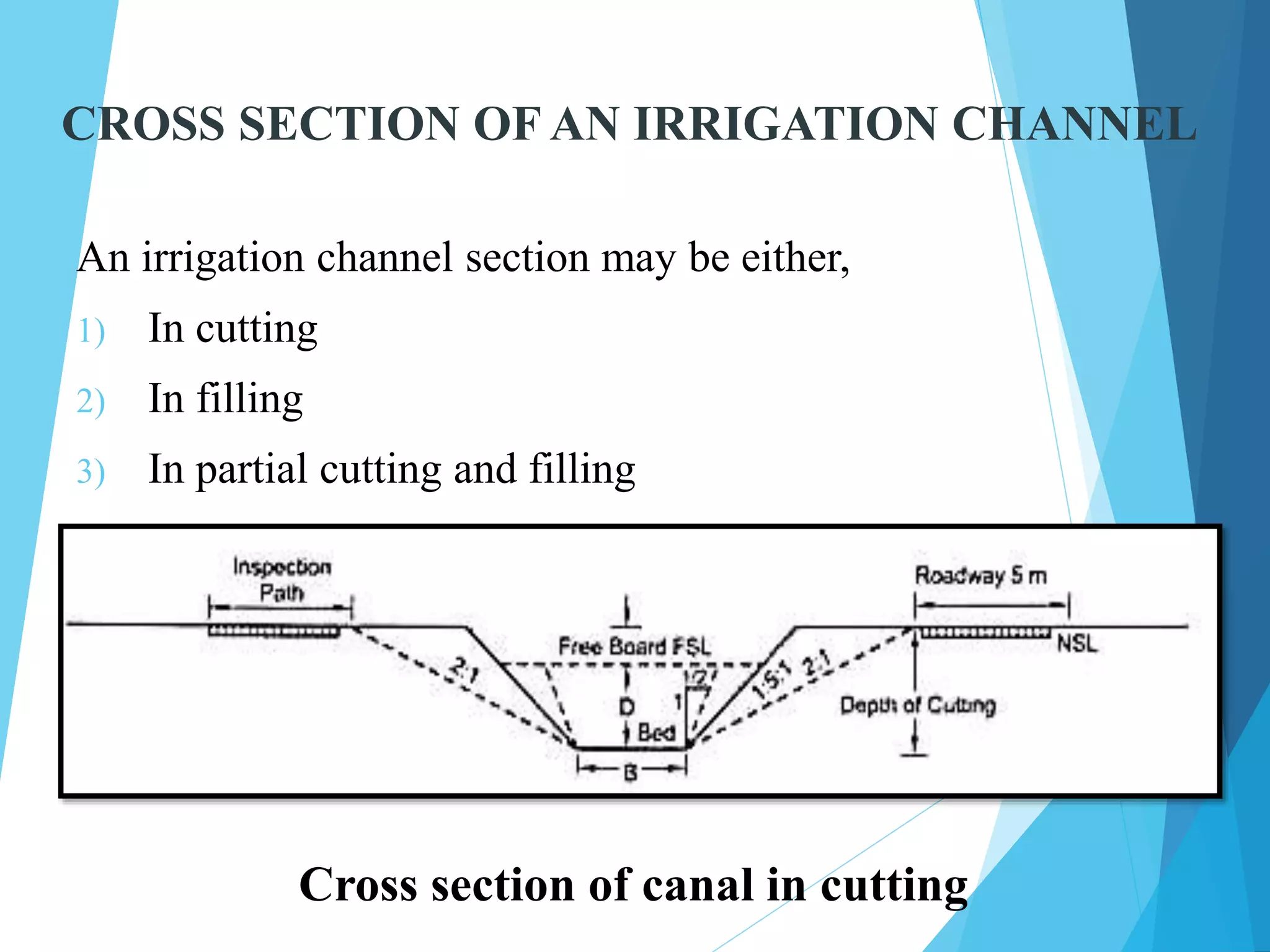
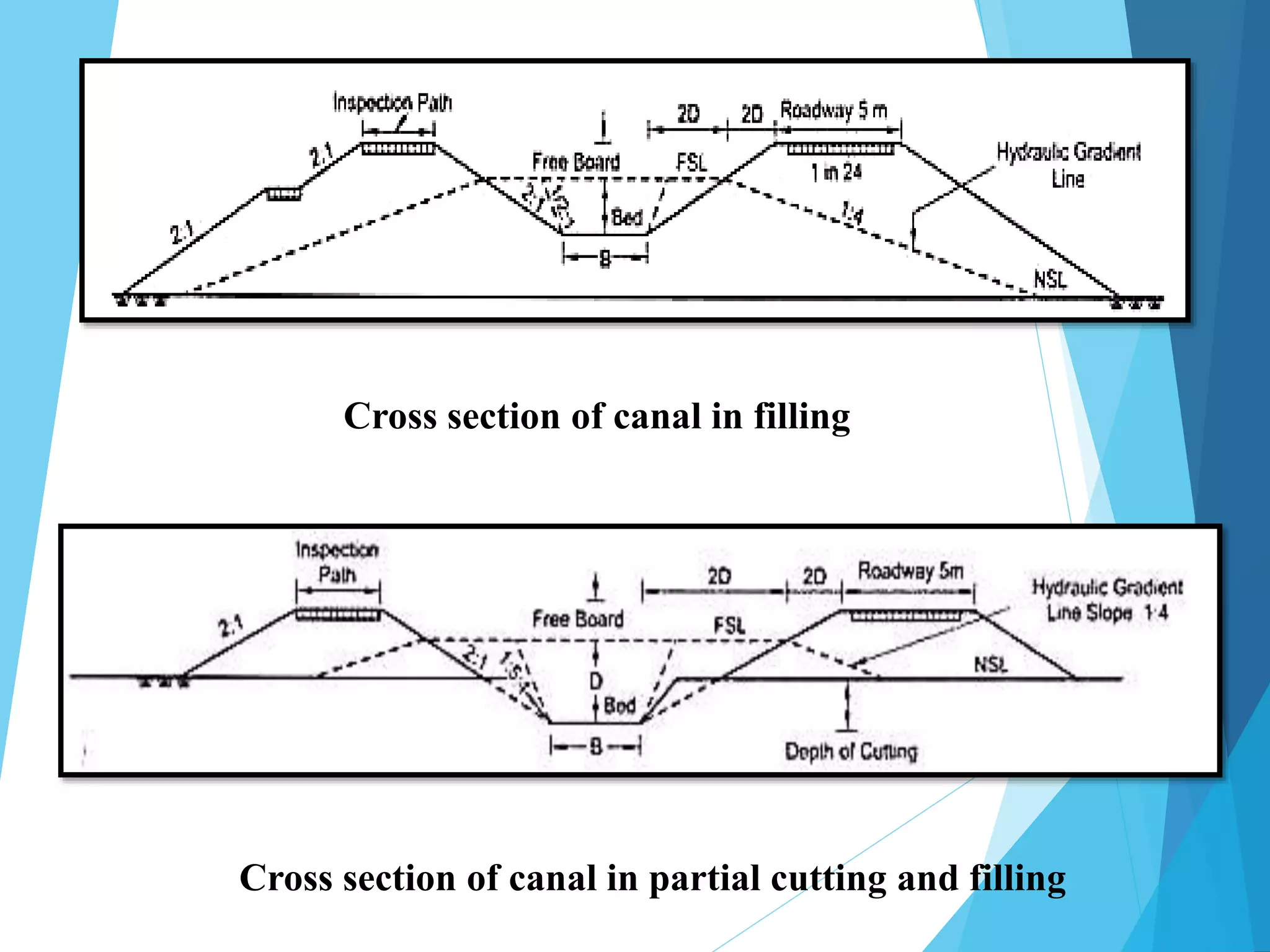
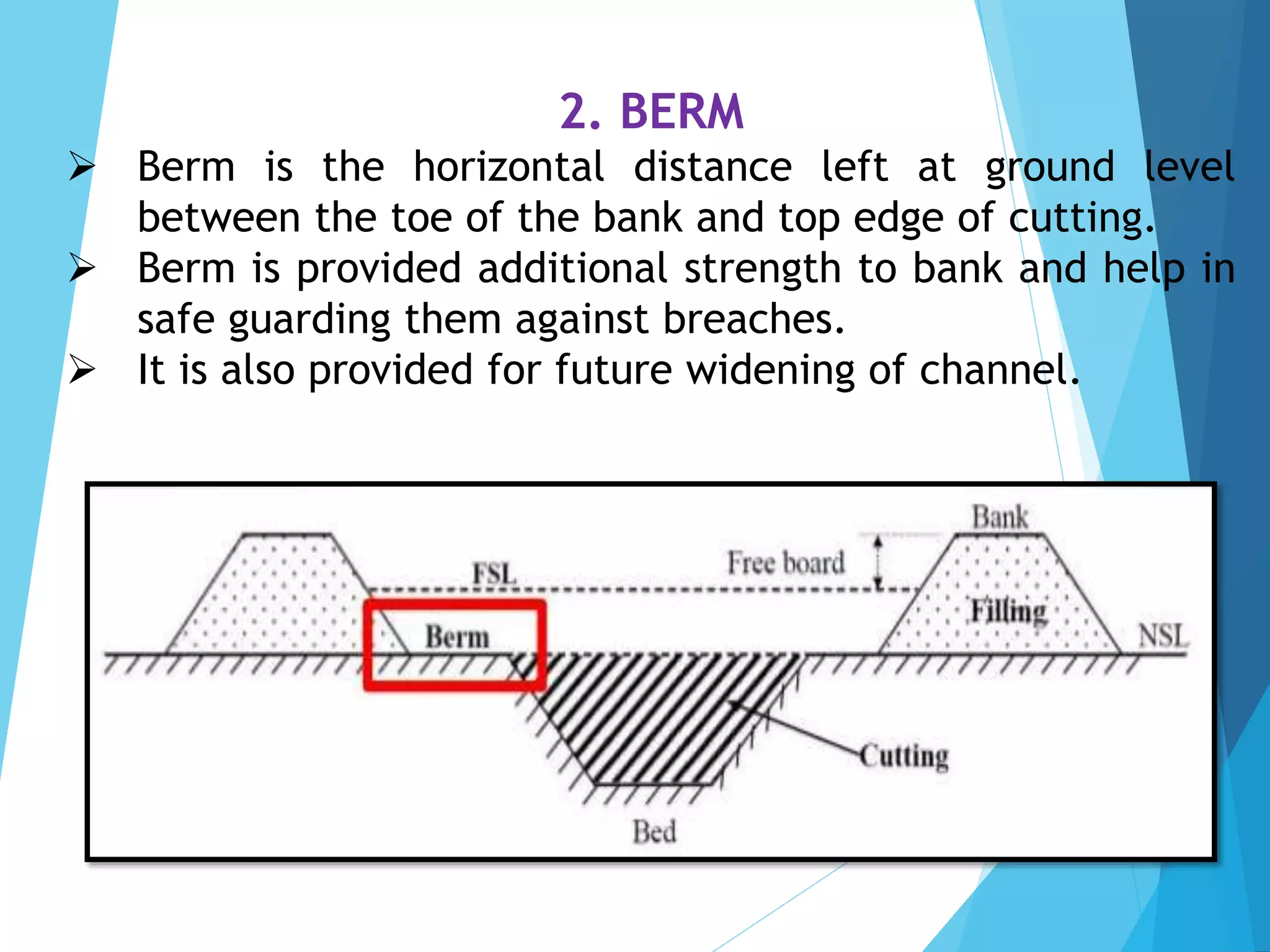
