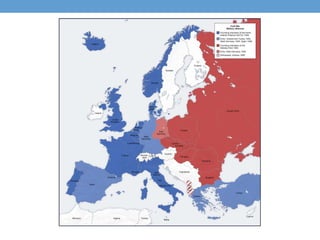
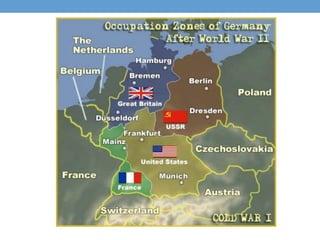
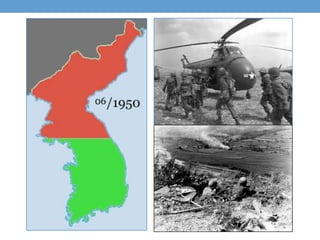
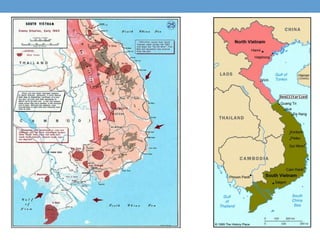
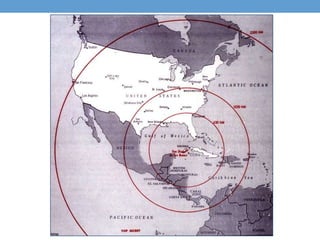
The document outlines the major events and time periods of the Cold War from 1945-1992. It was a war of ideologies between democracy led by the United States and its allies, and communism led by the Soviet Union. Key events included the establishment of NATO in 1949, the Korean War from 1950-1953, the Cuban Missile Crisis of 1962, Soviet domination of Eastern Europe after WWII, and the fall of communism in Eastern Europe and dissolution of the Soviet Union from 1989-1991.