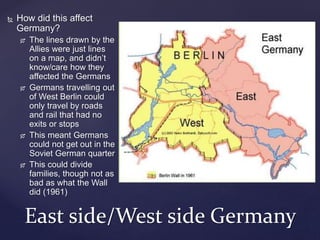
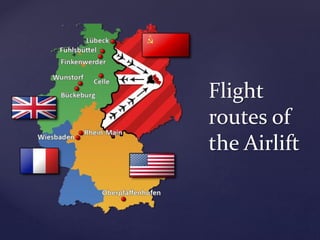
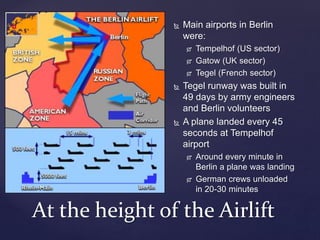
The Berlin Blockade occurred in 1948 when the Soviet Union blocked land access to West Berlin in response to the Western Allies introducing a new currency. To sustain West Berlin, the Allies launched an unprecedented airlift to supply the city. Over time the airlift proved successful and the blockade was lifted in 1949, further dividing Europe into Soviet-allied Eastern Bloc and Western-allied nations.