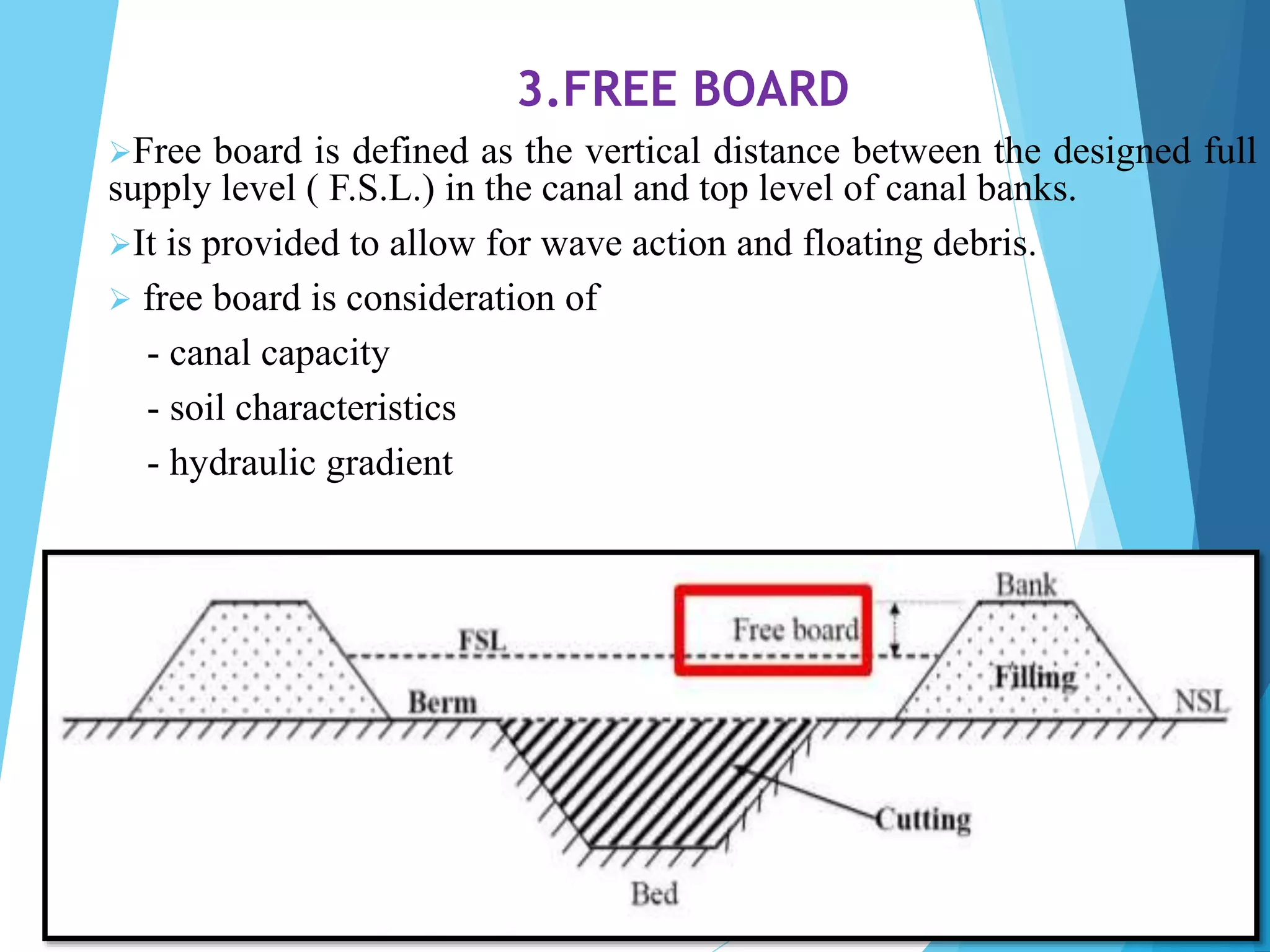
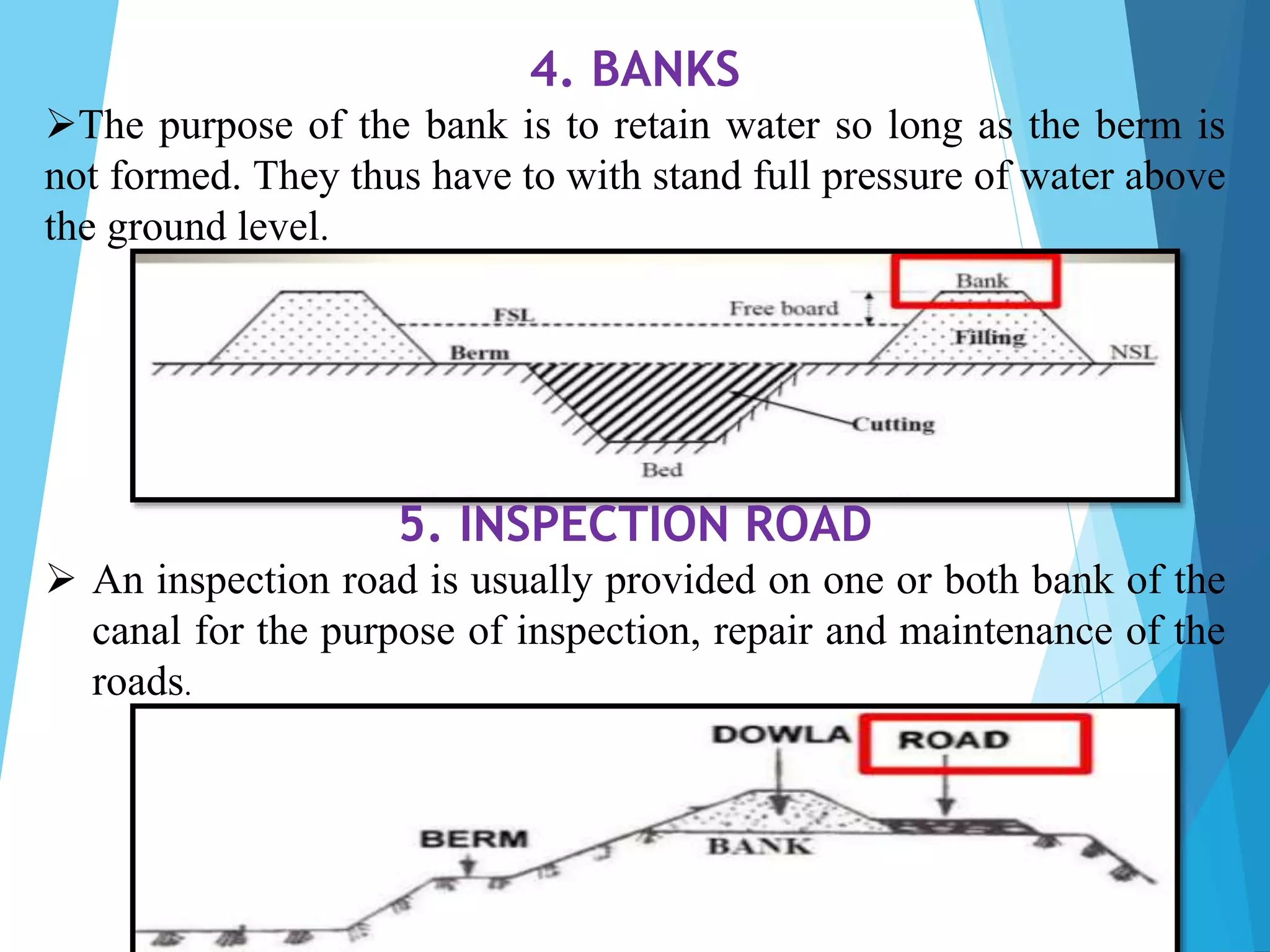
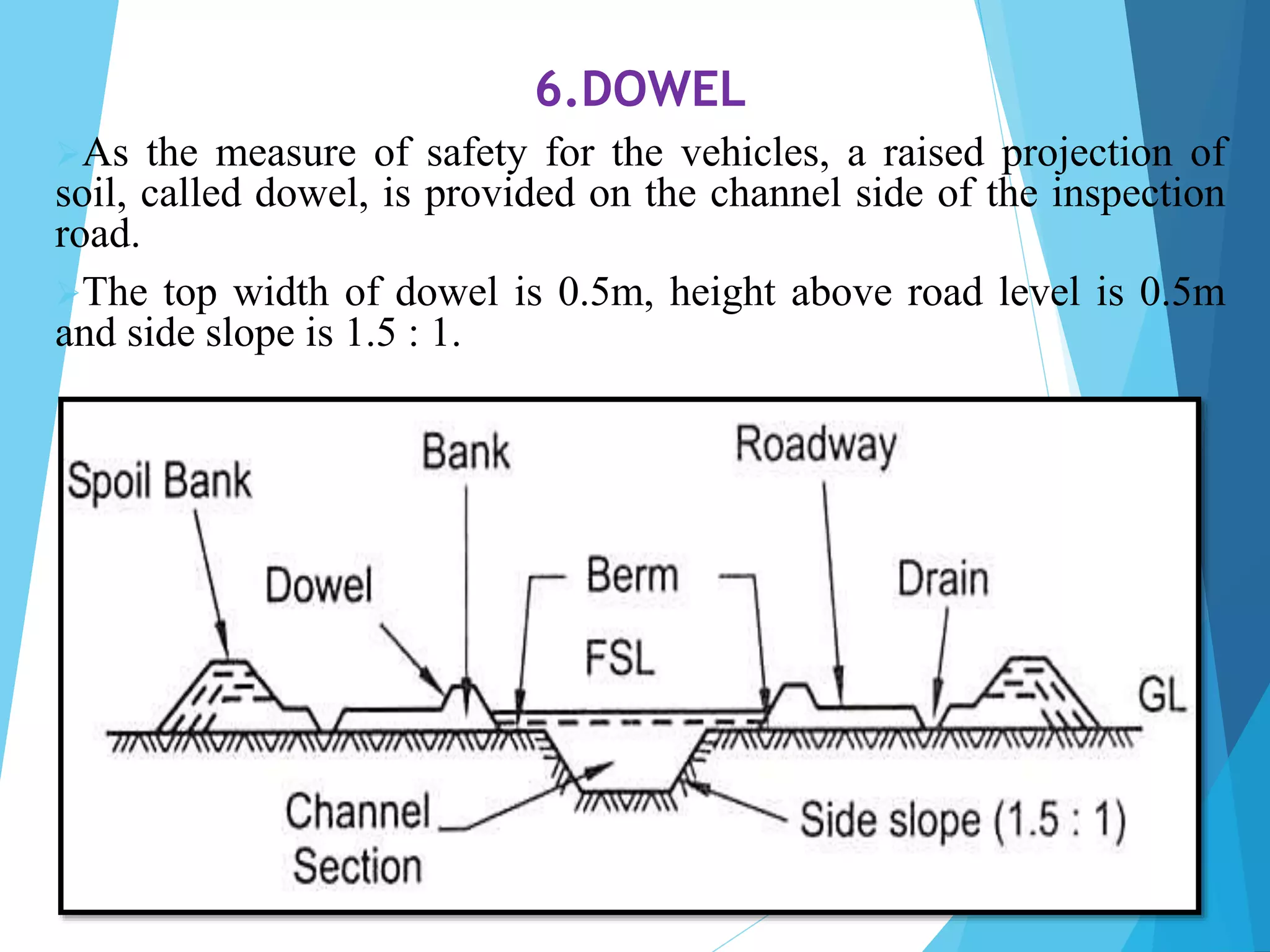
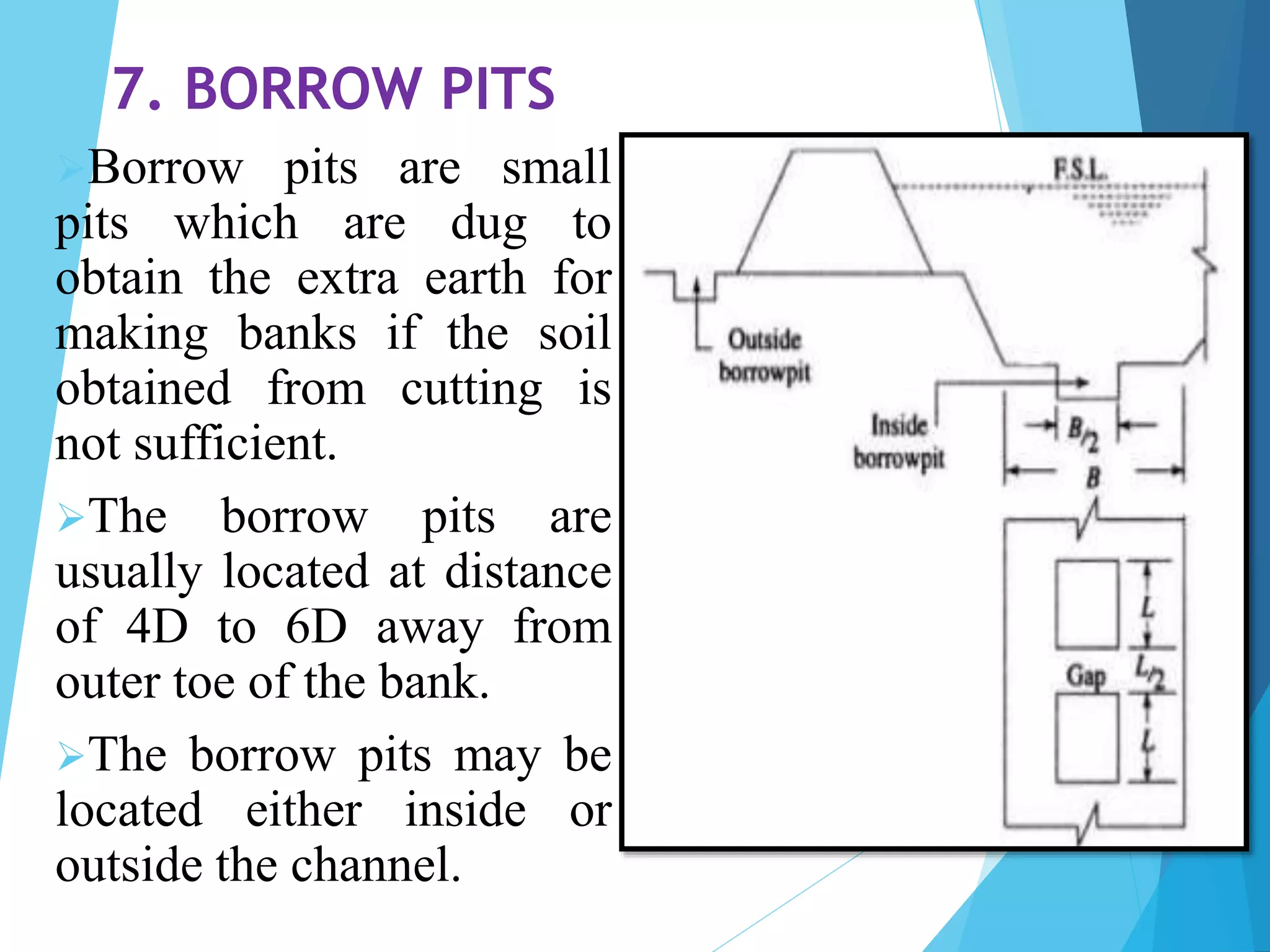
