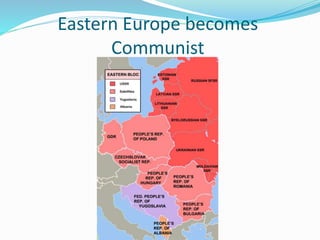
The Cold War was a period of hostility between the United States and Soviet Union from 1945 to 1990 that never resulted in direct military conflict, but instead manifested as an ideological and geopolitical rivalry. The two superpowers disagreed on the future of Europe following World War 2, with the US supporting capitalist democracies and the USSR establishing communist governments in Eastern Europe behind an "Iron Curtain." Notable events of the Cold War included the Berlin Blockade, Korean War, space race, Cuban Missile Crisis, and construction/fall of the Berlin Wall, until reforms under Soviet leader Gorbachev in the 1980s ultimately ended the Cold War.