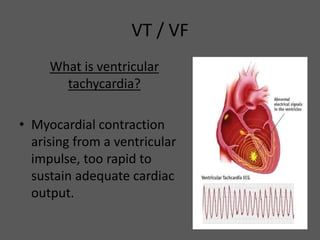
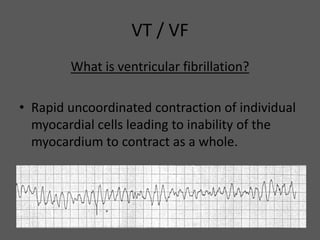
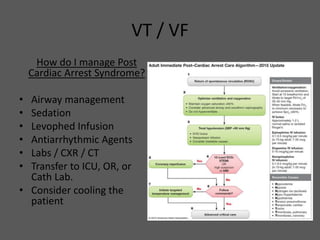
This document defines ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation, and outlines the ACLS algorithms for cardiac arrest caused by VT/VF. VT is defined as too rapid myocardial contraction preventing adequate cardiac output, while VF is rapid, uncoordinated myocardial cell contraction preventing coordinated contraction. Causes include ischemia, structural heart issues, electrolyte disturbances, and others. Immediate CPR and defibrillation improve odds of return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC). If ROSC is achieved, post-cardiac arrest care is needed to manage ischemia/reperfusion injury risks like low blood pressure and cardiac dysfunction.