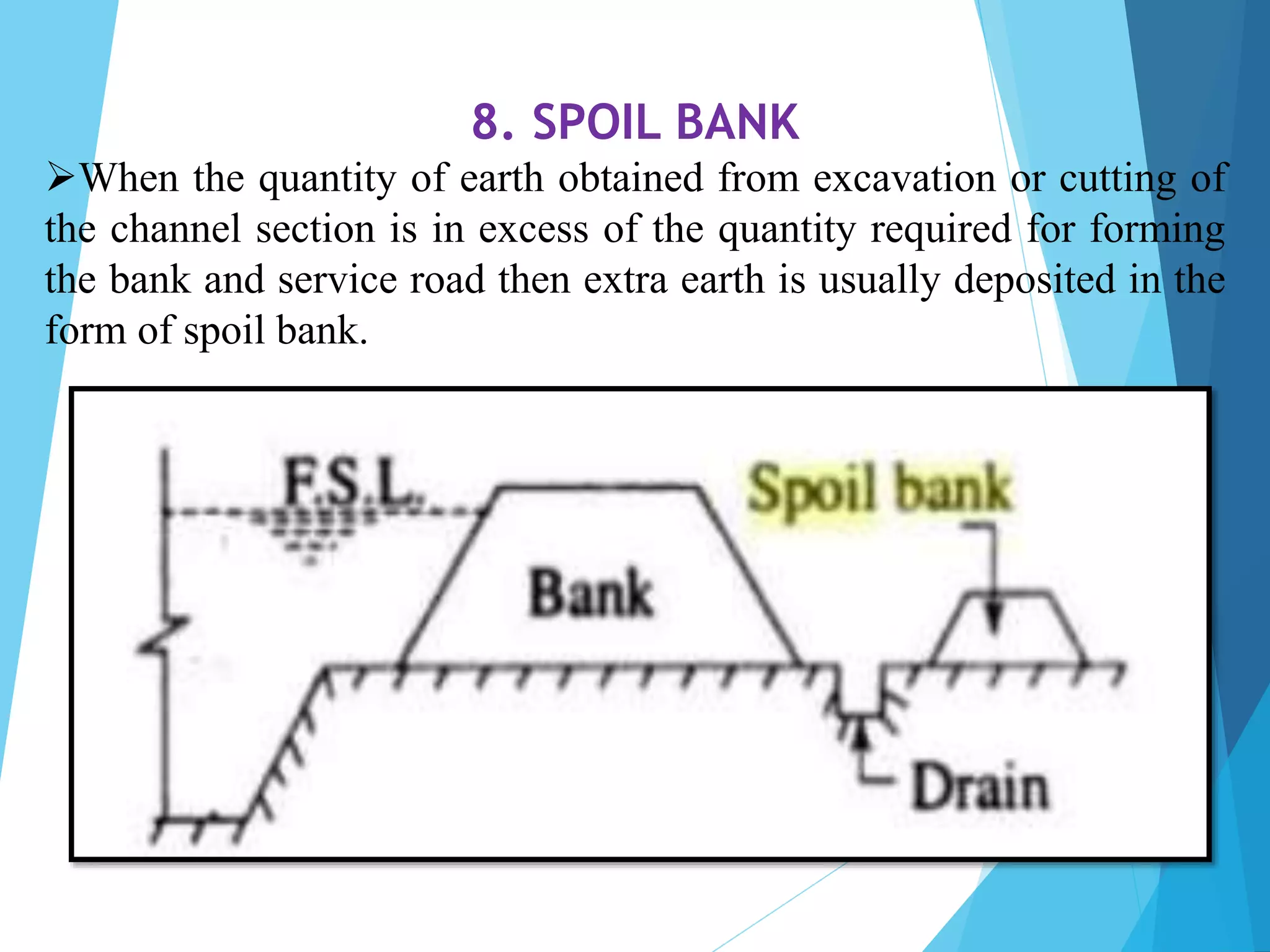
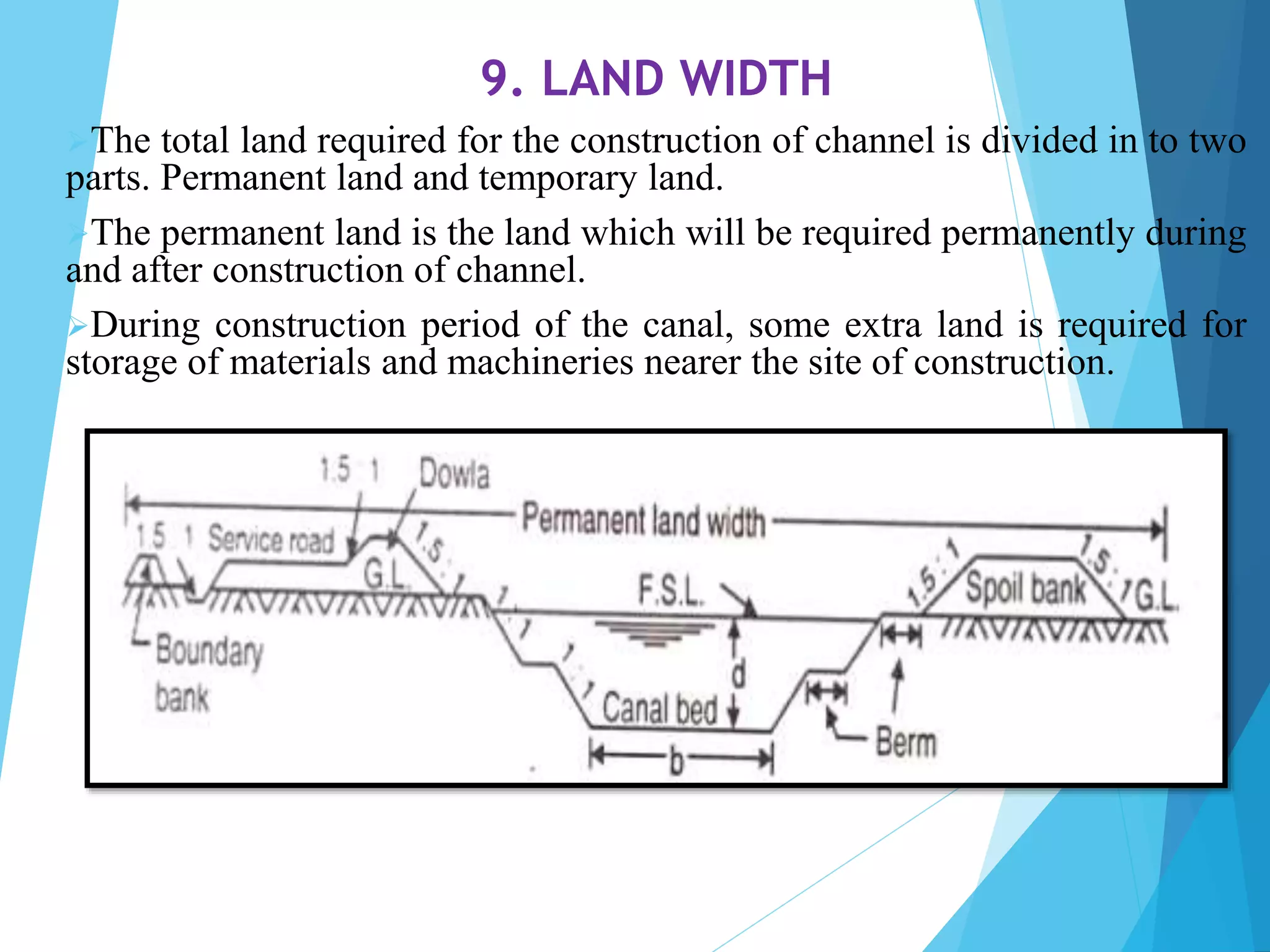
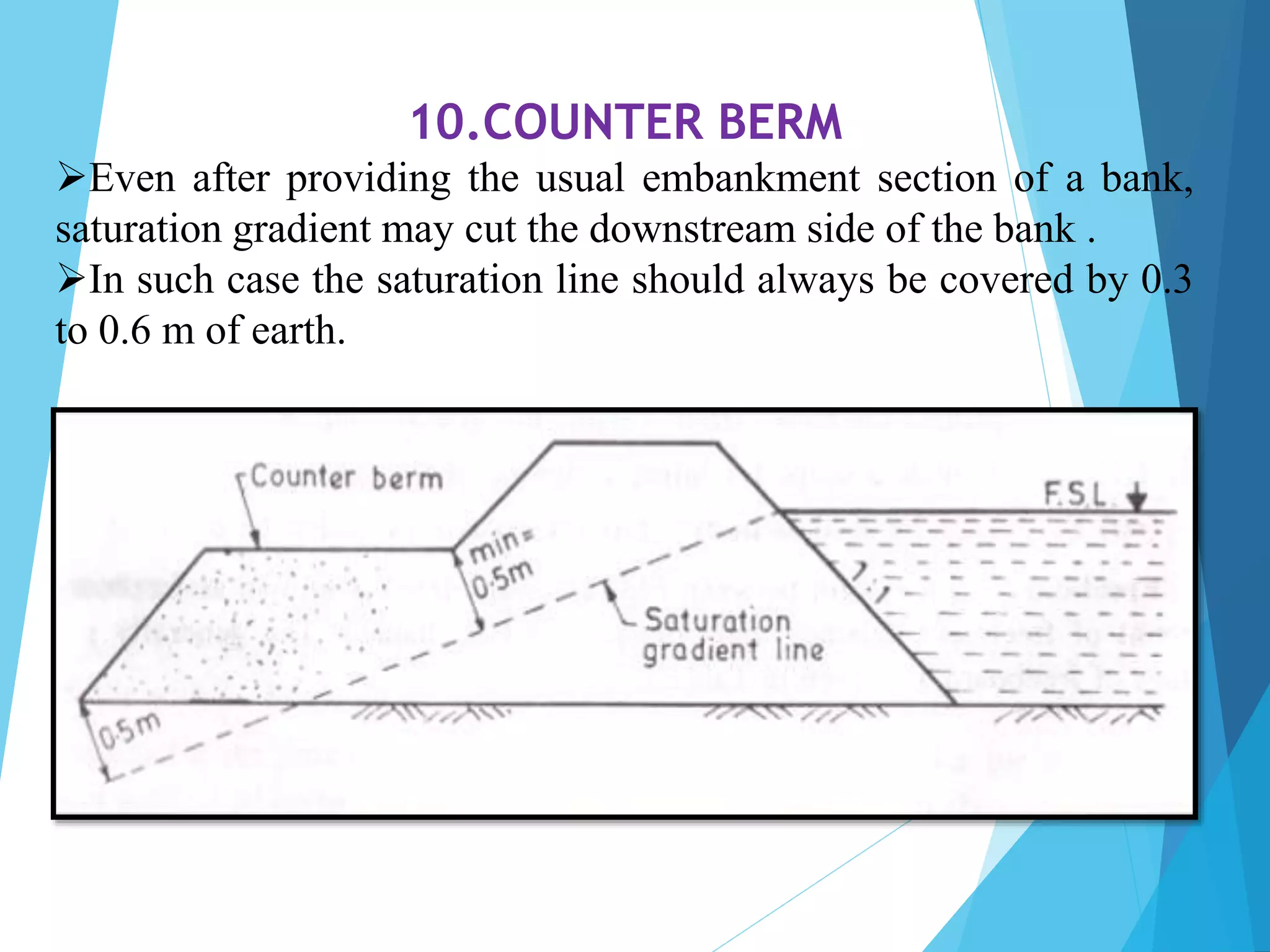
