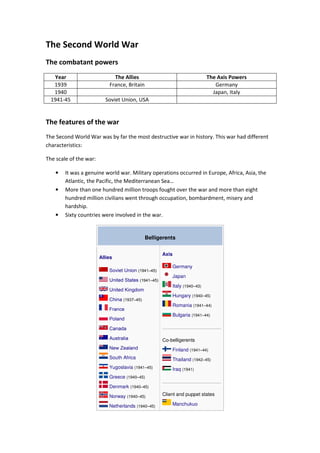
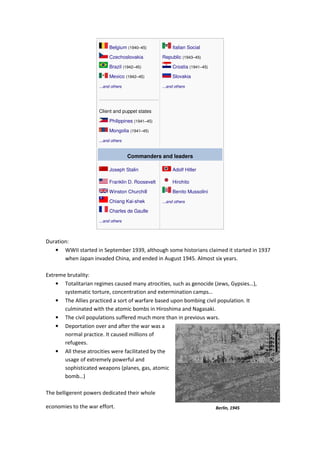
The document summarizes key details about World War 2, including its combatant powers and timeline from 1939-1945, its global scale and extreme brutality, and its stages from the early victories of the Axis powers to the eventual victory of the Allies. It also provides details on the Holocaust, describing how Nazi Germany systematically murdered approximately 6 million Jews across German-occupied Europe between 1933-1945 through ghettos, concentration camps, and extermination camps like Auschwitz.
![The Second World War (1939-1945)
Juan Carlos Ocaña Aybar
[4º ESO]
Geography and History – Bilingual Studies – IES Parque de Lisboa, Alcorcón (Madrid)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wwii-150317162659-conversion-gate01/75/Second-World-War-1-2048.jpg)