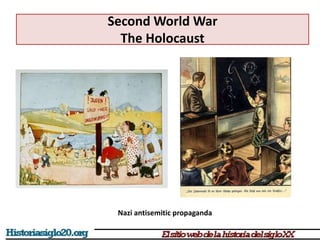
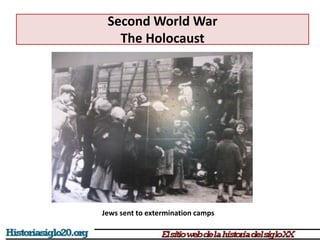
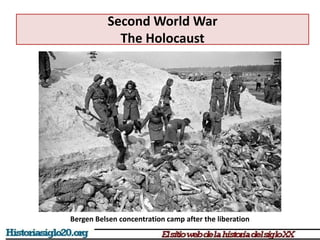
The document provides an overview of World War 2 from 1939-1945. It discusses the key combatant powers and timeline of major events including Germany's invasion of Poland in 1939, the turning point in 1941 when Germany invaded the USSR and Japan attacked Pearl Harbor bringing the US into the war, the Allied victories from 1942-1945 including D-Day and the bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, and the consequences of the war including over 55 million deaths and the Holocaust which killed approximately 6 million European Jews.