1) The document discusses the cross section of irrigation canals, including configurations for cutting, filling, and partial cutting/filling. It describes the main components of a canal cross section such as side slopes, berms, and banks.
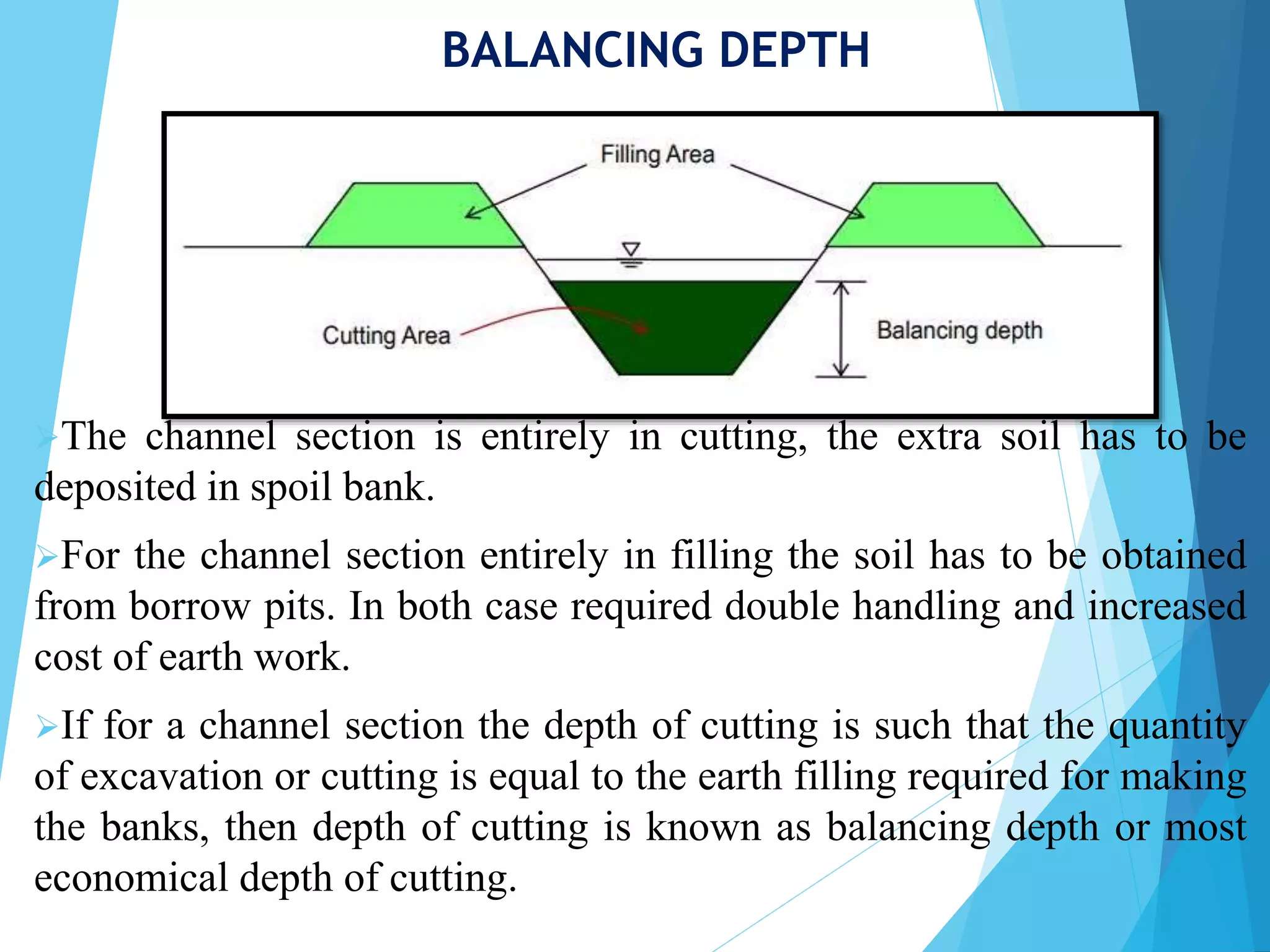
