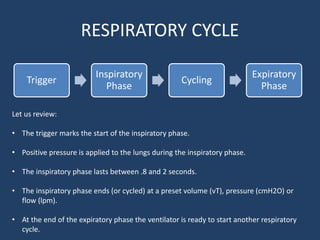
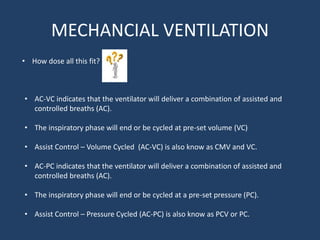
This document discusses the respiratory cycle during mechanical ventilation. It describes the trigger that initiates the inspiratory phase, during which positive pressure is delivered to the lungs for 0.8-2 seconds. The inspiratory phase ends based on a preset volume, pressure, or flow/pressure limit. The expiratory phase then begins. Different modes, like assist-control volume cycled (AC-VC), assist-control pressure cycled (AC-PC), and pressure support ventilation (PSV) are reviewed in terms of how they deliver controlled, assisted, or spontaneous breaths using these phases and limits.