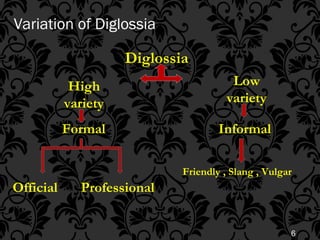
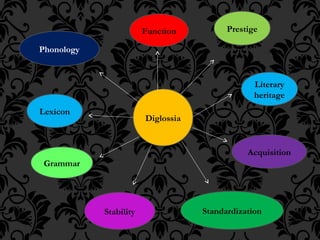
Diglossia refers to a stable language situation where two varieties of the same language are used by a language community. The high variety (H) has prestige and is used for formal, written communication while the low variety (L) lacks prestige and is used for informal, spoken communication. Some key aspects of diglossia include the high variety having prestige, a literary heritage, acquisition through formal education, standardization, a simpler grammar in the low variety, differing lexicons between the varieties, and the high variety having a divergent sound system from the low variety.