2) Balancing depth is defined as the depth of cutting where the quantity of excavated earth equals the amount required to form the canal banks, resulting in the most economical cross section.
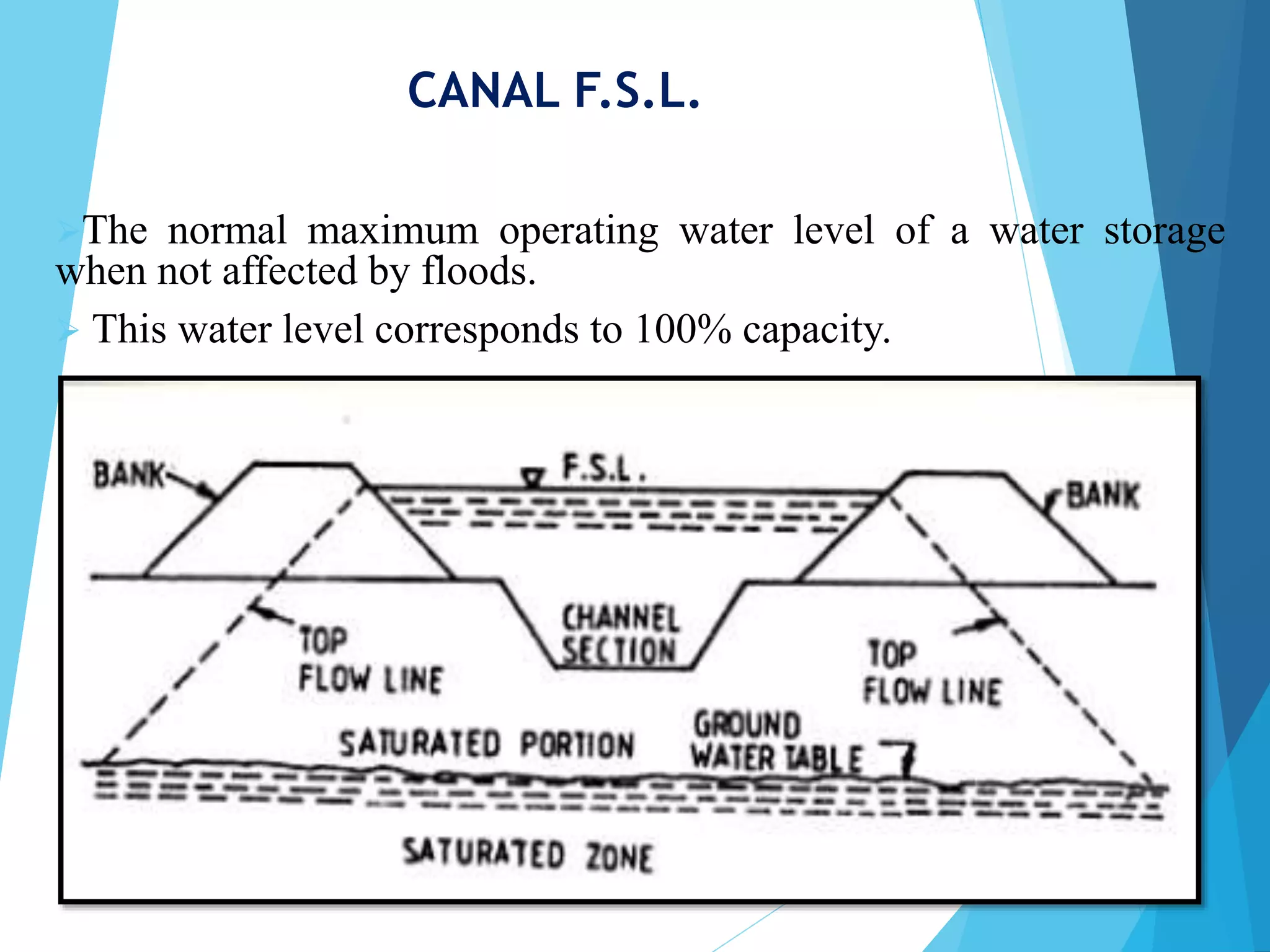
3) Canal FSL (Full Supply Level) refers to the normal maximum operating water level of a canal when not affected by floods, corresponding to 100% capacity.